Latest Blogs
Living with Scleroderma: Understanding the Symptoms and Treatment Options
Introduction What is scleroderma? Scleroderma is a rare autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues, causing an overproduction of collagen protein. Excess collagen makes the skin abnormally thick and fibrous and can affect other body tissues. Scleroderma is a chronic condition that may need lifelong management. If it affects an organ tissue, it can lead to life-threatening complications. Therefore, it's crucial to seek medical help if you experience symptoms such as joint pain, stiffness, or unusually thickened skin around your fingers and toes. What are the types of scleroderma? Health practitioners generally classify two main scleroderma types: Localised Scleroderma: This type usually affects only one part of your body (usually the skin). It causes waxy, thick patches or streaks to appear on your skin. Systemic Sclerosis: This variant can impact other organs in addition to your skin. It may involve parts of your respiratory system (organs that breathe and smell) and digestive system (organs that process food and drink). This type has three sub-types—diffuse, limited, and sine sclerosis. Understanding the scleroderma types and the one you are dealing with can help you manage and treat it effectively. What are scleroderma symptoms? Scleroderma symptoms can vary widely. Some people may not experience any symptoms initially, while others might notice thickened, waxy patches or streaks on the skin. Other common symptoms include joint pain, morning stiffness, extreme fatigue, and unexplained weight loss. Let's delve deeper into the specific symptoms of scleroderma for both localised and systemic variants: Localised Scleroderma Symptoms Individuals with localised scleroderma primarily experience skin thickening. The affected skin can appear in patches on the chest, around the stomach, limbs, hands and fingers, feet, and toes. It's rare for localised scleroderma to affect internal organs. Systemic Sclerosis Symptoms Systemic sclerosis can cause a wide array of symptoms. Thickened skin usually appears on your fingers or toes before spreading to the your body's centre. If you have Raynaud's syndrome (a condition often associated with scleroderma), the skin of the affected fingers and toes may change colour when exposed to cold. Alongside this, systemic sclerosis can cause many symptoms related to organs and tissues, such as numbness and swelling in the muscles, joint stiffness and loss of mobility, coughing and shortness of breath in the lungs, swallowing difficulty, heartburn, constipation or diarrhoea related to the digestive tract, abnormal heartbeat or fluid build-up around the heart, affecting cardiovascular health, kidney failure which can be life-threatening and sexual dysfunction. What causes scleroderma? The exact causes of scleroderma remain unknown. Some studies have found that it can run in families, but it’s not definitively proven to be a genetic disorder. What are the scleroderma risk factors? Certain groups are at a higher risk of developing scleroderma. People assigned female at birth (AFAB) are four times more likely to develop it than people assigned male at birth (AMAB). The condition is also more common in people between the ages of 30 and 50 and in black people, who often experience more severe scleroderma symptoms. What complications can scleroderma cause? Scleroderma lead to various complication. This condition can cause Raynaud's syndrome, which affects the small blood vessels in your fingers and toes, causing them to constrict more than usual in response to cold temperatures or stress. It often leads to colour changes in your fingers and toes due to reduced blood flow. Another complication is known as Sjögren's syndrome, which causes decreased moisture production by certain glands, usually the salivary glands, resulting in dry mouth and dry glands in the eyes. In more severe cases where multiple organs are affected (systemic sclerosis), scleroderma can lead to life-threatening complications, including: Kidney failure Pulmonary hypertension Pulmonary fibrosis Cardiovascular disease Congestive heart failure A weakened immune system Gastrointestinal diseases Cancer How is scleroderma diagnosed? A healthcare provider can diagnose scleroderma through a physical examination and some tests. You may need to visit a rheumatologist, a healthcare provider who specializes in treating autoimmune disorders. During your consultation, be open with your doctor about any symptoms you're experiencing, when you first noticed them, and if anything seems to make them worse. This information will help your healthcare provider create a comprehensive picture of your condition. What tests are used to diagnose scleroderma? Your healthcare provider may need to employ a series of diagnostic tests to confirm scleroderma. These could include: Blood tests: To evaluate how well your immune system is functioning Pulmonary function tests: To ascertain if your lungs or respiratory system are affected Biopsy: A procedure where a small sample of your skin or other affected tissue is removed for lab testing Endoscopy: A procedure where a small camera attached to a long, thin tube will be used to examine your throat or stomach to check If you have gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms. Additionally, imaging tests like an electrocardiogram (ECG), echocardiogram (Echo), chest X-ray, or computed tomography (CT) scan might be necessary to get a clear picture of the impact of scleroderma on your body. How is scleroderma treated? While there isn't a cure for scleroderma, numerous scleroderma treatment options can manage scleroderma symptoms and reduce their impact on your daily routine. These treatments could include: Skin treatments: Creams and moisturisers could be used to prevent dry skin. Immunosuppressants: These stop the immune system from damaging healthy cells and tissues. Medicines for specific symptoms: In case of high blood pressure, breathing difficulties, kidney failure or gastrointestinal disorders, respective medications can be administered. Physical therapy: This is beneficial for improving physical mobility. Light therapy (phototherapy): This uses UV light to treat thickened skin. Stem cell transplants: Severe cases might require a stem cell transplant to replace damaged blood cells with healthy donor cells. Conclusion Living with scleroderma can indeed be challenging. But with the right knowledge and medical care, managing this condition can become less daunting. An understanding of scleroderma causes, scleroderma symptoms, and scleroderma types can assist you in recognising the potential complications early and seeking timely scleroderma treatment. Regular check-ups and tests are critical to managing scleroderma. With Metropolis Labs, you have access to expert diagnostic services right at your doorstep. From at-home sample collections by trained professionals to advanced diagnostic tests performed in state-of-the-art labs, Metropolis is committed to delivering accurate results with personalised care
Thrombophlebitis: Essential Guide to Recognising Symptoms and Preventative Measures
What is thrombophlebitis? Thrombophlebitis is a health condition where a blood clot forms in one of your veins, typically in the legs, causing pain and swelling. Its severity varies, with minor cases being treatable and not dangerous. However, undetected or untreated severe cases can lead to serious complications. What are the different types of thrombophlebitis? Thrombophlebitis can occur anywhere in your body. Depending on its reason for occurrence or location, it has been classified into several types: Superficial Thrombophlebitis: Occurs in smaller veins, typically in the arms or legs. It is less severe than DVT but can be an indicator of a potential DVT occurrence. Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): A serious condition where a blood clot forms in a major vein, often in the legs. Untreated DVT can lead to a life-threatening condition called pulmonary embolism. Migratory Thrombophlebitis: This type involves the movement of blood clots from one vein to another, potentially involving multiple veins simultaneously. Septic Thrombophlebitis: It occurs due to an infection, either caused by thrombophlebitis or leading to it. It is especially dangerous as it can result in sepsis, a serious body-wide reaction to infection. What are the symptoms of thrombophlebitis? Identifying the symptoms of thrombophlebitis early can be crucial for timely treatment and the prevention of complications. Thrombophlebitis symptoms typically include: Swelling: Often sudden, it is most visible in veins close to your skin. Vein Changes: Veins affected by thrombophlebitis feel firmer than usual. Pain or Soreness: The area around and over the clot may feel tender or even painful. Other possible signs could be a colour change around the swollen area and warmth above and around the clot. What are the causes of thrombophlebitis? Understanding what causes a health condition is a significant step towards prevention. Let's take a closer look at the potential thrombophlebitis causes: Genetic Conditions: Certain inherited mutations can make your blood more susceptible to clotting. Varicose Veins: These spider-like veins on your legs increase the risk for thrombophlebitis in the same area. Trauma: Injuries near veins can lead to inflammation and subsequent clot formation. Medical Procedures and Medications: Certain medical procedures or hormone treatments may increase your risk. Lack of Movement: Extended periods of sitting or standing can lead to poor circulation, increasing the risk of clot formation. Remember, it is essential to consult with your healthcare provider if you identify with any of these thrombophlebitis causes. Who's at risk? While thrombosis can affect anyone, certain factors can increase your risk. Factors such as age play a crucial role; the risk starts to increase past the age of 45 and continues as you get older. Moreover, certain conditions, like cancer, obesity, lupus, and blood disorders, are potential risk factors. Lifestyle choices like smoking and dehydration also add to the risk. How is it diagnosed? Recognising early signs of thrombophlebitis can be challenging, as several conditions share similar symptoms. Consequently, healthcare providers often diagnose thrombophlebitis using a multi-pronged approach that includes physical examination, imaging tests, and lab tests. 1. Physical Examination A healthcare provider will look for visible signs of thrombophlebitis, like swelling or colour changes. They might palpate the affected area and listen to your pulses using a stethoscope. 2. Lab Tests Various lab tests can aid in the diagnosis of thrombophlebitis. These include blood tests that analyse your blood's clotting ability, look for evidence of existing clots, or detect signs of infection. 3. Imaging Tests An ultrasound using high-frequency sound waves is commonly used to visualise the clot. Tests using X-rays, especially with IV substances that highlight blockages, are also common. What tests will be done to diagnose this condition? In rare cases, migratory thrombophlebitis can be an indicator of certain types of cancer, particularly in the abdomen. When suspected, healthcare providers may conduct additional tests to rule out such cancers. How is thrombophlebitis treated? If caught early, thrombophlebitis treatment can be quite effective. It typically involves a combination of medications and supportive treatments, like: Pain Medications: Control pain with over-the-counter medicines or prescribed drugs for severe cases. Blood Thinners: Prevent further clotting with blood thinners. Thrombolytic Drugs: Break down existing clots using 'clot-busting' drugs. Antibiotics: In instances where an infection accompanies thrombophlebitis, antibiotics are essential. Severe thrombophlebitis may necessitate surgical intervention or other procedures like mechanical thrombectomy (removing the blood clot), vein removal or vein stripping, bypass surgery, sclerotherapy (sealing the affected vein), and catheter-based procedures (widening a narrowed vein or forming scar tissue to prevent blood flow to problematic areas). What are the complications of thrombophlebitis? While thrombophlebitis treatment is most often effective and uncomplicated, there are a few cases that can lead to complications if not addressed promptly. These include developing more serious conditions like deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism, both medical emergencies. Delayed thrombophlebitis treatment also increases the risk of long-term problems like chronic pain or scarring in the affected veins, which can hinder blood flow. How can I prevent this? Thrombophlebitis prevention primarily involves being proactive about your health. If you are at risk of clotting, your healthcare provider may prescribe blood thinners to prevent clot formation. Here are some ways to reduce your risk: Quit tobacco use. Avoid IV drug use. Stay mobile, especially if your job involves long periods of sitting. Take the prescribed medications as instructed by your doctor. Maintain adequate hydration. Regular health check-ups can catch potential problems early on. Maintain a healthy lifestyle with balanced nutrition and regular exercise. Wear support or compression garments recommended by your healthcare provider. Conclusion Facing a health condition like thrombophlebitis might seem daunting, but knowing about its symptoms, causes, prevention strategies, and treatment options can empower you to manage your health effectively. Remember that early recognition of thrombophlebitis symptoms, timely consultation with healthcare professionals for its diagnosis and treatment, and proactive thrombophlebitis prevention measures are pivotal in handling this condition efficiently. When it comes to reliable diagnostic services for thrombophlebitis, Metropolis Healthcare stands as a trusted partner. With expert technicians for at-home sample collection and advanced labs delivering accurate test results, Metropolis ensures personalised care for every patient.
Epididymitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Approaches
What is epididymitis? Epididymitis refers to the inflammation of the epididymis, a coiled tube located at the back of each testicle responsible for storing and transporting sperm. This inflammation can lead to intense discomfort or pain in the testicular region. As daunting as this may sound, there's no need for panic. Let's understand this condition better so we can be well-equipped to manage it effectively. What’s the difference between epididymitis and orchitis? While both conditions involve swelling in the male reproductive system and share similar symptoms like testicular pain and swelling, there's a key distinction between them. Epididymitis refers specifically to inflammation of the epididymis (the tube at the back of the testicle), while orchitis pertains to inflammation of one or both testicles themselves. Occasionally, these two conditions occur together, resulting in a combined condition known as "epididymo-orchitis". Who does epididymitis affect? Epididymitis doesn't discriminate by age. It can affect males at any stage of life but is commonly observed in individuals between the ages of 14 and 35. According to the data, there are an estimated 600,000 cases of epididymitis reported annually in the United States alone. What are the symptoms of epididymitis? Epididymitis symptoms might range from mild to severe, depending on the degree of inflammation. Common epididymitis symptoms include: Persistent pain in the scrotum that may extend to the entire groin area Swelling and redness in one or both testicles The presence of blood in semen Fever and chills Painful urination, also known as dysuria What causes epididymitis? Understanding epididymitis causes is crucial for effective prevention and management. In most cases, the condition occurs due to an infection by bacteria such as E. coli, Mycoplasma, or Chlamydia, which can be sexually transmitted. However, epididymitis can also occur from other infections like mumps or, rarely, tuberculosis. Other potential causes include: Urinary reflux into the epididymis due to heavy lifting Blockage in the urethra Enlarged or infected prostate gland Use of a catheter Surgery on the prostate, urethra, or bladder Traumatic groin injury It's crucial to note that you can get epididymitis without having an STD, as non-sexually transmitted infections like urinary tract infections can spread to your epididymis. Can you get epididymitis without having an STD? Yes, epididymitis can be contracted through non-sexually transmitted infections. Infections in the prostate or urinary tract can spread to the epididymis leading to this condition. Is epididymitis contagious? While epididymitis itself isn't classified as a sexually transmitted disease (STD), it can spread through sexual contact if caused by bacteria associated with STDs like Chlamydia or Gonorrhoea. How is epididymitis diagnosed? When it comes to epididymitis diagnosis, a healthcare provider will perform a physical examination of your scrotum to identify any tender spots or lumps. They may also order a urine test to check for bacteria, and in some cases, an ultrasound may be used for diagnostic imaging. How is epididymitis treated? In most instances, epididymitis treatment involves a course of antibiotics lasting one to two weeks. Commonly prescribed medications include doxycycline, ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, or trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. Along with antibiotics, measures like rest, applying ice packs to the affected area, drinking ample fluids, elevating the scrotum, and taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can help relieve epididymitis symptoms. What are the complications of epididymitis? If left untreated, epididymitis can lead to complications such as an abscess in the scrotum or skin ruptures due to swelling and infection. In rare cases, it can also cause fertility issues by damaging the epididymis. Will epididymitis go away? With the correct epididymitis treatment approach, epididymitis will gradually subside. However, prompt medical intervention is essential to avoid complications and ensure a speedy recovery. What can happen if epididymitis is left untreated? Unattended epididymitis could escalate into chronic epididymitis, which may lead to abscess formation on the scrotum or even infertility. In more severe cases, the infection could spread throughout the body. Therefore, timely medical intervention is crucial. How can I reduce my risk for epididymitis? Prevention is better than cure! Here are some practical ways you can reduce your risk of epididymitis: Use condoms during sexual activities. Avoid strenuous lifting or heavy physical activity. Limit long periods of sitting that may put pressure on the scrotum. What can I expect if I have epididymitis? If you've been diagnosed with this condition, don't fret. With the right antibiotics and home care measures, your symptoms will soon be alleviated. Continued discomfort and swelling may persist for weeks or even months after completing antibiotic treatment, but they will gradually subside. How long can epididymitis last? The discomfort caused by epididymitis normally begins to subside after three days of treatment. However, a full recovery might take weeks or even months. When should I see a doctor? If you spot any epididymitis symptoms, such as testicular pain or swelling, it's crucial to reach out to a healthcare provider immediately. In cases of sudden or severe testicular pain, immediately seek emergency medical help. Conclusion Epididymitis, though potentially painful and distressing, can be effectively managed with timely diagnosis and treatment. Prioritising your health is of utmost importance in managing this condition. If you suspect any symptoms related to this condition, don't hesitate to reach out to Metropolis Healthcare – a leading chain of diagnostic labs across India, known for their accurate pathology testing and health check-up services.
Gastrointestinal Disease: Understanding Symptoms, Causes, Types, and Treatment
Introduction What are gastrointestinal diseases? Gastrointestinal diseases is a broad term which encompasses conditions that impact the digestive system, stretching from the mouth to the anus. These diseases can broadly be classified into two categories: functional and structural. Each category manifests itself differently, has varying symptoms, and requires distinct modes of treatment. What are functional gastrointestinal diseases? Functional gastrointestinal diseases are typically characterised by abnormal movements in the gastrointestinal tract, despite appearing normal during examinations. Common examples of symptoms of functional gastrointestinal disease symptoms constipation, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), excess gas, and bloating. Many factors can disrupt the GI tract's motility, such as: Eating a diet low in fibre Lack of regular exercise Changes in routine, such as travelling High intake of dairy products Stress Overuse of certain medications What are structural gastrointestinal diseases? Unlike functional disorders, structural gastrointestinal diseases are accompanied by visual disturbances in the digestive tract along with its abnormal functioning. Treatment of these conditions often requires a surgical intervention. Examples of structural gastrointestinal disease symptoms include haemorrhoids, diverticular disease, colonic polyps, colon cancer, and inflammatory bowel disease. If you are experiencing gastrointestinal disease symptoms such as blood in your stool or persistent abdominal pain, it may indicate a structural gastrointestinal disease. Don’t ignore these signs; consult a doctor immediately. What are some of the common gastrointestinal diseases that can be treated? Whether functional or structural in nature, many gastrointestinal disease treatments can be effectively managed with appropriate plans. Below we explore some of the common disorders: Constipation As a common functional disorder, constipation makes bowel movements difficult and infrequent. A diet rich in fiber, followed by a regular physical activity and addressing the urge to defecate can effectively manage this condition. Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) IBS is characterised by abnormal contractions of the intestinal muscles, which causes symptoms like abdominal pain, excess gas, bloating, and irregular bowel habits. Lifestyle changes and prescribed medications can help in managing IBS. Haemorrhoids Haemorrhoids, a structural disorder, is a condition characterized by swollen veins in the anal canal that cause discomfort and bleeding. Depending on the severity, treatment may involve medications or surgery. Perianal Abscesses A perianal abscess is a structural gastrointestinal disease in which a pus-filled cavity forms near the anus due to an infection of the anal glands. Symptoms include anal pain and possibly fever. Treatment consists of draining the abscess under local anesthesia. Anal Fistula Following an abscess, an abnormal tube-like passage or fistula might form between the anal canal and the skin near the anal opening. This structural gastrointestinal disease causes discomfort, pain, and bleeding and usually warrants a surgical intervention for closure. Diverticular Disease Diverticula are small pouches that are formed in the wall of the digestive tract. When these become inflamed or infected, it leads to a condition known as diverticulitis, a type of structural gastrointestinal disease. Symptoms of this condition range from abdominal pain to changes in bowel habits. Severe cases may require a surgical intervention. Colon Polyps and Cancer Colon polyps are small clumps of cells that form on the lining of the colon. Although most polyps are harmless, some can progress to colon cancer over time. Regular screening is crucial for the early detection and treatment of this gastrointestinal disease. Symptoms of colon cancer include changes in bowel habits, blood in the stool, and unexplained weight loss. Colitis Colitis is an inflammation of the lining of the large intestine which is caused by an infection, ischemia (insufficient blood supply), or any other causes. This condition often presents gastrointestinal disease symptoms such as diarrhoea, abdominal pain, and rectal bleeding. Treatment depends on the underlying cause and severity. Remember, consulting a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis is important to ensure appropriate gastrointestinal disease treatment. Can gastrointestinal diseases be prevented? Although not all of the gastrointestinal disease causes can be completely prevented, but a healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce your risk. Regular exercise, a balanced diet rich in fibre, adequate hydration and stress management are some preventive measures that you can adopt. Furthermore, regular health check-ups for early detection of potential health issues are advisable. Paying attention to changes in bowel habits or unusual symptoms can also lead to early detection of potential gastrointestinal disease. These includes persistent abdominal pain, unexpected weight loss, unusual fatigue or changes in bowel movements. Other types of gastrointestinal diseases Apart from those mentioned above, there are numerous other functional and structural gastrointestinal conditions such as: Peptic ulcer disease Gastroenteritis Celiac disease Crohn's disease Each type of gastrointestinal disease type presents a unique challenge that require a specific diagnostic approaches and treatment plans. Conclusion Navigating through the path of gastrointestinal diseases can be intimidating. However, with an accurate knowledge about various gastrointestinal disease types, their causes and their symptoms, you are better equipped to manage your health. Prompt diagnosis through appropriate tests plays a crucial role in gastrointestinal disease treatment. Metropolis Healthcare, with its advanced diagnostic labs and at-home collection services, ensures that you have access to reliable pathology testing and health check-ups at your convenience. Trust them to provide accurate insights and personalised care, empowering you to prioritise your health. Remember, your well-being is within your control with the right knowledge and professional medical care.
Everything You Need to Know About Buerger’s Disease
Introduction Living with Buerger's disease can be intimidating, but understanding it is the first step to manage it effectively. This guide to Buerger's disease provides essential insight into the disease, covering it's symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment, and self-care strategies. Whether you are recently diagnosed or seeking more information, this full resource aims to give you knowledge and support to navigate your trip with Buerger's disease. What Is Buerger’s Disease? Buerger's disease, or thromboangiitis obliterans, is a non-atherosclerotic (group of abnormalities in the coronary arteries) inflammatory disease that primarily affects small and medium-sized arteries, commonly in the limbs. This results in progressive vessel occlusion (cerebral vessels become progressively occluded, leading to insufficient perfusion of brain tissue), leading to ischemia (blood flow (and thus oxygen) is restricted or reduced in a body part) and tissue damage, which is often associated with smoking. What Are The Symptoms Of Buerger’s Disease? Common symptoms of Buerger’s disease include: Ischemic rest pain : Severe pain in the hands or feet, which often occurs during taking a rest due to Buerger's disease. Claudication: Muscle cramps due to insufficient blood flow, usually in the calf muscle, are a symptom of Buerger's disease. Raynaud's phenomenon: Changes in the color of the skin of the fingers or toes, appearing as red, blue, or pale discoloration, are also important symptoms of Buerger's disease to watch out for. Numbness or tingling: Numbness or tingling in the fingers or toes caused by Buerger's disease. Ulcerations: Open sores or wounds on the toes, feet, or fingers, often due to poor circulation, may indicate Buerger's disease. What Causes Buerger’s Disease? Buerger's disease is caused by inflammation in the small and medium-sized blood vessels. The exact Buerger's disease cause remains unclear, but several factors can contribute to its development. Some potential contributing Buerger's disease causes include: Tobacco consumption, particularly smoking, is the main risk factor. Genetic factors may play a role, as the disease is more common in certain ethnic groups. Abnormalities of the immune system leading to inflammation of the blood vessels are believed to be the cause. Some researchers believe that Buerger's disease may result from an abnormal reaction to tobacco or other environmental exposures. What Are The Risk Factors For Buerger’s Disease? Common risk factors for Buerger’s disease include: Smoking: Smoking is the most important risk factor for Burger's disease, and almost all those affected are current or former smokers. Age: Buerger’s disease usuallyoccurs before the age of 50. Arterial occlusions: Presence of infrapopliteal arterial occlusions (a condition that can lead to critical limb ischaemia (CLI), a potentially life-threatening disease affecting the limbs), especially in the lower limbs. Limb involvement: The risk increases either with involvement of the upper limb or with phlebitis migrans, a form of migratory thrombophlebitis. Other risk factors: Other risk factors of Buerger's disease may includegenetic predisposition, autoimmune response, or hypersensitivity to tobacco components. What Are The Complications Of Buerger’s Disease? Complications of Buerger’s disease include: Gangrene: Tissue death due to lack of blood flow, leading to blackening and decay. Ulcerations: Open sores or ulcers may develop on the fingers and toes, which are particularly susceptible to infection. Infection: Secondary infections can develop due to Buerger’s disease in the ulcerated areas, which can lead to serious complications. Amputation: In severe cases, affected fingers or limbs may need to be surgically removed. Systemic complications such as occlusion of coronary, splenic, renal, or mesenteric arteries may arise rarely. How Is Buerger’s Disease Diagnosed? Buerger’s disease is diagnosed through a combination of clinical assessments, like medical history review, and diagnostic tests: Clinical Examination: The diagnosis of Buerger's disease usually begins with a thorough clinical examination, focusing on symptoms such as ischemic ischemic rest pain, claudication, and characteristic skin changes. Medical history: A detailed history of Buerger's disease, including smoking habits and other Buerger's disease risk factors, helps in making the diagnosis. Physical Examination: Examination may reveal decreased or absent pulses, cold extremities, and signs of tissue ischemia, aiding in the diagnosis. Differential Diagnosis: Buerger's disease must be differentiated from other conditions causing peripheral vascular disease, such as atherosclerosis and vasculitis. What Tests Will Be Done To Diagnose Buerger’s Disease? For Buerger's disease diagnosis, several tests may be conducted: Vascular Tests: Buerger's tests assess the blood flow and may include Doppler ultrasound to evaluate arterial blood flow velocity and waveform characteristics. Imaging Studies: Angiography or magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) may be performed to visualize blood vessels and detect any abnormalities, such as arterial blockages. Laboratory Tests: While there are no specific buerger tests for daignoses, a comprehensive serology may be performed to rule out other conditions. Urine Test: A urine test may also be performed to assess kidney function and rule out other possible causes of buergers disease symptoms. How Is Buerger’s Disease Treated? Buerger's disease treatment includes: Smoking Cessation: Immediate cessation of tobacco use is crucial to halt Buerger's disease progression. Medications: Antiplatelet agents and vasodilators may be prescribed to improve the blood flow and manage Buerger's disease symptoms. Surgery: In severe cases of Buerger's disease, surgical intervention such as sympathectomy or bypass grafts may be required to restore blood flow. Wound care: Ulcer management and wound care are essential for Buerger's disease treatment disease to prevent infection and tissue damage. What Medications Are Used For Buerger’s Disease? Medications commonly used for Buerger’s disease include: Vasodilators: Vasodilators such as calcium channel blockers, can be used to improve the blood flow. Antiplatelet Agents: Anti-platelet agents Like cilostazol and clopidogrel, are used to prevent the platelet aggregation and improve circulation. Pentoxifylline: Pentoxifylline a medication that improves blood flow by decreasing its viscosity and enhancing its ability to flow through the blood vessels. Prostacyclin and Prostaglandin Derivatives: May also be prescribed to improve the blood flow and Buerger's disease. What Treatments Are Used For Buerger’s Disease? Treatment approaches for Buerger’s disease include: Lifestyle Changes Cessation of tobacco use: Complete discontinuation of all forms of tobacco, including cigarettes, electronic cigarettes, vaping, and marijuana, is imperative. Pharmacotherapy Antihypertensive agents: Medications to enhance blood flow by reducing blood pressure Antiplatelet therapy: Administration of aspirin to prevent thrombus formation Endothelin receptor antagonist: Use of bosentan (Tracleer) for severe cases to augment blood flow Therapeutic Interventions Intermittent pneumatic compression: Application of periodic mechanical pressure to the affected limbs to improve circulation Surgical Management Amputation: Surgical removal of necrotic or severely infected limbs in advanced cases. Adjunctive Measures Regular physical activity: Approved exercises to promote vascular health Dermal surveillance: Routine inspection and care of skin to prevent and manage infections Oral hygiene maintenance: Regular dental check-ups to mitigate the risk of periodontal disease Avoidance of secondhand smoke: Steering clear of all forms of passive smoke exposure What Are The Side Effects Of The Treatment? Side effects of treatments can vary depending on the specific medication or therapy used. Common side effects of Buerger's disease may include: Gastrointestinal Disturbances: Such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, or constipation because of Buerger's disease. Cardiovascular Effects: Including changes in blood pressure or heart rate. Hematological Abnormalities: Such as anemia, leukopenia, or thrombocytopenia. Neurological Symptoms: Such as dizziness, headache, or neuropathy. Dermatological Reactions: Such as rash, itching, or skin irritation. Musculoskeletal Complaints: Such as muscle weakness, joint pain, or bone pain. Metabolic Effects: Including changes in glucose levels, electrolyte imbalances, or weight gain/loss. Psychological Effects: Such as mood changes, anxiety, or depression. What Is The Outlook For Buerger’s Disease? For individuals with Buerger's disease, the outlook can be challenging, especially without tobacco cessation. However, quitting smoking and proper management can improve symptoms and slow disease progression. Supportive care and lifestyle changes, coupled with medical interventions, offer hope for a better quality of life and reduce Buerger's disease complications. How Do I Take Care Of Myself? To manage Buerger's disease, it's crucial to cease tobacco use completely. Follow doctors' recommendations for self-care. Adhere to a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise and a balanced diet. Seek medical attention for any complications promptly. Surgical intervention may be necessary for severe cases of Buerger's disease. Conclusion In conclusion, understanding Buerger’s Disease is crucial for effectively managing its symptoms and improving quality of life. From recognizing early signs of Buerger's disease to seeking appropriate medical care and adopting lifestyle changes like smoking cessation, self-care plays a vital role. Metropolis Labs offers reliable blood testing services, including Buerger's disease pathology tests essential for diagnosing and monitoring Buerger’s Disease. With their convenient at-home sample collection and advanced diagnostic facilities, Metropolis Labs ensures accurate results and seamless healthcare experiences for individuals managing this condition. To learn more about Metropolis Labs and their comprehensive pathology services, visit Metropolis Labs.
Understanding Hiatal Hernia: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Strategies!
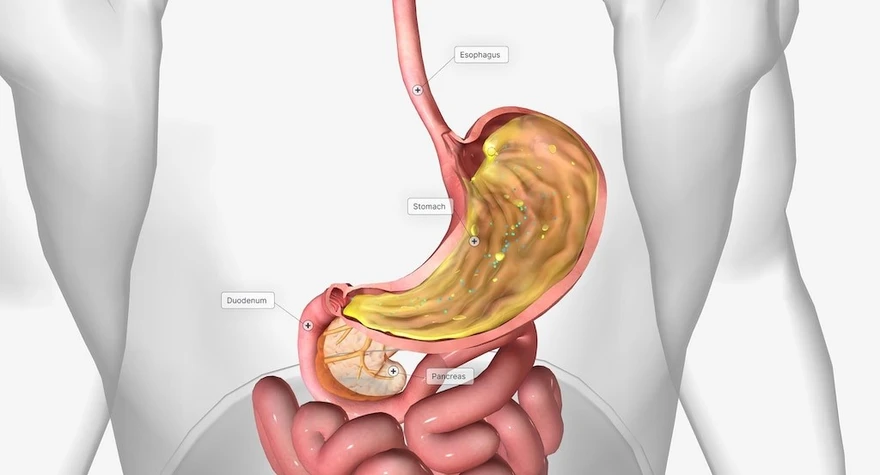
Introduction: Hiatal hernia—a condition that affects millions worldwide, often without them even realising it. Picture this: a small opening in the diaphragm allowing a portion of the stomach to slowly move into the chest cavity. It's a common occurrence, especially as we age, yet its impact can be profound. While some experience no symptoms, others grapple with acid reflux, chest pain, and difficulty swallowing, among other discomforts. In this article, we'll journey through the intricacies of hiatal hernia, shedding light on its symptoms, causes, and treatment options, empowering you to navigate this condition with knowledge and confidence. What is a Hiatal Hernia? A hiatal hernia happens when the part of your stomach pushes through the weak spot or opening in your diaphragm into the chest cavity. The diaphragm is a muscle barrier that separates your abdominal cavity from your chest cavity. What are the Different Hiatal Hernia Types? Hiatal hernias can be categorised into two main types: sliding hiatal hernia and paraoesophagheal hiatal hernia. Let's explore each hiatal hernia types in detail: Sliding Hiatal Hernia: This is the most common hiatal hernia type, accounting for around 95% of cases. In a sliding hiatal hernia, the junction where the oesophagus (food pipe) meets the stomach and the upper part of your stomach itself slides up into the chest through the hiatus, which is the opening in the diaphragm. This type of hernia is often associated with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) (leaking of acid from your stomach into your oesophagus) because the movement of the stomach into the chest can weaken the lower oesophageal sphincter (LES)(a muscular ring that prevents stomach contents from moving back into the oesophagus), allowing stomach acid to reflux or enter back into the oesophagus. Symptoms of a sliding hiatal hernia can include heartburn, acid reflux, regurgitation, chest pain, and difficulty swallowing. Paraesophageal Hiatal Hernia: Paraesophageal hiatal hernia, also known as a rolling hiatal hernia, is less common but can be more serious than sliding hernias. In a paraoesophagheal hiatal hernia, the gastroesophageal junction remains in its normal position, but a portion of your stomach moves through the hiatus and sits beside the oesophagus in the chest cavity. Unlike sliding hernias, paraoesophagheal hernias do not typically cause GERD symptoms. Instead, they may lead to symptoms such as chest pain, difficulty swallowing, feeling full quickly, and anaemia due to bleeding from ulcers in the herniated stomach. Paraoesophageal hernias are also categorised into three subtypes: Type I: The gastroesophageal junction remains below the diaphragm, but a portion of the stomach moves into the chest cavity. Type II: Similar to Type I, but with the addition of other abdominal organs moving into the chest alongside the stomach. Type III: This is the most severe subtype, characterised by the presence of a large portion of the stomach and other abdominal organs moving into the chest cavity. What are Hiatal Hernia Symptoms? Hiatal hernia symptoms can vary from person to person but commonly include: Heartburn Chest pain Difficulty swallowing Sore throat Indigestion Burping Bad breath Dry cough Nausea These symptoms may worsen after eating, lying down, or bending over. What Causes a Hiatal Hernia? Hiatal hernias typically happen when there is a weakening or disruption of the muscles and tissues surrounding the hiatus, which is the opening in your diaphragm through which the oesophagus passes before connecting to the stomach. It is difficult to pinpoint single hiatal hernia causes as several factors such as ageing-related muscle weakening, obesity-induced abdominal pressure, pregnancy-related displacement of organs and hormonal changes, strain from heavy lifting or straining, congenital structural abnormalities, and injury-induced muscle weakening around the hiatus can be listed under hiatal hernia causes. What are the Risk Factors of Hiatal Hernia? Several factors increase the risk of developing hiatal hernia, including obesity, advanced age, smoking, and certain medical conditions such as persistent coughing or vomiting. Genetics may also be the risk factor behind this condition. How is a Hiatal Hernia Diagnosed? Diagnosing hiatal hernia typically involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. These hiatal hernia diagnostic tests include: Chest X-ray: It also known as a radiograph, utilises radiation to capture static, black-and-white images of the interior of your chest cavity, including the area where your oesophagus is located. Upper Endoscopy: In an upper endoscopy, a flexible tube with a camera on the end (endoscope) is inserted through the mouth and into the oesophagus, stomach, and duodenum. This allows your healthcare provider to directly visualise the oesophagus and stomach and identify any abnormalities, such as inflammation or irritation caused by acid reflux. Oesophageal pH Monitoring: Oesophageal pH monitoring measures the acidity levels in the oesophagus over a while. This test helps determine the frequency and severity of acid reflux episodes, providing valuable information about the extent of reflux-related symptoms and their impact on oesophageal health. Oesophageal Manometry: Oesophageal manometry evaluates the strength and coordination of the muscles in the oesophagus and lower oesophageal sphincter (LES). By measuring muscle contractions and relaxation, this test assesses the functionality of the LES and identifies any abnormalities in oesophageal motility that may contribute to hiatal hernia symptoms. What is the Treatment for a Hiatal Hernia? Hiatal hernia treatment aims to relieve symptoms and prevent complications. Depending on the severity of your condition, hiatal hernia treatment options may include medications and surgery. Medications: Over-the-counter and prescription hiatal hernia medications such as antacids, proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), and H2-receptor antagonists can help reduce acid production and reduce the symptoms of acid reflux and heartburn. Surgery: In cases where medications are ineffective, hiatal hernia surgery may be recommended to repair the hernia and strengthen the lower oesophageal sphincter (a muscular ring that prevents stomach contents from moving back into the oesophagus). Laparoscopic surgery is a minimally invasive approach that offers faster recovery and fewer complications compared to traditional open surgery. Hiatal Hernia Surgery Hiatal hernia surgery involves returning the stomach to its normal position and repairing the opening in the diaphragm. This procedure may also involve strengthening your lower oesophageal sphincter to prevent reflux. While recovery times may vary, most hiatal hernia patients can resume normal activities within a few weeks after surgery. How Can I Treat My Hiatal Hernia at Home? In addition to medical treatment, certain lifestyle modifications can help manage hiatal hernia symptoms effectively. These hiatal hernia self-care include maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding large meals, elevating the head of the bed while sleeping, and refraining from smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. Conclusion Living with hiatal hernia can be challenging, but with proper understanding and management, you can effectively reduce the symptoms and improve your quality of life. Remember to consult with your healthcare provider for personalised treatment recommendations suitable to your individual needs. At Metropolis Labs, we understand the importance of personalised care and convenience in managing health conditions like hiatal hernia. Our in-house visit services make it easy for you to get the necessary tests done from the comfort of your home, while our informative blogs provide valuable insights into various health topics.
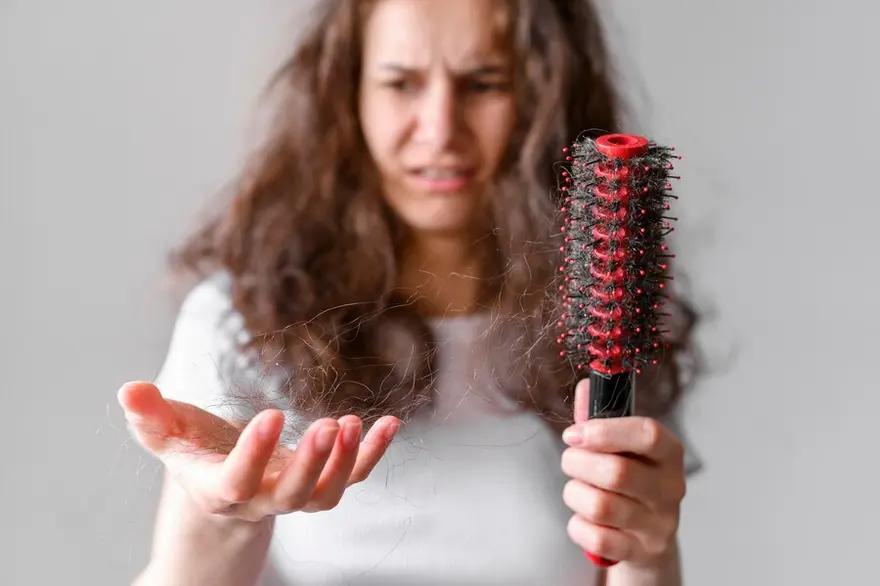
मानसून सीजन में बालों का झड़ना कैसे रोकें
परिचय हम मानसून के मौसम को खुशियों, चिलचिलाती गर्मी से राहत और अविश्वसनीय सुंदरता से जोड़ते हैं। हालाँकि, यह मौसम कुछ अनचाहे मेहमानों को भी साथ लाता है जिन्हें हेयर फॉल कहते हैं। क्लाइमेट चेंज हमारे बालों पर बुरा असर डाल सकता है, जिससे उनके टूटने और झड़ने की संभावना बढ़ जाती है। लेकिन हमें बरसात के मौसम में इस बढ़े हुए बालों के झड़ने का अनुभव क्यों होता है? यह लेख मानसून के दौरान बालों के झड़ने के कारणों की जांच करके इन चिंताओं को संबोधित करता है और मानसून में बालों के झड़ने को रोकने के लिए प्रैक्टिकल टिप्स प्रदान करता है। मानसून में बाल क्यों झड़ते हैं? मानसून के दौरान, हमारे बाल बहुत कुछ सहते हैं - लगातार आर्द्रता (ह्यूमिडिटी) के संपर्क में रहने से लेकर मौसम की बदलती परिस्थितियों तक। परिणामस्वरूप, हमारे बाल कमजोर हो जाते हैं और टूटने लगते हैं। सामान्य परिस्थितियों में, एक औसत व्यक्ति एक दिन में लगभग 50-100 बाल खोता है, हालाँकि, मानसून के मौसम में यह संख्या बढ़कर 250 से अधिक हो सकती है! इस वृद्धि का मुख्य कारण वातावरण में उच्च आर्द्रता (ह्यूमिडिटी) स्तर की उपस्थिति है जिससे हमारे बाल हाइड्रोजन अवशोषित करते हैं। यह प्रक्रिया हमारे बालों को भंगुर और कमजोर बनाती है, जो सीधे मानसून के दौरान बालों के झड़ने में वृद्धि की ओर ले जाती है। इसके अतिरिक्त, आवश्यक तेलों की कमी और बारिश के पानी के संपर्क में आने से आपके बाल उलझ सकते हैं, जिससे बालों को और अधिक नुकसान होता है। मानसून में बालों के झड़ने के कारण आइए मानसून में बालों के झड़ने के कुछ सामान्य कारणों पर गहराई से विचार करें: - उच्च आर्द्रता (ह्यूमिडिटी): हवा में नमी की बढ़ी हुई मात्रा बालों को कमजोर कर देती है, जिससे वे टूटने और उलझने लगते हैं। - पसीना और गंदगी जमा होना: आर्द्र (ह्यूमिड) मौसम के कारण पसीना आता है, जो आगे गंदगी के साथ मिलकर बालों के रोमछिद्रों को बंद कर देता है और मानसून में बाल झड़ने का कारण बनता है। - फंगल संक्रमण: नम वातावरण स्कैल्प पर फफूंद की वृद्धि को बढ़ावा दे सकता है, जिससे रूसी जैसी समस्याएं पैदा हो सकती हैं, जो बालों के झड़ने का कारण बन सकती हैं। - एसिड रेन: बारिश के पानी में प्रदूषक इसे अम्लीय बना सकते हैं, जिससे बालों को नुकसान होता है और बालों का झड़ना बढ़ जाता है। - गीले बालों को संभालना: बाल गीले होने पर कमजोर होते हैं, और बार-बार गीला करने और सुखाने से वे आसानी से टूट सकते हैं। - खराब आहार: बरसात के मौसम के दौरान आहार संबंधी आदतों में बदलाव, जैसे ताजी सब्जियों और फलों का कम सेवन, बालों के स्वास्थ्य को प्रभावित कर सकता है। - तनाव और जीवनशैली में बदलाव: तनाव और जीवनशैली में बदलाव, जिसमें बदले हुए रूटीन और कम शारीरिक गतिविधि शामिल हैं, बालों के स्वास्थ्य को प्रभावित कर सकते हैं और मानसून में बालों के झड़ने में योगदान कर सकते हैं। मानसून में बालों की देखभाल कैसे करें? मानसून के मौसम में बालों को अतिरिक्त देखभाल की आवश्यकता होती है क्योंकि बढ़ी हुई आर्द्रता (ह्यूमिडिटी) फ्रिज़, स्कैल्प संक्रमण और बालों के झड़ने का कारण बन सकती है। मानसून में बालों के झड़ने को रोकने और स्वस्थ बाल बनाए रखने के लिए, उन्हें साफ और सूखा रखना, हल्के बालों की देखभाल उत्पादों का उपयोग करना और अत्यधिक स्टाइलिंग से बचना महत्वपूर्ण है। नियमित रूप से बालों में तेल लगाना और माइल्ड शैम्पू का उपयोग करने से बालों की प्राकृतिक नमी को बनाए रखने और नुकसान को रोकने में मदद मिल सकती है। इसके अतिरिक्त, बालों को बारिश के पानी से बचाने और स्टिफ हेयरस्टाइल से बचने से बालों और स्कैल्प पर तनाव कम हो सकता है। ऑयली बालों के लिए टिप्स - बार-बार धोना: अतिरिक्त तेल और गंदगी को हटाने के लिए अपने बालों को नियमित रूप से माइल्ड और क्लियर शैम्पू से धोएं। - भारी कंडीशनर से बचें: हल्के कंडीशनर का प्रयोग करें और सिर की त्वचा पर अतिरिक्त तेल जमा होने से बचाने के लिए केवल बालों के सिरे पर ही ध्यान केंद्रित करें। - ड्राई शैम्पू: बालों को धोने के बीच में अतिरिक्त तेल को सोखने के लिए ड्राई शैम्पू का प्रयोग करें ताकि आपके बाल ताजा दिखें। - ठंडे पानी से धोना: सिर के रोमछिद्रों को बंद करने और तेल के स्राव को कम करने के लिए अपने बालों को ठंडे पानी से धोएं। सूखे बालों के लिए टिप्स - हाइड्रेटिंग शैम्पू और कंडीशनर: खोई हुई नमी को वापस लाने और बालों को नमी प्रदान करने के लिए मॉइस्चराइजिंग शैम्पू और कंडीशनर का उपयोग करें। - नियमित तेल लगाना: सूखे बालों को पोषण देने और उन्हें मजबूत बनाने के लिए नियमित रूप से अपने बालों और सिर की त्वचा पर नारियल या जैतून जैसे प्राकृतिक तेल लगाएं। - हीट स्टाइलिंग को सीमित करें: अपने बालों को और अधिक सूखने से रोकने के लिए, हेयर ड्रायर, स्ट्रेटनर और कर्लिंग आयरन जैसे गर्म स्टाइलिंग टूल्स का अत्यधिक उपयोग करने से बचें। - लीव-इन कंडीशनर: अतिरिक्त नमी और फ्रिज़ के खिलाफ सुरक्षा प्रदान करने के लिए लीव-इन कंडीशनर या हेयर सीरम का उपयोग करें। मानसून में बालों के झड़ने को रोकने के टिप्स मानसून में बालों के झड़ने को रोकने के लिए यहां कुछ प्रभावी रणनीतियां दी गई हैं: - बाल धोने के बाद उन्हें प्राकृतिक रूप से सूखने दें। - खुरदुरे तौलिये के बजाय माइक्रोफाइबर तौलिये का उपयोग करें। - स्ट्रेटनर या कर्लर जैसे स्टाइलिंग टूल्स का अत्यधिक उपयोग करने से बचें। - अपने बालों को सुलझाने के लिए चौड़े दांतों वाली कंघी का उपयोग करें। - बारिश में बाहर निकलते समय अपने सिर और बालों को ढक कर रखें। - सिर की त्वचा को हाइड्रेट रखने के लिए नियमित रूप से बालों में तेल लगाएं। बाल झड़ने की प्रारंभिक स्क्रीनिंग क्यों महत्वपूर्ण है? बालों के झड़ने का शीघ्र पता लगाना महत्वपूर्ण है, क्योंकि इससे बालों के झड़ने के मूल कारण की शीघ्र पहचान करने में मदद मिल सकती है, जिससे शीघ्र हस्तक्षेप और उपचार संभव हो सकता है। बालों के झड़ने का प्रारंभिक पता लगाने से बालों के झड़ने को रोकने और उपचार की प्रभावशीलता बढ़ाने में मदद मिल सकती है। यह हार्मोनल असंतुलन, पोषण संबंधी कमी और स्कैल्प संक्रमण जैसी अंतर्निहित स्थितियों का निदान करने में भी मदद कर सकता है जो बालों के झड़ने का कारण हो सकती हैं। अक्सर पूछे जाने वाले प्रश्न (FAQs) क्या मानसून के दौरान बालों का झड़ना सामान्य है? हाँ, मानसून के मौसम में मौसम की बदलती परिस्थितियों और बढ़ी हुई आर्द्रता (ह्यूमिडिटी) के कारण बालों के झड़ने में वृद्धि का अनुभव होना सामान्य है। क्या मानसून में बालों का झड़ना बढ़ जाता है? हाँ, मानसून के दौरान उच्च आर्द्रता (ह्यूमिडिटी) और बार-बार मौसम परिवर्तन से बालों के झड़ने में वृद्धि हो सकती है। आप मानसून से संबंधित बालों की समस्याओं का इलाज कैसे कर सकते हैं? अपने स्कैल्प को साफ रखकर, अच्छी स्वच्छता बनाए रखकर, संतुलित आहार खाकर और हल्के बालों की देखभाल करने वाले उत्पादों का उपयोग करके, आप मानसून से संबंधित बालों की समस्याओं का प्रभावी ढंग से प्रबंधन कर सकते हैं। निष्कर्ष आपको मानसून में अत्यधिक बालों के झड़ने की चिंता करने की ज़रूरत नहीं है। इन जानकारियों और सुझावों के साथ, अब आप बरसात के मौसम में बालों के झड़ने को रोकने के लिए बेहतर तरीके से तैयार हैं ताकि आप बारिश का आनंद बिना बालों की चिंता किए ले सकें। याद रखें कि हर व्यक्ति के बाल अनोखे होते हैं; जो उपाय एक के लिए काम करता है वह दूसरे के लिए भी काम करें यह जरूरी नहीं है। इसलिए, व्यक्तिगत सलाह के लिए स्वास्थ्य सेवा प्रदाताओं से परामर्श करने की सिफारिश की जाती है। विभिन्न डायग्नोस्टिक्स और स्वास्थ्य जांच सेवाओं के बारे में अधिक जानकारी के लिए मेट्रोपोलिस लैब्स का पता लगाने पर विचार करें जो कई स्वास्थ्य चिंताओं का समाधान करती हैं। उनके घर पर नमूना संग्रह सेवा और उन्नत डायग्नोस्टिक लैब के साथ सटीक परिणाम सुनिश्चित करना, मेट्रोपोलिस हेल्थकेयर के साथ अपने स्वास्थ्य को प्राथमिकता देना संभव है!
 Home Visit
Home Visit Upload
Upload









1720012827.webp)











 WhatsApp
WhatsApp