Latest Blogs
क्या आपके शरीर में लगातार दर्द और अकड़न हो रही है? ये सेहत से जुड़ी समस्याएं आपको पता होनी चाहिए
शरीर में दर्द होना आम बात है। यह तनाव, थकान या छोटी-मोटी चोटों की वजह से हो सकता है। हल्के बुखार के साथ सिरदर्द और शरीर में दर्द भी सामान्य लक्षण होते हैं। आमतौर पर, इससे ठीक होने में 4-5 दिन लगते हैं और यह कोई गंभीर समस्या नहीं होती। लेकिन यह जानना ज़रूरी है कि आपके बुखार के साथ शरीर में दर्द क्यों हो रहा है। कुछ मामलों में, यह फ्लू, डेंगू, मलेरिया, चिकनगुनिया या कोविड-19 जैसी बीमारियों का गंभीर संकेत हो सकता है। इन सभी बीमारियों के लक्षण मिलते-जुलते होते हैं, जैसे बुखार, मतली, ठंड लगना और शरीर में दर्द। अगर इन लक्षणों को नजरअंदाज किया जाए तो समस्या और बढ़ सकती है। कुछ मामलों में, सिर्फ बुखार या शरीर में दर्द ही एकमात्र लक्षण होता है। ये सभी बीमारियां संक्रामक होती हैं, इसलिए सावधानी बरतना जरूरी है, जैसे आइसोलेशन में रहना। घर पर ही सामान्य दवाइयां लें, और अगर 4 दिनों बाद भी लक्षण बने रहें, तो डॉक्टर से सलाह लें। साधारण बुखार लक्षण साधारण बुखार के लक्षणों में सिरदर्द, शरीर में दर्द, मतली, ठंड लगना, उल्टी और गंभीर मामलों में दस्त शामिल हो सकते हैं। आमतौर पर, यह 3 दिनों के भीतर ठीक हो जाता है। हालांकि, अगर बच्चों में बुखार 101°F तक पहुंच जाए, तो इसे आपात स्थिति मानकर तुरंत इलाज कराना चाहिए। कारण जब कोई बाहरी कण आपके शरीर में प्रवेश करता है, तो आपकी रोग प्रतिरोधक क्षमता इससे लड़ने लगती है। इस प्रक्रिया के दौरान शरीर का तापमान 99°F से 101°F तक बढ़ सकता है। हालांकि, यह एक अच्छा संकेत होता है, जो बताता है कि आपकी प्रतिरक्षा प्रणाली सही तरीके से काम कर रही है। फ्लू लक्षण इंफ्लूएंजा या फ्लू के सामान्य लक्षणों में बुखार, सिरदर्द, आंखों में दर्द, गले में खराश, खांसी और जकड़न शामिल हैं। अगर आप स्वाइन फ्लू की चपेट में आते हैं, तो मतली, उल्टी और दस्त भी हो सकते हैं। फ्लू कितना खतरनाक होगा, यह वायरस पर निर्भर करता है। इसके लक्षण सामान्य सर्दी जैसे होते हैं, लेकिन यह उससे कहीं अधिक गंभीर होता है। कारण इंफ्लूएंजा या फ्लू एक वायरस जनित बीमारी है, जो इंफ्लूएंजा वायरस के प्रकार A, B, C और D से होती है। हर प्रकार का असर अलग होता है। आमतौर पर, मरीज 1-4 दिनों में ठीक हो जाते हैं, लेकिन बुजुर्गों और बच्चों के लिए यह गंभीर हो सकता है। अधिकतर मामलों में, यह तब फैलता है जब कोई व्यक्ति संक्रमित व्यक्ति की छींक या खांसी से निकलने वाली सूक्ष्म बूंदों को सांस के जरिए अंदर लेता है। अगर आप किसी संक्रमित सतह को छूने के बाद अपनी नाक, मुंह या आंखों को छूते हैं, तो आपको भी संक्रमण हो सकता है। कोविड-19 लक्षण कोविड-19 के सामान्य लक्षणों में बुखार, मांसपेशियों में दर्द, सिरदर्द, गले में खराश, ऑक्सीजन की कमी के कारण सांस लेने में दिक्कत, खांसी, स्वाद और गंध खो जाना, बहती नाक, आंखों में लालिमा और उल्टी शामिल हैं। हर मरीज में ये लक्षण नहीं दिखते; कुछ लोग बिना किसी लक्षण के भी संक्रमित हो सकते हैं (असंक्रमित मामले)। कोविड-19 से ग्रसित व्यक्ति को कम से कम 14 दिनों के लिए आइसोलेट करना जरूरी होता है। कारण कोविड-19 एक वायरस Sars-CoV-2 या कोरोना वायरस के कारण होता है। यह हल्के से लेकर तेज बुखार के साथ अत्यधिक शरीर दर्द का कारण बन सकता है और कुछ मामलों में, वायरस के वेरिएंट के अनुसार, यह जानलेवा भी हो सकता है। डेंगू, चिकनगुनिया और मलेरिया लक्षण इन तीनों मच्छर जनित बीमारियों के लक्षण काफी हद तक एक जैसे होते हैं। हल्के से तेज बुखार, जोड़ों में तेज दर्द, सिरदर्द, उल्टी और दस्त इनमें आम लक्षण हैं। मलेरिया में इसके अलावा खांसी और ठंड लगने जैसे लक्षण भी देखे जाते हैं। कारण डेंगू और चिकनगुनिया वायरस के कारण होते हैं और एडीज मच्छर के काटने से फैलते हैं। वहीं, मलेरिया एक परजीवी के कारण होता है, जो एनाफिलीज मच्छर के जरिए फैलता है। अगर आपकी रोग प्रतिरोधक क्षमता कमजोर है, तो ये बीमारियां जानलेवा साबित हो सकती हैं। कब आपको गंभीर होने की जरूरत है? तेज बुखार और शरीर में दर्द: अगर 3 दिनों के बाद भी बुखार कम नहीं होता और शरीर में तेज दर्द व सिरदर्द बढ़ता जा रहा है, तो इसे हल्के में न लें। लगातार उल्टी: अगर आपको लगातार उल्टी हो रही है या उल्टी में खून आ रहा है, तो यह खतरे का संकेत हो सकता है। ऐसे में तुरंत डॉक्टर से सलाह लें। ऑक्सीजन स्तर में कमी: अगर सांस लेने में तकलीफ हो रही है, साथ ही तेज बुखार और शरीर में दर्द है, तो यह कोविड-19 का गंभीर लक्षण हो सकता है। ऐसे में तुरंत इलाज कराना जरूरी है। जरूरी जांचें सामान्य बुखार के लिए किसी विशेष जांच की जरूरत नहीं होती। फ्लू या इंफ्लूएंजा की पुष्टि के लिए फीवर प्रोफाइल ब्लड टेस्ट किए जाते हैं। डेंगू, मलेरिया और चिकनगुनिया जैसी मच्छर जनित बीमारियों का पता लगाने के लिए ब्लड टेस्ट जरूरी होते हैं। कोविड-19 की जांच स्वैब सैंपल और ब्लड टेस्ट के जरिए की जाती है। सभी जांच डॉक्टर की सलाह के अनुसार किसी मान्यता प्राप्त पैथोलॉजी लैब में करानी चाहिए। लक्षणों की प्रकृति के अनुसार टेस्ट अलग-अलग हो सकते हैं। निदान और दवाईयां आमतौर पर, सामान्य बुखार के लिए डॉक्टर बुखार कम करने वाली दवाएं देते हैं। संक्रमण न फैले, इसके लिए पूरी तरह आराम करने और आइसोलेशन में रहने की सलाह दी जाती है। अगर लक्षण गंभीर हों, तो डॉक्टर जांच के नतीजों के आधार पर दवाएं बदल सकते हैं और इलाज जारी रखते हैं। यदि आवश्यक हो, तो डॉक्टर आपको अस्पताल में भर्ती करने का फैसला ले सकते हैं। निष्कर्ष हर साल नए वायरस सामने आ रहे हैं, जिससे नई बीमारियां फैल रही हैं। लापरवाही करने से गंभीर परिणाम हो सकते हैं। अगर 3 दिनों के बाद भी तेज बुखार और शरीर में अधिक दर्द बना रहे, तो तुरंत डॉक्टर से संपर्क करें। हालांकि, घबराने की जरूरत नहीं है। Metropolis Healthcare एक प्रमुख लैब है, जो आपकी जरूरत के अनुसार घर से सैंपल कलेक्ट करती है। आपको 24 घंटे के भीतर ऑनलाइन रिपोर्ट मिल जाती है। यह लैब सभी आवश्यक प्रोटोकॉल का पालन करती है और इसकी टीम में 200 प्रमुख पैथोलॉजिस्ट और 2000+ तकनीशियन हैं, जो सटीक डायग्नोस्टिक समाधान प्रदान करते हैं।
कोलेस्टेसिस: पित्त प्रवाह में रुकावट के कारण और उपचार रणनीतियाँ
कोलेस्टेसिस क्या है? कोलेस्टेसिस एक ऐसी स्थिति है जिसमें लिवर से छोटी आंत तक पित्त का प्रवाह कम हो जाता है या पूरी तरह रुक जाता है, जिससे पित्त लिवर और रक्तप्रवाह में जमा होने लगता है। पित्त वसा को पचाने और वसा में घुलने वाले विटामिन (A, D, E और K) को अवशोषित करने के लिए आवश्यक होता है। जब पित्त प्रवाह बाधित होता है, तो कोलेस्टेसिस के लक्षण दिखाई देते हैं, जैसे पीलिया (त्वचा और आंखों का पीला पड़ना), गहरा पेशाब, हल्के रंग का मल, तेज खुजली और थकान। कोलेस्टेसिस लिवर रोगों, कुछ दवाओं, संक्रमणों या पित्त नलिकाओं में रुकावट के कारण हो सकता है। लक्षणों को नियंत्रित करने और संभावित लिवर क्षति को रोकने के लिए शुरुआती निदान और उपचार बहुत जरूरी है। कोलेस्टेसिस हमारे शरीर को कैसे प्रभावित करता है? कोलेस्टेसिस शरीर के कई अंगों और प्रणालियों को प्रभावित कर सकता है: लिवर और पित्त नलिकाएं: पित्त के जमाव से लिवर, पित्ताशय, अग्न्याशय और पित्त नलिकाओं में सूजन और क्षति हो सकती है, जिससे दर्द, मतली और संक्रमण का खतरा बढ़ जाता है। पाचन तंत्र: आंतों में पित्त की कमी वसा के पाचन को बाधित करती है, जिससे अपच, दस्त और वसायुक्त मल (स्टीटोरेहा) हो सकता है। इससे आवश्यक पोषक तत्वों का अवशोषण भी प्रभावित हो सकता है। त्वचा और आंखें: रक्त में बिलीरुबिन के बढ़ने से पीलिया होता है, जिससे त्वचा और आंखों का सफेद हिस्सा पीला पड़ जाता है। त्वचा में पित्त तत्वों के जमा होने से तेज खुजली (प्रुरिटस) भी हो सकती है। संपूर्ण स्वास्थ्य: लंबे समय तक कोलेस्टेसिस बने रहने से पोषण की कमी, हड्डियों की कमजोरी और वसा में घुलने वाले विटामिनों के अवशोषण में बाधा के कारण रक्तस्राव का खतरा बढ़ सकता है। क्या कोलेस्टेसिस जानलेवा हो सकता है? अगर कोलेस्टेसिस का सही तरीके से प्रबंधन नहीं किया जाए, तो यह जानलेवा हो सकता है। इसके संभावित जटिलताओं में शामिल हैं: लिवर की खराबी: लंबे समय तक कोलेस्टेसिस बने रहने से गंभीर लिवर क्षति और सिरोसिस हो सकता है। संक्रमण: पित्त नलिकाओं में रुकावट के कारण कोलांगाइटिस (पित्त नलिकाओं का संक्रमण) हो सकता है, जो समय पर इलाज न मिलने पर घातक साबित हो सकता है। पोषण की कमी: लंबे समय तक कोलेस्टेसिस रहने से वसा में घुलने वाले विटामिनों और अन्य आवश्यक पोषक तत्वों की कमी हो सकती है, जिससे गंभीर स्वास्थ्य समस्याएं उत्पन्न हो सकती हैं। कोलेस्टेसिस के कारण क्या हैं? कोलेस्टेसिस के कारणों को मुख्य रूप से दो प्रकारों में विभाजित किया जा सकता है: इन्ट्राहेपेटिक (लिवर के भीतर) और एक्स्ट्राहेपेटिक (लिवर के बाहर)। इन्ट्राहेपेटिक कोलेस्टेसिस आमतौर पर लिवर से जुड़ी बीमारियों या प्रणालीगत कारकों के कारण होता है, जबकि एक्स्ट्राहेपेटिक कोलेस्टेसिस आमतौर पर पित्त नलिकाओं में किसी शारीरिक रुकावट की वजह से होता है। दोनों के कारण अलग-अलग होते हैं और इनका उपचार भी भिन्न होता है। सही कारण की पहचान करना महत्वपूर्ण है, क्योंकि यह उपचार की दिशा तय करने में मदद करता है, जिससे पित्त प्रवाह को बहाल किया जा सके और संभावित जटिलताओं से बचाव किया जा सके। एक्स्ट्राहेपेटिक कोलेस्टेसिस और इन्ट्राहेपेटिक कोलेस्टेसिस के संभावित कारण क्या हैं? एक्स्ट्राहेपेटिक और इन्ट्राहेपेटिक कोलेस्टेसिस के अलग-अलग कारण होते हैं, जो इस बात पर निर्भर करते हैं कि पित्त प्रवाह लिवर के अंदर बाधित हो रहा है (इन्ट्राहेपेटिक) या लिवर के बाहर (एक्स्ट्राहेपेटिक)। दोनों ही स्थितियों में पित्त प्रवाह बाधित हो जाता है, जो वसा के पाचन और विषाक्त पदार्थों के निष्कासन के लिए आवश्यक होता है। लिवर को प्रभावित करने वाले कारण (इन्ट्राहेपेटिक कोलेस्टेसिस) शामिल हैं: क्रोनिक लिवर डिजीज - सिरोसिस और प्राइमरी बाइलरी कोलांगाइटिस (PBC) जैसी स्थितियां लिवर की कोशिकाओं और पित्त नलिकाओं को धीरे-धीरे नुकसान पहुंचाती हैं, जिससे पित्त प्रवाह बाधित होता है और इन्ट्राहेपेटिक कोलेस्टेसिस हो सकता है। एक्यूट हेपेटाइटिस - हेपेटाइटिस A, B और C जैसे वायरल संक्रमणों के कारण लिवर में सूजन आ सकती है, जिससे अस्थायी रूप से पित्त उत्पादन प्रभावित होता है और इन्ट्राहेपेटिक कोलेस्टेसिस विकसित हो सकता है। गर्भावस्था - गर्भावस्था के दौरान इन्ट्राहेपेटिक कोलेस्टेसिस (ICP) हार्मोनल परिवर्तनों के कारण पित्त प्रवाह में बाधा डाल सकता है। यह आमतौर पर डिलीवरी के बाद ठीक हो जाता है, लेकिन भ्रूण के लिए संभावित जोखिमों के कारण इसे निगरानी में रखना आवश्यक होता है। टोटल पैरेंटेरल न्यूट्रिशन (TPN) - लंबे समय तक TPN (एक प्रकार का इंट्रावेनस पोषण) का उपयोग करने से इन्ट्राहेपेटिक कोलेस्टेसिस हो सकता है, क्योंकि आंतों में पित्त प्रवाह की कमी से लिवर में पित्त जमा हो सकता है। दवाइयां - कुछ दवाएं, जैसे एनाबॉलिक स्टेरॉयड और कुछ एंटीबायोटिक्स, लिवर को नुकसान पहुंचाकर या पित्त प्रवाह में बाधा डालकर कोलेस्टेसिस को जन्म दे सकती हैं। इस प्रभाव की तीव्रता व्यक्ति और दवा के प्रकार पर निर्भर करती है। आपकी एक्स्ट्राहेपेटिक बाइल डक्ट्स को प्रभावित करने वाले कारणों में शामिल हैं: बिलियरी स्ट्रिक्चर - बिलियरी स्ट्रिक्चर, यानी पित्त नलिकाओं का संकीर्ण होना, सूजन या निशान (स्कार टिशू) बनने के कारण हो सकता है, जिससे पित्त प्रवाह बाधित हो जाता है। यह आमतौर पर सर्जरी, चोट या सूजन के कारण होता है और पित्त निकासी को बहाल करने के लिए उपचार की आवश्यकता होती है। बाइल डक्ट ऑब्स्ट्रक्शंस - गॉलस्टोन, ट्यूमर या सिस्ट जैसी रुकावटें लिवर के बाहर पित्त नलिकाओं को अवरुद्ध कर सकती हैं, जिससे पित्त आंतों तक नहीं पहुंच पाता। आमतौर पर ये रुकावटें कॉमन बाइल डक्ट या अग्न्याशय के सिर (पैंक्रियाटिक हेड) में होती हैं, जिससे एक्स्ट्राहेपेटिक कोलेस्टेसिस विकसित होता है। अग्नाशय या पित्त नलिकाओं के ट्यूमर भी इन नलिकाओं पर दबाव डालकर पित्त प्रवाह को बाधित कर सकते हैं। कोलेस्टेसिस के लक्षण क्या हैं? कोलेस्टेसिस के लक्षण पित्त अम्लों और अन्य पदार्थों के रक्तप्रवाह में जमा होने के कारण उत्पन्न होते हैं, क्योंकि पित्त प्रवाह बाधित हो जाता है। ये लक्षण हल्के से लेकर गंभीर तक हो सकते हैं और त्वचा, पाचन तंत्र और संपूर्ण स्वास्थ्य को प्रभावित कर सकते हैं। मुख्य कोलेस्टेसिस लक्षणों में शामिल हैं: पीलिया (Jaundice): रक्त में बिलीरुबिन के बढ़ने के कारण त्वचा और आंखों में पीलापन आ जाता है, जो आमतौर पर पित्त प्रवाह में रुकावट का संकेत देता है। खुजली (Pruritus): यह अक्सर तेज और पूरे शरीर में होती है, जो कोलेस्टेसिस का सबसे असहज लक्षण हो सकता है। यह त्वचा में जमा पित्त अम्लों के कारण होती है। गाढ़ा मूत्र और हल्के रंग का मल: जब बिलीरुबिन आंतों तक नहीं पहुंच पाता, तो मल का रंग हल्का हो जाता है, जबकि मूत्र गहरे रंग का हो सकता है। पेट दर्द: आमतौर पर ऊपरी दाहिने पेट में दर्द महसूस होता है, खासकर अगर गॉलस्टोन या पित्त नलिकाओं में रुकावट कोलेस्टेसिस का कारण बन रही हो। थकान और कमजोरी: कई लोगों को लगातार थकान और अस्वस्थता महसूस होती है। मतली और भूख न लगना: पाचन संबंधी परेशानियां आम होती हैं, जिससे भूख कम लगती है और कभी-कभी वजन भी घट सकता है। अतिरिक्त लक्षणों में शामिल हो सकते हैं: बुखार: आमतौर पर तब होता है जब संक्रमण मौजूद हो, विशेष रूप से बिलियरी ऑब्स्ट्रक्शन के मामलों में। जल्दी चोट लगना या खून बहना: शरीर में विटामिन K का अवशोषण सही से न होने के कारण, जो रक्त का थक्का जमाने के लिए आवश्यक होता है। वसा युक्त, दुर्गंधयुक्त मल (Steatorrhea): वसा के अवशोषण में कमी के कारण मल चिकना और बदबूदार हो सकता है। ये लक्षण आमतौर पर लिवर या पित्त नलिकाओं की समस्या को दर्शाते हैं और उचित निदान एवं उपचार के लिए तुरंत चिकित्सा जांच आवश्यक होती है, ताकि लक्षणों से राहत मिल सके और पित्त प्रवाह को सुधारने में मदद मिल सके। कोलेस्टेसिस का निदान कैसे किया जाता है? कोलेस्टेसिस के निदान के लिए कई चरणों की आवश्यकता होती है ताकि इसकी पुष्टि की जा सके और इसके मूल कारण की पहचान की जा सके। इसके लिए शारीरिक परीक्षण, रक्त परीक्षण, इमेजिंग और कभी-कभी इनवेसिव प्रक्रियाओं का उपयोग किया जाता है। 1. रक्त परीक्षण: लिवर फंक्शन टेस्ट बिलीरुबिन और लिवर एंजाइम्स जैसे अल्कलाइन फॉस्फेटेज (ALP) और गामा-ग्लूटामाइल ट्रांसफरेज (GGT) के स्तर को मापते हैं, जो कोलेस्टेसिस में बढ़ जाते हैं। संक्रमण की जांच के लिए हेपेटाइटिस वायरस परीक्षण किए जाते हैं, जिससे संक्रामक कारणों की पहचान की जा सकती है। एंटीबॉडी स्क्रीनिंग से ऑटोइम्यून लिवर डिजीज का पता लगाया जाता है, जो कोलेस्टेसिस में योगदान कर सकती है। 2. इमेजिंग परीक्षण: एब्डोमिनल अल्ट्रासाउंड लिवर, गॉलब्लैडर और पित्त नलिकाओं की स्पष्ट तस्वीर प्रदान करता है, जिससे गॉलस्टोन या ट्यूमर जैसी रुकावटों का पता लगाया जा सकता है। MRI या CT स्कैन अधिक विस्तृत चित्र प्रदान करते हैं और बिलियरी सिस्टम की सटीक जांच में सहायक होते हैं। मैग्नेटिक रेज़ोनेंस कोलांजियोपैंक्रिएटोग्राफी (MRCP) या एंडोस्कोपिक रेट्रोग्रेड कोलांजियोपैंक्रिएटोग्राफी (ERCP) विशेष इमेजिंग तकनीकें हैं, जो पित्त नलिकाओं का अधिक बारीकी से अध्ययन करने और अवरोधों की पहचान करने में मदद करती हैं। 3. नैदानिक परीक्षण: लिवर बायोप्सी में लिवर से एक छोटा ऊतक नमूना लिया जाता है, जिसे माइक्रोस्कोप के तहत जांचा जाता है। इससे लिवर में सूजन, स्कारिंग या अन्य असामान्यताओं का पता चल सकता है। एंडोस्कोपिक प्रक्रियाओं के माध्यम से पित्त नलिकाओं का सीधा अवलोकन किया जाता है, जिसमें आवश्यक होने पर ऊतक के नमूने लेने या अवरोध हटाने की सुविधा भी होती है। कोलेस्टेसिस का उपचार कैसे किया जाता है? कोलेस्टेसिस का उपचार इसके कारण का समाधान करने, लक्षणों को कम करने और जटिलताओं को रोकने पर केंद्रित होता है। उपचार की विधि इस बात पर निर्भर करती है कि यह स्थिति तीव्र है या पुरानी। एक्यूट कारणों के लिए: दवाइयों को बंद करना: कुछ दवाएं कोलेस्टेसिस का कारण बन सकती हैं या उसे बढ़ा सकती हैं, और इन्हें बंद करने से लक्षणों में सुधार हो सकता है। संक्रमण का उपचार: यदि कोलेस्टेसिस का कारण संक्रमण, जैसे कि एक्यूट हेपेटाइटिस है, तो इसे नियंत्रित करने के लिए एंटीवायरल दवाओं का उपयोग किया जाता है। अवरोध को दूर करना: गॉलस्टोन और पित्त नलिकाओं में अन्य रुकावटों का इलाज एंडोस्कोपिक प्रक्रियाओं या शल्य चिकित्सा के माध्यम से किया जा सकता है, जिससे सामान्य पित्त प्रवाह बहाल होता है। गर्भावस्था से संबंधित कोलेस्टेसिस: गर्भावस्था में कोलेस्टेसिस के लिए मां और बच्चे की करीबी निगरानी जरूरी होती है। कुछ मामलों में, जल्दी प्रसव की सलाह दी जा सकती है। क्रोनिक कारणों के लिए: पित्त प्रवाह दवाइयां: यूर्सोडिओक्सीकोलिक एसिड (UDCA) को अक्सर पित्त प्रवाह को सुधारने और लिवर की सूजन को कम करने के लिए दिया जाता है, जो पुरानी लिवर बीमारियों में सहायक होता है, जो कोलेस्टेसिस का कारण बनती हैं। पोषण समर्थन: कोलेस्टेसिस से वसा-घुलनशील विटामिन्स (A, D, E, और K) की कमी हो सकती है। विटामिन सप्लीमेंट्स की आवश्यकता हो सकती है। मूल लिवर रोग का उपचार: सिरोसिस या ऑटोइम्यून हेपेटाइटिस जैसी पुरानी लिवर बीमारियों का इलाज पित्त प्रवाह को सुधारने और लक्षणों को कम करने में मदद कर सकता है। सर्जिकल हस्तक्षेप: यदि ट्यूमर या पित्त नलिकाओं को नुकसान पहुंचा है और ये कोलेस्टेसिस में योगदान कर रहे हैं, तो सर्जरी की आवश्यकता हो सकती है। लिवर ट्रांसप्लांटेशन: गंभीर मामलों में, जहां लिवर का नुकसान व्यापक और अपरिवर्तनीय हो, लिवर ट्रांसप्लांट ही एकमात्र प्रभावी उपचार हो सकता है। मूल कारण पर ध्यान केंद्रित करके, कोलेस्टेसिस का उपचार लक्षणों और समग्र स्वास्थ्य में महत्वपूर्ण सुधार ला सकता है। कोलेस्टेसिस वाले लोगों के लिए आउटलुक क्या है? कोलेस्टेसिस वाले व्यक्तियों का प्रक्षेपण (आउटलुक) इसके मूल कारण और उपचार पर प्रतिक्रिया के आधार पर भिन्न होता है। कई मामलों में, तीव्र कोलेस्टेसिस उस उत्प्रेरक कारक को ठीक करने के बाद ठीक हो जाता है। हालांकि, लिवर रोगों या आनुवंशिक स्थितियों के कारण पुराना कोलेस्टेसिस जीवनभर प्रबंधन और जटिलताओं की निगरानी की आवश्यकता हो सकती है। समय पर निदान और उचित उपचार से कोलेस्टेसिस के परिणाम और जीवन की गुणवत्ता में महत्वपूर्ण सुधार हो सकता है। निष्कर्ष याद रखें, समय पर हस्तक्षेप और उचित प्रबंधन गंभीर जटिलताओं को रोकने और लिवर स्वास्थ्य को बढ़ावा देने के लिए महत्वपूर्ण हैं। यदि आपको अपने लिवर की कार्यप्रणाली के बारे में चिंता है या विश्वसनीय निदान सेवाओं की आवश्यकता है, तो मेट्रोपोलिस हेल्थकेयर की सेवाओं को देखना एक अच्छा विकल्प हो सकता है। भारत भर में स्थित उन्नत लैब्स के नेटवर्क के साथ, मेट्रोपोलिस सटीक पैथोलॉजी परीक्षण और घर पर नमूना संग्रह की सुविधाएं प्रदान करता है, जो आपके स्वास्थ्य सफर में आपकी सहायता कर सकता है। आज ही अपनी सेहत का ध्यान रखें और बेहतर कल के लिए अपने लिवर स्वास्थ्य को प्राथमिकता दें।
जाइगेंटिज्म: अत्यधिक वृद्धि के कारण, लक्षण और उपचार
जाइगेंटिज्म क्या है? जाइगेंटिज्म एक दुर्लभ चिकित्सा स्थिति है, जो बचपन में, विशेष रूप से लंबी हड्डियों के एपिफ़िसिस (वृद्धि प्लेट्स) के जुड़ने से पहले, वृद्धि हार्मोन (GH) के अत्यधिक उत्पादन के कारण होती है। इसके परिणामस्वरूप असामान्य रूप से लंबा कद और मांसपेशियों और आंतरिक अंगों का आकार बढ़ना होता है। जाइगेंटिज्म वाले व्यक्तियों का कद सामान्यत: बहुत तेजी से बढ़ता है, और कभी-कभी यह 7 फीट से भी अधिक हो सकता है। जाइगेंटिज्म के सबसे सामान्य कारणों में से एक आमतौर पर पिट्यूटरी ग्रंथि पर एक सौम्य ट्यूमर, जिसे पिट्यूटरी एडेनोमा कहा जाता है, है, जो वृद्धि हार्मोन के अत्यधिक स्राव को उत्तेजित करता है। अन्य संभावित कारणों में हार्मोन नियंत्रण को प्रभावित करने वाली आनुवंशिक उत्परिवर्तन शामिल हो सकती हैं। जाइगेंटिज्म के शुरुआती लक्षणों में जूते और हाथों के आकार में वृद्धि, चेहरे के लक्षणों में noticeable बदलाव (जैसे बड़ा हुआ जबड़ा) और हड्डियों और ऊतकों की तेजी से वृद्धि के कारण जोड़ों में दर्द शामिल हो सकते हैं। निदान में सामान्यतः एक विस्तृत चिकित्सा इतिहास, शारीरिक परीक्षण और हार्मोन स्तर मापने के लिए रक्त परीक्षण शामिल होते हैं। पिट्यूटरी ट्यूमर की पहचान के लिए एमआरआई स्कैन जैसे इमेजिंग परीक्षण किए जा सकते हैं। जाइगेंटिज्म का उपचार आमतौर पर ट्यूमर की शल्य चिकित्सा हटाने, यदि वह मौजूद हो, और हार्मोन स्तर को नियंत्रित करने के लिए दवाइयाँ शामिल होती हैं। समय रहते हस्तक्षेप करना इस स्थिति के प्रबंधन में महत्वपूर्ण है और संभावित जटिलताओं, जैसे मधुमेह, उच्च रक्तचाप और हृदय संबंधी समस्याओं को कम करने में मदद कर सकता है। नियमित निगरानी और एक व्यापक उपचार योजना जाइगेंटिज्म वाले व्यक्तियों के लिए परिणामों में महत्वपूर्ण सुधार कर सकती है। जाइगेंटिज्म और एक्रोमेगली में क्या अंतर है? हालांकि दोनों ही स्थितियों में वृद्धि हार्मोन (GH) का अत्यधिक स्राव होता है, लेकिन मुख्य अंतर इस बात में है कि अत्यधिक GH उत्पादन कब होता है: जाइगेंटिज्म तब होता है जब GH का अत्यधिक स्राव लंबे हड्डियों के एपिफ़िसिस के जुड़ने से पहले होता है, सामान्यतः बचपन या किशोरावस्था में। इसका परिणाम होता है लंबा कद और शरीर की समानुपाती वृद्धि। एक्रोमेगली तब होती है जब GH का अत्यधिक स्राव एपिफ़िसिस के जुड़ने के बाद होता है, सामान्यतः वयस्कता में। इसका परिणाम होता है विकृत हड्डियाँ, मोटे चेहरे के लक्षण, और बढ़े हुए हाथ-पैर बिना कद में वृद्धि के। जाइगेंटिज्म किसे प्रभावित करता है? जाइगेंटिज्म मुख्य रूप से बच्चों और किशोरों को प्रभावित करता है, जब तक वे शारीरिक रूप से पूरी तरह परिपक्व नहीं हो जाते। अध्ययन से यह पता चलता है कि यह लड़कों में अधिक सामान्य है, जिसमें पिट्यूटरी जाइगेंटिज्म के लगभग 78% मामले लड़कों में देखे जाते हैं। जाइगेंटिज्म कितना सामान्य है? जाइगेंटिज्म एक बहुत ही दुर्लभ स्थिति है, और यह अक्रोमेगाली से भी कम सामान्य है, जो खुद एक दुर्लभ स्थिति है। जबकि इसका सटीक प्रसार अच्छी तरह से दस्तावेजीकृत नहीं है, यह अनुमानित किया गया है कि पिट्यूटरी जाइगेंटिज्म लगभग 8 से 11 लोगों को प्रति मिलियन जनसंख्या में प्रभावित करता है। बच्चों में सामान्य वृद्धि कैसे होती है? बच्चों में सामान्य वृद्धि एक जटिल प्रक्रिया है, जिसे कई महत्वपूर्ण कारक नियंत्रित करते हैं। यह प्रक्रिया तब शुरू होती है जब पिट्यूटरी ग्रंथि रक्तप्रवाह में वृद्धि हार्मोन (GH) जारी करती है। GH लीवर को इंसुलिन जैसे वृद्धि कारक-1 (IGF-1) उत्पन्न करने के लिए प्रेरित करता है, जो वृद्धि और विकास के लिए आवश्यक है। IGF-1 हड्डियों, मांसपेशियों और अन्य ऊतकों की वृद्धि को बढ़ावा देता है। इसके अलावा, वृद्धि प्लेटें, जिन्हें एपिफिजीयल प्लेट्स कहा जाता है, जो लंबी हड्डियों के अंत में स्थित होती हैं, ऊँचाई बढ़ाने के लिए आवश्यक होती हैं। ये वृद्धि प्लेटें हड्डियों के बढ़ने की अनुमति देती हैं, जब तक कि वे धीरे-धीरे किशोरावस्था के अंतिम चरण में मिल नहीं जातीं, जो ऊँचाई वृद्धि का अंत होता है। कई कारक इस वृद्धि प्रक्रिया को प्रभावित करते हैं, जिनमें आनुवंशिकी, पोषण, शारीरिक गतिविधि, और समग्र स्वास्थ्य शामिल हैं। पर्याप्त पोषण, विशेष रूप से प्रोटीन, विटामिन और खनिजों का पर्याप्त सेवन, वृद्धि का समर्थन करने के लिए आवश्यक है। नियमित शारीरिक गतिविधि भी बच्चों में स्वस्थ वृद्धि और विकास को बढ़ावा देती है, जिससे उन्हें अपनी पूरी वृद्धि क्षमता प्राप्त करने में मदद मिलती है। जाइगेंटिज्म के लक्षण क्या हैं? जाइगेंटिज्म से पीड़ित बच्चों में कई विशिष्ट लक्षण हो सकते हैं, जो हार्मोनल असंतुलन को दर्शाते हैं। कुछ सामान्य जाइगेंटिज्म लक्षणों में शामिल हैं: अत्यधिक रैखिक वृद्धि और लंबा कद बड़े हाथ और पैर मोटे चेहरे की विशेषताएँ (आगे उभरी हुई माथा, चौड़ी नाक की सेतू, बाहर निकला हुआ जबड़ा) दांतों का सामान्य से अधिक अंतर बार-बार सिरदर्द अधिक पसीना आना जोड़ों में दर्द प्रजनन का देर से होना (देरी से यौवन) नींद की समस्याएँ, जैसे कि नींद की आपत्ति (sleep apnea) आवाज़ में बदलाव पेशी कमजोरी गैलैक्टोरिया (स्तन से दूध का स्राव) लड़कियों में मासिक धर्म की अनियमितताएँ दृष्टि समस्याएँ अगर आपको अपने बच्चे में असामान्य वृद्धि या इनमें से किसी भी जाइगेंटिज्म लक्षण का सामना हो रहा है, तो डॉक्टर से परामर्श करना महत्वपूर्ण है। जल्दी हस्तक्षेप करने से उचित निदान और उपचार मिल सकता है, जिससे आपके बच्चे के स्वास्थ्य परिणामों में सुधार हो सकता है। जाइगेंटिज्म के लक्षणों की जल्दी पहचान उपचार विकल्पों में महत्वपूर्ण बदलाव ला सकती है। जाइगेंटिज्म के कारण क्या हैं? जाइगेंटिज्म के सबसे सामान्य कारणों में से एक है एक गैर-कैंसरस पिट्यूटरी ट्यूमर, जिसे सोमैटोट्रॉपिनोमा कहा जाता है, जो अत्यधिक वृद्धि हार्मोन का स्राव करता है। इस वृद्धि हार्मोन का अत्यधिक उत्पादन तेजी से विकास और वृद्धि का कारण बनता है, जिससे जाइगेंटिज्म के विशिष्ट लक्षण उत्पन्न होते हैं। कुछ अन्य संभावित जाइगेंटिज्म के कारण हैं जो हार्मोनल नियंत्रण को प्रभावित करने वाली विभिन्न आनुवंशिक बीमारियाँ हो सकती हैं और अत्यधिक वृद्धि को बढ़ावा देती हैं। इनमें से कुछ आनुवंशिक विकार हैं: कार्नी कॉम्प्लेक्स: एक दुर्लभ सिंड्रोम जो कई ट्यूमरों और हार्मोनल असंतुलन का कारण बन सकता है। मैकक्यून-आल्ब्राइट सिंड्रोम: एक स्थिति जो हड्डियों, त्वचा, और हार्मोन उत्पादन को प्रभावित करती है, जिसके परिणामस्वरूप विभिन्न असामान्यताएँ उत्पन्न होती हैं। मल्टीपल एंडोक्राइन न्यूप्लेसिया टाइप 1 (MEN-1): एक आनुवंशिक विकार जो कई एंडोक्राइन ग्रंथियों में ट्यूमरों का कारण बनता है। न्यूरोफाइब्रोमाटोसिस टाइप 1: एक आनुवंशिक विकार जिसमें नसों पर गैर-कैंसरस ट्यूमर विकसित होते हैं, जो हार्मोन स्तरों को प्रभावित कर सकते हैं। आइसोलेटेड फैमिलियल सोमैटोट्रॉपिनोमा: एक वंशानुगत स्थिति जिसमें परिवार के सदस्य वृद्धि हार्मोन-निर्गत ट्यूमरों का सामना कर सकते हैं। X-लिंक्ड एक्रोजाइगेंटिज्म: एक दुर्लभ आनुवंशिक स्थिति जो अत्यधिक वृद्धि हार्मोन उत्पादन से जुड़ी होती है। कुछ मामलों में, जाइगेंटिज्म इडियोपैथिक हो सकता है, जिसका मतलब है कि इसका सटीक कारण ज्ञात नहीं है। इसीलिए स्वास्थ्य सेवा प्रदाताओं के लिए यह महत्वपूर्ण है कि वे अत्यधिक जांच करें ताकि जाइगेंटिज्म के कारणों को समझा जा सके। इन कारणों की पहचान करना प्रभावी उपचार योजनाएँ तैयार करने में मदद कर सकता है जो स्थिति या संभावित जाइगेंटिज्म जटिलताओं को प्रबंधित करने में सहायक हो सकती हैं। जाइगेंटिज्म का निदान कैसे किया जाता है? जाइगेंटिज्म का निदान विभिन्न तरीकों से किया जाता है, जो वृद्धि पैटर्न और हार्मोनल असंतुलन का मूल्यांकन करने के लिए होते हैं। यह प्रक्रिया एक क्लिनिकल मूल्यांकन से शुरू होती है, जिसमें एक गहन शारीरिक परीक्षा और चिकित्सा इतिहास शामिल होता है, ताकि अत्यधिक वृद्धि और चेहरे में बदलाव जैसे लक्षण पहचाने जा सकें। प्रयोगशाला परीक्षण में इंसुलिन जैसे वृद्धि कारक 1 (IGF-1) के स्तर की माप और वृद्धि हार्मोन (GH) दबाव परीक्षण शामिल होते हैं, ताकि GH हाइपरसेक्रेशन की पुष्टि की जा सके। इसके अतिरिक्त, प्रोलैक्टिन, कोर्टिसोल, एस्ट्राडियोल (लड़कियों में), टेस्टोस्टेरोन (लड़कों में), और थायरॉयड हार्मोन के स्तर का मूल्यांकन किया जाता है। इमेजिंग अध्ययन, जैसे CT या MRI स्कैन, का उपयोग भी किया जाता है ताकि पिट्यूटरी ट्यूमर्स का पता लगाया जा सके, जो इस स्थिति के लिए जिम्मेदार हो सकते हैं। जाइगेंटिज्म का निदान करने के लिए कौन से परीक्षण किए जाएंगे? जाइगेंटिज्म का निदान करने के लिए, स्वास्थ्य सेवा प्रदाता सामान्यत: हार्मोन स्तरों का मूल्यांकन करने और संभावित अंतर्निहित कारणों की पहचान करने के लिए कई परीक्षणों की सिफारिश करते हैं। रक्त परीक्षण इस निदान प्रक्रिया में महत्वपूर्ण होते हैं। इनमें वृद्धि हार्मोन (GH) और इंसुलिन- जैसे वृद्धि तत्व 1 (IGF-1) स्तरों को मापना शामिल है, क्योंकि उच्च स्तर के संकेत होते हैं कि हाइपरसेक्शन हो रहा है। इसके अतिरिक्त, अन्य पिट्यूटरी हार्मोन जैसे एड्रेनोकोर्टिकोट्रॉपिक हार्मोन (ACTH), थायरॉयड- उत्तेजक हार्मोन (TSH), ल्यूटिनाइजिंग हार्मोन (LH), फॉलिकल- उत्तेजक हार्मोन (FSH), और प्रोलैक्टिन का परीक्षण करना समग्र मूल्यांकन के लिए महत्वपूर्ण है। कोर्टिसोल और थायरॉयड कार्य परीक्षण भी पूरे हार्मोनल संतुलन का मूल्यांकन करने के लिए किए जाते हैं, साथ ही लड़कों में टेस्टोस्टेरोन और लड़कियों में एस्ट्राडायोल की माप भी की जाती है। ओरल ग्लूकोज टॉलरेंस टेस्ट (OGTT) किया जा सकता है ताकि GH हाइपरसेक्शन की पुष्टि की जा सके, क्योंकि ग्लूकोज सेवन के बाद GH स्तरों को सामान्यत: घटना चाहिए। रक्त परीक्षणों के अलावा, पिट्यूटरी ग्रंथि का MRI जैसे इमेजिंग अध्ययन महत्वपूर्ण होते हैं ताकि किसी भी ट्यूमर का पता चल सके, जबकि छाती और पेट के CT स्कैन का उपयोग अजनबी GH स्राव को निकालने के लिए किया जा सकता है। जाइगेंटिज्म का इलाज कैसे किया जाता है? जाइगेंटिज्म का इलाज मुख्य रूप से GH स्तरों को कम करने और जटिलताओं का प्रबंधन करने के उद्देश्य से किया जाता है। इसके मुख्य उपचार विकल्पों में शामिल हैं: जाइगेंटिज्म के लिए सर्जरी सर्जरी पिट्यूटरी ट्यूमर से होने वाले अधिकांश जाइगेंटिज्म मामलों के लिए प्राथमिक उपचार है। इसका उद्देश्य ट्यूमर को निकालना या घटाना है ताकि GH उत्पादन को कम किया जा सके। यह आमतौर पर ट्रांस्फीनॉइडल सर्जरी के माध्यम से किया जाता है, जहां ट्यूमर तक नाक और साइनस गुहाओं के जरिए पहुंचा जाता है। हालांकि, क्योंकि जाइगेंटिज्म अक्सर देर से निदान होता है, ट्यूमर बड़े हो सकते हैं, और सर्जरी अकेले उपचारात्मक नहीं हो सकती। अतिरिक्त उपचार जैसे रेडिएशन या दवाइयों की आवश्यकता हो सकती है। जाइगेंटिज्म के लिए रेडिएशन थेरेपी अगर सर्जरी ट्यूमर को पूरी तरह से नहीं हटा पाती या सर्जरी के बाद GH स्तर ऊंचे रहते हैं, तो जाइगेंटिज्म के इलाज में रेडिएशन थेरेपी भी शामिल हो सकती है। रेडिएशन बीम को शेष ट्यूमर ऊतक पर लक्षित किया जाता है ताकि समय के साथ GH स्तर को कम किया जा सके। इसके प्रभावों को आने वाले वर्षों में देखा जा सकता है। दवाइयां यदि सर्जरी संभव नहीं है या सहायक उपचार के रूप में दवाइयां दी जाती हैं, तो जाइगेंटिज्म का प्रबंधन करने में मदद कर सकती हैं। ओक्ट्रीओटाइड और लैन्रियोटाइड जैसी दवाइयां GH स्राव को दबा सकती हैं, जबकि ब्रोमोक्रिप्टीन और कैबेरगोलिन GH स्तरों को कम कर सकते हैं। हालांकि, बच्चों में इन दवाओं की प्रभावशीलता का अध्ययन वयस्कों में एक्रोमेगली के मुकाबले उतना ज्यादा नहीं किया गया है। जाइगेंटिज्म उपचार के जटिलताएँ क्या हैं? जाइगेंटिज्म उपचार से कुछ जटिलताएँ उत्पन्न हो सकती हैं जो रोगी के समग्र स्वास्थ्य और भलाई को प्रभावित कर सकती हैं। सबसे सामान्य समस्याओं में से एक है हाइपोपिटुटेरिज़्म, जो लगभग 60% उपचारित रोगियों में होता है, और इसमें एक या एक से अधिक पिट्यूटरी हार्मोन की कमी हो जाती है, जिसके कारण जीवन भर हार्मोन रिप्लेसमेंट थेरेपी की आवश्यकता होती है। अन्य संभावित जाइगेंटिज्म जटिलताएँ में एड्रिनल इंसफिशियेंसी शामिल है, जो अधूरी एड्रिनल हार्मोन उत्पादन से संबंधित होती है, और डायबिटीज इंसिपिडस, एक दुर्लभ स्थिति जिसमें अत्यधिक प्यास और अधिक पेशाब आता है। इसके अतिरिक्त, रोगियों को हाइपोगोनैडिज्म का सामना हो सकता है, जिसमें सेक्स हार्मोन का उत्पादन कम हो जाता है, और हाइपोथायरायडिज्म, जिससे थायरॉइड हार्मोन का स्तर कम हो जाता है। क्या जाइगेंटिज्म को रोका जा सकता है? जाइगेंटिज्म को रोका नहीं जा सकता क्योंकि यह ट्यूमर या आनुवंशिक स्थितियों के कारण होता है। नियमित चेक-अप्स और समय पर उपचार के माध्यम से इस स्थिति का शीघ्र पता चल सकता है, जिससे उपचार करना और जटिलताओं को रोकना संभव होता है। जाइगेंटिज्म के लिए दृष्टिकोण क्या है? जाइगेंटिज्म से पीड़ित व्यक्तियों के लिए दृष्टिकोण समय पर और प्रभावी उपचार के साथ काफी अनुकूल हो सकता है। अतिरिक्त विकास हार्मोन (GH) के कारण होने वाले कई बदलावों को पलटा जा सकता है, जिससे समग्र पूर्वानुमान में महत्वपूर्ण सुधार हो सकता है। हालांकि, हड्डियों, जोड़ों और दिल पर दीर्घकालिक प्रभाव सामान्य हैं और इसके लिए लगातार प्रबंधन की आवश्यकता हो सकती है। पिट्यूटरी सर्जरी अक्सर GH स्तर को महत्वपूर्ण रूप से कम करने में सफल होती है, फिर भी नियमित निगरानी आवश्यक होती है ताकि किसी भी अवशेष या नए लक्षणों का समाधान किया जा सके। उचित उपचार और प्रबंधन के साथ, जीवन प्रत्याशा सामान्य हो सकती है। कुल मिलाकर, सही दृष्टिकोण के साथ, जाइगेंटिज्म से पीड़ित व्यक्ति स्वस्थ और पूर्ण जीवन जी सकते हैं, हालांकि संभावित स्वास्थ्य समस्याओं को प्रभावी ढंग से प्रबंधित करने के लिए सतर्कता महत्वपूर्ण है। जाइगेंटिज्म के परिणाम स्वरूप होने वाली जटिलताएं क्या हैं? जाइगेंटिज्म से जुड़ी कुछ संभावित जटिलताएँ हैं, जो जीवन की गुणवत्ता पर महत्वपूर्ण प्रभाव डाल सकती हैं। इनमें शामिल हैं: हृदय रोग: एक बड़ा दिल और हृदय विफलता का बढ़ा हुआ जोखिम गंभीर हो सकता है। दृष्टि हानि: ऑप्टिक तंत्रिकाओं पर दबाव पड़ने के कारण दृष्टि खो सकती है। जोड़ों में दर्द और गठिया: मरीजों को जोड़ों में दर्द और गठिया का सामना करना पड़ सकता है, साथ ही अंगों का आकार बढ़ने से समग्र कार्यक्षमता पर असर पड़ सकता है। सिरदर्द और कमजोरी: मरीजों को सिरदर्द, कमजोरी और तंत्रिका संपीड़न के लक्षण अनुभव हो सकते हैं। शारीरिक परिवर्तन: चेहरे की विशेषताओं का मोटा होना, बड़े हाथ और पैर, मोटी त्वचा और अत्यधिक पसीना आना भी आम है, जो शारीरिक असुविधा और मानसिक तनाव का कारण बन सकते हैं। डॉक्टर से कब मिलें? अगर माता-पिता अपने बच्चे में असामान्य वृद्धि के लक्षण देखते हैं, तो उन्हें डॉक्टर से संपर्क करना चाहिए, जैसे: सहपाठियों की तुलना में बहुत तेजी से बढ़ना बहुत बड़े हाथ और पैर चेहरे की विशेषताओं का मोटा होना सिरदर्द या दृष्टि संबंधित समस्याएँ जोड़ों में दर्द अत्यधिक पसीना आना समय पर निदान होने से लक्षणों का प्रबंधन और जटिलताओं को रोकने के लिए उपचार में मदद मिलती है। निष्कर्ष जाइगेंटिज्म एक दुर्लभ लेकिन गंभीर स्थिति है, जिसे त्वरित चिकित्सा ध्यान की आवश्यकता होती है। यदि आपको संदेह है कि आपके बच्चे में जाइगेंटिज्म के लक्षण हो सकते हैं, तो डॉक्टर से संपर्क करने में संकोच न करें। समय पर उपचार इस स्थिति के प्रबंधन के लिए महत्वपूर्ण है और सर्वोत्तम परिणाम सुनिश्चित करने के लिए आवश्यक है। मेट्रोपोलिस हेल्थकेयर में, हम जाइगेंटिज्म जैसी स्थितियों के प्रबंधन के लिए सही निदान के महत्व को समझते हैं। हमारे विशेषज्ञ तकनीशियनों की टीम विकास हार्मोन और अन्य आवश्यक परीक्षणों के लिए घर पर सैंपल संग्रह की सुविधा प्रदान करती है। हमारे अत्याधुनिक लैब्स और गुणवत्ता के प्रति प्रतिबद्धता के साथ, आप उपचार निर्णयों को मार्गदर्शन देने के लिए विश्वसनीय परिणामों के लिए हम पर भरोसा कर सकते हैं। आज ही अपने परीक्षण बुक करें और एक स्वस्थ भविष्य की ओर पहला कदम बढ़ाएं।
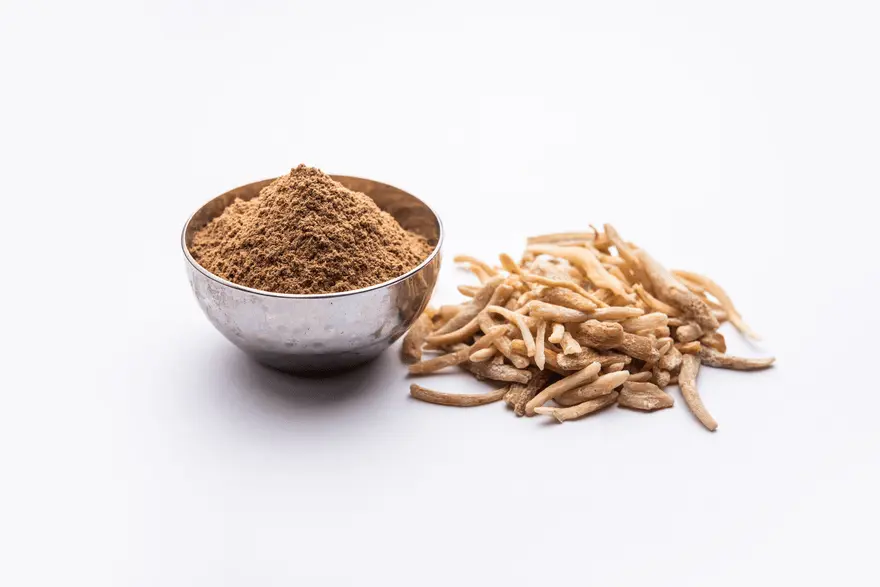
सफेद मूसली: स्वास्थ्य लाभ, पोषण, उपयोग और अन्य जानकारी
क्या आपने कभी किसी हेल्थ-रिलेटेड टॉपिक पर इंटरनेट पर खोज की और स्वयं को और अधिक उलझा हुआ पाया? जब हम भारतीय पारंपरिक चिकित्सा की दुनिया में कदम रखते हैं, तो हमारा मकसद उलझन नहीं, बल्कि स्पष्टता लाना है। आज हम आयुर्वेद में इस्तेमाल होने वाली एक अद्भुत जड़ी-बूटी सफेद मूसली के रहस्यों को जानने निकले हैं। "व्हाइट गोल्ड" के नाम से मशहूर यह शक्तिशाली पौधा सदियों से अपने असंख्य फायदों के लिए सराहा जाता रहा है। लेकिन असल में सफेद मूसली क्या है? इसके क्या-क्या उपयोग हैं? और क्या इसके कोई संभावित साइड इफेक्ट्स भी हो सकते हैं? आइए, इस "चमत्कारी जड़" के रहस्य को मिलकर समझते हैं! सफेद मूसली क्या है? सफेद मूसली, जिसका वैज्ञानिक नाम Chlorophytum borivilianum है, एक दुर्लभ भारतीय जड़ी-बूटी है, जो अपनी औषधीय खूबियों के लिए जानी जाती है। यह अपने छोटे सफेद फूलों और कंद जैसी जड़ों के कारण पहचानी जाती है। इसकी यही जड़ें औषधीय गुणों का मुख्य स्रोत होती हैं और इसमें भरपूर मात्रा में बायोएक्टिव कंपाउंड्स और खनिज मौजूद होते हैं। "दिव्य औषधि" या "व्हाइट गोल्ड" के नाम से मशहूर, सफेद मूसली को आयुर्वेद में ताकत और रोग प्रतिरोधक क्षमता बढ़ाने के लिए इस्तेमाल किया जाता है। इसमें सैपोनिन्स और एल्कलॉइड्स प्रचुर मात्रा में पाए जाते हैं, जिससे यह थकान, गठिया और कई पुरानी बीमारियों के इलाज में कारगर मानी जाती है। सफेद मूसली के गुण सफेद मूसली में एडेप्टोजेनिक (Adaptogenic) गुण होते हैं, जिसका मतलब है कि यह शरीर को विभिन्न शारीरिक, रासायनिक और जैविक दबावों से निपटने में मदद करती है। इसमें कई तरह के फाइटोकेमिकल्स मौजूद होते हैं, खासकर सैपोनिन्स, जो एंटीऑक्सीडेंट और एंटी-इंफ्लेमेटरी गुणों के लिए जाने जाते हैं। इसके अलावा, यह प्रोटीन, कार्बोहाइड्रेट, डाइटरी फाइबर और एल्कलॉइड्स जैसे जरूरी पोषक तत्वों से भरपूर होती है। सफेद मूसली के फायदे सफेद मूसली को इसकी एडेप्टोजेनिक विशेषताओं और समृद्ध पोषण सामग्री के कारण कई स्वास्थ्य लाभों के लिए जाना जाता है। प्रजनन स्वास्थ्य को बढ़ावा देती है सफेद मूसली का सबसे महत्वपूर्ण लाभ प्रजनन स्वास्थ्य में सुधार करना है। यह आयुर्वेद में एक प्राकृतिक कामोत्तेजक (Natural Aphrodisiac) के रूप में इस्तेमाल की जाती है, जो पुरुषों और महिलाओं दोनों में यौन शक्ति को बढ़ाने में मदद करती है। यह लिबिडो बढ़ाने और यौन संबंधित समस्याओं को दूर करने में कारगर मानी जाती है, जिससे समग्र प्रजनन स्वास्थ्य में सुधार होता है। ऊर्जा और स्टैमिना बढ़ाती है सफेद मूसली की एक और बड़ी खासियत यह है कि यह ऊर्जा और ताकत बढ़ाने में मदद करती है। इसमें प्राकृतिक स्टेरॉयड्स होते हैं, जो मांसपेशियों की मजबूती और ताकत को बढ़ाने में सहायक होते हैं। यह स्टैमिना और सहनशक्ति बढ़ाने का काम करती है, जिससे यह एथलीट्स और फिटनेस प्रेमियों के बीच काफी लोकप्रिय है। पाचन तंत्र को दुरुस्त करती है सफेद मूसली पाचन स्वास्थ्य को बेहतर करने में भी मददगार होती है। इसमें मौजूद डाइटरी फाइबर पाचन को सुचारू रूप से चलाने में सहायता करता है और कब्ज की समस्या को दूर करने में सहायक होता है। हार्मोन संतुलित करने में मदद करती है सफेद मूसली के हार्मोन बैलेंसिंग गुण काबिले-तारीफ हैं। इसमें मौजूद फाइटोन्यूट्रिएंट्स शरीर में हार्मोन के उत्पादन को नियंत्रित करने में मदद कर सकते हैं, खासकर वे हार्मोन जो तनाव और चिंता से जुड़े होते हैं। शरीर से टॉक्सिन्स निकालने में सहायक सफेद मूसली में मूत्रवर्धक (Diuretic) गुण पाए जाते हैं, जिससे यह शरीर से विषाक्त पदार्थों को बाहर निकालने में मदद करती है। यह पेशाब की मात्रा बढ़ाकर डिटॉक्सिफिकेशन में सहायक हो सकती है, जिससे मूत्र मार्ग संक्रमण (UTI) और गुर्दे से जुड़ी समस्याओं में राहत मिल सकती है। तनाव और अवसाद को कम करने में मददगार सफेद मूसली के एडेप्टोजेनिक गुण इसे तनाव और चिंता को प्रबंधित करने में प्रभावी बनाते हैं। यह मन को शांत करने, मानसिक स्पष्टता बढ़ाने और तनाव कम करने में मदद करती है, जिससे यह डिप्रेशन और एंग्जायटी के लक्षणों को कम करने में सहायक साबित हो सकती है। डायबिटीज को नियंत्रित करने में सहायक डायबिटीज के मरीजों के लिए सफेद मूसली का पोषण मूल्य (Nutrition Value) बेहद फायदेमंद हो सकता है। ऐसा माना जाता है कि यह ब्लड शुगर लेवल को नियंत्रित करने में मदद कर सकती है, जिससे मधुमेह को बेहतर तरीके से प्रबंधित किया जा सकता है। वजन प्रबंधन में मदद करती है सफेद मूसली में मौजूद फाइबर पेट को ज्यादा देर तक भरा हुआ महसूस कराता है, जिससे अत्यधिक खाने या बार-बार खाने की आदत को कम करने में मदद मिलती है। इस प्रकार, यह वजन नियंत्रित करने में सहायक होती है। स्तनपान को बढ़ावा देती है नई माताओं को अक्सर इस बात की चिंता रहती है कि वे अपने बच्चे के लिए पर्याप्त दूध उत्पादन कर रही हैं या नहीं। ऐसे में सफेद मूसली के फायदे स्तनपान कराने वाली माताओं के लिए काफी फायदेमंद साबित हो सकते हैं! ऐसा माना जाता है कि सफेद मूसली दूध उत्पादन को बढ़ावा देने में मदद करती है, जिससे नवजात शिशु को आवश्यक पोषण मिल सके। हालांकि, स्तनपान के दौरान सफेद मूसली या किसी भी अन्य सप्लीमेंट का सेवन करने से पहले डॉक्टर से परामर्श लेना जरूरी है। हृदय स्वास्थ्य को बढ़ावा देती है आज के दौर में हृदय रोग एक बड़ी समस्या बन चुके हैं, और हर कोई दिल को स्वस्थ रखने के लिए उपाय खोज रहा है। क्या हो अगर कोई प्राकृतिक जड़ी-बूटी हृदय के कार्य को बेहतर बना सके? सफेद मूसली पारंपरिक रूप से हृदय स्वास्थ्य को बढ़ाने के लिए उपयोग की जाती रही है। हालांकि, इसे किसी भी निर्धारित दवा या हेल्दी लाइफस्टाइल का विकल्प नहीं माना जाना चाहिए। किसी भी नए सप्लीमेंट को लेने से पहले अपने डॉक्टर से परामर्श अवश्य लें। गठिया के इलाज में सहायक जो लोग गठिया (Arthritis) के दर्द और असहजता से गुजरते हैं, वे इस तकलीफ को अच्छी तरह समझ सकते हैं। ऐसे में सफेद मूसली गठिया के लक्षणों को कम करने में मदद कर सकती है। इसके सूजन-रोधी (Anti-inflammatory) गुण जोड़ों की सूजन और दर्द को कम करने में प्रभावी हो सकते हैं, जिससे गठिया से पीड़ित लोगों को राहत मिल सकती है। त्वचा और बालों के लिए फायदेमंद हर कोई घने, चमकदार बाल और दमकती त्वचा चाहता है! यदि आप भी इस ओर ध्यान दे रहे हैं, तो सफेद मूसली से भरपूर स्किन और हेयर केयर रूटीन आपको इस लक्ष्य तक पहुंचाने में मदद कर सकता है। इसके एंटीऑक्सीडेंट गुण त्वचा पर एजिंग के असर को कम करने और स्वस्थ बालों की ग्रोथ को बढ़ाने में मदद कर सकते हैं। सफेद मूसली का उपयोग कैसे करें? अगर आप सोच रहे हैं कि सफेद मूसली को अपने स्वास्थ्य दिनचर्या में कैसे शामिल करें, तो यहां कुछ सामान्य तरीके दिए गए हैं: पाउडर रूप में: सफेद मूसली की सूखी जड़ों को पीसकर पाउडर बना लिया जाता है। इसे गर्म पानी या दूध के साथ मिलाकर लिया जा सकता है। सेवन की सही मात्रा के लिए अपने डॉक्टर से सलाह जरूर लें। कैप्सूल के रूप में: यदि आपको पाउडर लेना असुविधाजनक लगता है, तो आप सफेद मूसली कैप्सूल का विकल्प चुन सकते हैं। यह एक आसान और सुविधाजनक तरीका है। हर्बल मिश्रण: सफेद मूसली को अन्य आयुर्वेदिक जड़ी-बूटियों जैसे अश्वगंधा और शिलाजीत के साथ मिलाकर भी लिया जा सकता है, जिससे इसके अतिरिक्त लाभ मिल सकते हैं। याद रखें, कोई भी नया सप्लीमेंट शुरू करने से पहले डॉक्टर से परामर्श लेना आवश्यक है, ताकि यह आपके स्वास्थ्य के लिए सुरक्षित और प्रभावी रहे। इरेक्टाइल डिसफंक्शन के लिए सफेद मूसली के फायदे क्या है? इरेक्टाइल डिसफंक्शन एक गंभीर चिंता का विषय हो सकता है, जो आत्मसम्मान और निजी रिश्तों पर प्रभाव डाल सकता है। सौभाग्य से, सफेद मूसली के मुख्य लाभों में से एक इसका यौन स्वास्थ्य को बढ़ाने की क्षमता है। एक प्राकृतिक कामोत्तेजक (aphrodisiac) के रूप में, सफेद मूसली पोषण हार्मोन संतुलन को सुधारकर कामेच्छा को बढ़ाने और इरेक्टाइल डिसफंक्शन को कम करने में मदद कर सकता है। यौन प्रदर्शन को बेहतर बनाने के लिए सफेद मूसली के फायदे क्या है? सिर्फ इरेक्टाइल डिसफंक्शन को प्रबंधित करने के लिए ही नहीं, बल्कि सफेद मूसली को पुरुषों में यौन प्रदर्शन को बेहतर बनाने के लिए भी जाना जाता है। इसके हार्मोन-संतुलन गुण इसे अधिक प्रभावी बनाते हैं, जिससे यौन ऊर्जा और सहनशक्ति में वृद्धि हो सकती है। सफेद मूसली के साइड इफेक्ट्स हालांकि सफेद मूसली अपने स्वास्थ्य लाभों के लिए प्रसिद्ध है, लेकिन कुछ लोगों में इसके कुछ साइड इफेक्ट्स भी हो सकते हैं। सामान्य सफेद मूसली के दुष्प्रभावों में पाचन समस्याएं शामिल हो सकती हैं, जैसे पेट में ऐंठन, डायरिया और मतली। अधिक मात्रा में सेवन करने से इसकी मूत्रवर्धक (diuretic) विशेषता के कारण डिहाइड्रेशन और इलेक्ट्रोलाइट असंतुलन हो सकता है। हालांकि एलर्जी प्रतिक्रियाएं दुर्लभ हैं, लेकिन कुछ लोगों में त्वचा पर चकत्ते, खुजली या सूजन हो सकती है। मधुमेह के मरीजों को इसे सावधानी से लेना चाहिए, क्योंकि यह ब्लड शुगर लेवल को प्रभावित कर सकता है। गर्भवती और स्तनपान कराने वाली महिलाएं, साथ ही कुछ स्वास्थ्य समस्याओं से ग्रसित लोग, सफेद मूसली का सेवन करने से पहले डॉक्टर से सलाह लें ताकि किसी भी संभावित इंटरैक्शन या जटिलताओं से बचा जा सके। हमेशा अनुशंसित खुराक का पालन करें। निष्कर्ष यह स्पष्ट है कि सफेद मूसली के कई संभावित स्वास्थ्य लाभ हैं, जैसे स्तनपान को समर्थन देना, हृदय स्वास्थ्य में सुधार और यौन स्वास्थ्य को बढ़ावा देना। हालांकि, इसका सही तरीके से और विशेषज्ञों की सलाह के तहत उपयोग करना बहुत जरूरी है। मेट्रोपोलिस हेल्थकेयर में, हम जानते हैं कि सूचित स्वास्थ्य निर्णय लेना कितना महत्वपूर्ण है। हमारी विशेषज्ञों की टीम आपको विश्वसनीय डायग्नोस्टिक सेवाएं प्रदान करने के लिए प्रतिबद्ध है, जिसमें घर से सैंपल कलेक्शन की सुविधा भी शामिल है। हमारी सेवाओं के बारे में अधिक जानने के लिए मेट्रोपोलिस हेल्थकेयर वेबसाइट पर विजिट करें। याद रखें, सही जानकारी और देखभाल के साथ, आपका स्वास्थ्य आपकी प्राथमिकता में हमेशा बना रह सकता है।
चिकनगुनिया क्या है? लक्षण, इलाज, कारण और बचाव
चिकनगुनिया एक वायरल बुखार है, जो संक्रमित एडिस एजिप्टी (Aedes aegypti) और एडिस एल्बोपिक्टस (Aedes albopictus) मच्छरों के काटने से फैलता है। चिकनगुनिया वायरस "अल्फावायरस (Alphavirus) जीनस" का सदस्य है, जो टोगाविरिडी (Togaviridae) परिवार में आता है। "चिकनगुनिया" शब्द किमाकोंडे भाषा से लिया गया है, जिसका मतलब है "मुड़ जाना" या "झुककर चलना", क्योंकि इस बीमारी से पीड़ित लोग जोड़ों में तेज दर्द की वजह से झुककर चलने लगते हैं। रात में काटने वाले मच्छर इस वायरस के प्रमुख वाहक नहीं होते। इस बीमारी में अचानक बुखार आता है, जो 2 से 12 दिन तक रह सकता है। इसके साथ छोटे जोड़ों में सूजन के साथ या बिना सूजन के तेज दर्द हो सकता है। यह दर्द बहुत गंभीर हो सकता है, लेकिन आमतौर पर कुछ दिनों या हफ्तों में ठीक हो जाता है। हालांकि, कुछ मामलों में जोड़ों का दर्द महीनों तक बना रह सकता है। कुछ मरीजों में त्वचा पर चकत्ते (rash) भी हो सकते हैं। इस हेल्थ गाइड में हम जानेंगे कि चिकनगुनिया क्या है, इसके लक्षण, कैसे फैलता है, इसका निदान कैसे किया जाता है, और इससे बचाव के तरीके। चिकनगुनिया के लक्षण क्या हैं? चिकनगुनिया का इन्क्यूबेशन पीरियड (संक्रमण से लक्षण आने तक का समय) आमतौर पर 3 से 7 दिन होता है। इस बीमारी के सबसे आम लक्षण तेज बुखार और जोड़ो में दर्द होते हैं। इसके अलावा, सिरदर्द, मांसपेशियों में दर्द, जोड़ों की सूजन, और शरीर पर चकत्ते (rash) भी हो सकते हैं। संक्रमित मच्छर के काटने के 2 से 12 दिन बाद लक्षण दिखाई देने लगते हैं। नीचे चिकनगुनिया के प्रमुख लक्षण दिए गए हैं: बुखार: कुछ समय बाद चिकनगुनिया से संक्रमित व्यक्ति को तेज बुखार होता है, जो 2 से 12 दिन तक रह सकता है। यह बुखार आमतौर पर अपने आप ठीक हो जाता है। हालांकि, अगर बुखार ज्यादा बढ़ जाए, तो डॉक्टर से संपर्क करें, जो बुखार कम करने के लिए दवा दे सकते हैं। जोड़ों में दर्द: बहुत तेज और असहनीय हो सकता है, जो अक्सर कई जोड़ों को प्रभावित करता है। यह दर्द कुछ हफ्तों तक बना रह सकता है और कुछ मामलों में महीनों तक भी बना रह सकता है। सिरदर्द: चिकनगुनिया में सिर में दर्द या भारीपन महसूस हो सकता है। अगर सिरदर्द बहुत तेज हो, तो तुरंत डॉक्टर से संपर्क करें, क्योंकि यह किसी और गंभीर बीमारी का संकेत भी हो सकता है। मांसपेशियों में दर्द: हाथों और पैरों में मांसपेशियों में दर्द आमतौर पर महसूस किया जाता है, जिससे चलना-फिरना मुश्किल हो सकता है। दर्द कम करने के लिए डॉक्टर द्वारा सुझाई गई दर्द निवारक दवाएं ली जा सकती हैं। जोड़ों की सूजन: हाथों, कलाई और पैरों में सूजन चिकनगुनिया का एक और सामान्य लक्षण है। चकत्ते (रैश): बीमारी के दूसरे या तीसरे दिन शरीर पर खुजली वाले चकत्ते (rash) दिखाई दे सकते हैं, जो पूरे शरीर में फैल सकते हैं। कुछ मामलों में छोटे-छोटे फफोले भी हो सकते हैं। चिकनगुनिया संक्रमित मच्छरों के काटने से फैलने वाली वायरल बीमारी है। अगर आपको ऊपर बताए गए कोई भी लक्षण महसूस हों, तो डॉक्टर से सलाह जरूर लें। जल्द निदान और सही इलाज से गंभीर जटिलताओं को रोका जा सकता है। हालांकि चिकनगुनिया का कोई विशेष इलाज नहीं है, लेकिन इसके लक्षणों को दर्द निवारक और बुखार कम करने वाली दवाओं से नियंत्रित किया जा सकता है। चिकनगुनिया के कारण क्या हैं? चिकनगुनिया होने के कई कारण हो सकते हैं, लेकिन मुख्य कारण चिकनगुनिया वायरस का संक्रमण है। यह संक्रमण एडीज मच्छर (Aedes mosquito) के काटने से फैलता है। जो लोग उन इलाकों में रहते हैं या यात्रा करते हैं जहां यह वायरस मौजूद है, उन्हें संक्रमित मच्छर के काटने से चिकनगुनिया होने का खतरा रहता है। मच्छर के काटने के बाद वायरस रक्त प्रवाह (bloodstream) में प्रवेश कर जाता है और तेज बुखार, जोड़ों में दर्द और अन्य लक्षण पैदा कर सकता है। नीचे चिकनगुनिया के कुछ आम कारण दिए गए हैं: चिकनगुनिया वायरस से संक्रमण: यह वायरस मच्छरों के काटने से फैलता है और संक्रमित व्यक्ति में बुखार, जोड़ो में दर्द और त्वचा पर चकत्ते (rashes) हो सकते हैं। कुछ मामलों में, चिकनगुनिया निमोनिया (pneumonia) या मेनिन्जाइटिस (meningitis) जैसी गंभीर जटिलताएं भी पैदा कर सकता है। अन्य कारण: कुछ अन्य वायरस भी चिकनगुनिया जैसे लक्षण पैदा कर सकते हैं, जैसे डेंगू वायरस और ज़िका वायरस। इसके अलावा, कुछ दवाएं (जैसे क्विनिन) भी चिकनगुनिया जैसे लक्षण दिखा सकती हैं। चिकनगुनिया का इलाज मुख्य रूप से लक्षणों को कम करने और शरीर की रोग प्रतिरोधक क्षमता (immune system) को मजबूत करने पर आधारित होता है। फिलहाल इस वायरस का कोई निश्चित इलाज उपलब्ध नहीं है, इसलिए बचाव ही सबसे अच्छा उपाय है। चिकनगुनिया से बचने के लिए मच्छरों के काटने से बचें और उन क्षेत्रों में जाने से बचें जहां यह वायरस अधिक फैल रहा हो। क्या चिकनगुनिया जानलेवा है? अधिकतर मामलों में चिकनगुनिया घातक नहीं होता और संक्रमित लोग बिना किसी गंभीर जटिलता के ठीक हो जाते हैं। एक बार चिकनगुनिया हो जाने के बाद, फिर से संक्रमण का खतरा बहुत कम हो जाता है। हालांकि, अगर बुखार और अन्य लक्षण दिखने लगें, तो तुरंत डॉक्टर से सलाह लेना जरूरी है ताकि डेंगू जैसी अन्य बीमारियों को नज़रअंदाज किया जा सके, जिनका इलाज चिकनगुनिया से अलग होता है। हालांकि चिकनगुनिया आमतौर पर जानलेवा नहीं होता, लेकिन यह बहुत ज्यादा दर्दनाक और कमजोर करने वाला संक्रमण साबित हो सकता है। कुछ मरीजों को संक्रमण के महीनों या यहां तक कि वर्षों बाद भी जोड़ों में असहनीय दर्द बना रह सकता है। कभी-कभी दर्द और सूजन इतनी अधिक हो जाती है कि यह विकलांगता (disability) का कारण भी बन सकती है। बच्चे, बुजुर्ग और पहले से किसी बीमारी से ग्रस्त लोग (जैसे हाइपोटेंशन या हृदय रोग वाले मरीज) इस संक्रमण के प्रति अधिक संवेदनशील होते हैं। अगर चिकनगुनिया ऐसे कमजोर प्रतिरक्षा वाले व्यक्ति को हो जाए, तो यह गंभीर और जानलेवा जटिलताओं का कारण बन सकता है। इसलिए संक्रमण से बचाव और समय पर इलाज कराना बहुत जरूरी है। चिकनगुनिया से बचाव अधिकतर स्वस्थ वयस्कों को चिकनगुनिया संक्रमण होने के बावजूद अस्पताल में भर्ती होने की जरूरत नहीं पड़ती। लेकिन इस बीमारी के दौरान दर्द इतना तेज़ हो सकता है कि मरीज को एक या दो हफ्ते तक बिस्तर पर ही रहना पड़ सकता है। संक्रमण के दौरान पर्याप्त मात्रा में पानी और तरल पदार्थ पीना बहुत ज़रूरी है, क्योंकि तेज़ बुखार से डिहाइड्रेशन (पानी की कमी) हो सकता है। संक्रमित व्यक्ति को मच्छरदानी में सोने और अन्य सुरक्षा उपाय अपनाने की सलाह दी जाती है ताकि बीमारी फैलने से रोकी जा सके। संक्रमित व्यक्ति को विशेष देखभाल की जरूरत होती है। तेज़ दर्द और तेज़ बुखार से कमजोरी, डिहाइड्रेशन और दूसरी जटिलताएं हो सकती हैं, खासकर उन लोगों में जो पहले से किसी बीमारी से पीड़ित हैं। बुजुर्गों और गंभीर स्वास्थ्य समस्याओं से जूझ रहे लोगों को विशेष सावधानी बरतनी चाहिए, क्योंकि बुखार और दर्द के कारण सांस लेने में दिक्कत या अन्य गंभीर समस्याएं भी हो सकती हैं। इसलिए, ऐसे मरीजों का डॉक्टर की निगरानी में रहना बेहद जरूरी है। चिकनगुनिया की जांच चिकनगुनिया की पहचान के लिए मुख्यतः दो तरह की जांचें की जाती हैं – एंटीबॉडी की जांच और वायरल RNA का पता लगाना। मेट्रोपोलिस हेल्थकेयरनिम्नलिखित परीक्षण उपलब्ध कराता है: चिकनगुनिया IgM एंटीबॉडी टेस्ट RTPCR द्वारा चिकनगुनिया RNA की पहचान IgM एंटीबॉडी टेस्ट एक स्क्रीनिंग टेस्ट है। अगर यह टेस्ट पॉजिटिव आता है, तो उसे PCR टेस्ट से कंफर्म किया जाना चाहिए। IgM एंटीबॉडीज आमतौर पर 3-4 दिनों में बननी शुरू हो जाती हैं और 3 महीने से ज्यादा समय तक बनी रह सकती हैं। RTPCR टेस्ट सबसे सटीक और विश्वसनीय माना जाता है क्योंकि यह संक्रमण की शुरुआती अवस्था में ही वायरस की मौजूदगी का पता लगा लेता है और बीमारी की पुख्ता पहचान करने में मदद करता है। चिकनगुनिया की रोकथाम और उपचार चिकनगुनिया से बचाव की शुरुआत मच्छरों के काटने से बचने से होती है। इसे रोकने के कुछ तरीके नीचे दिए गए हैं: मच्छर के मौसम में या ऐसे देशों की यात्रा के दौरान जहां इसका प्रकोप फैला हो, विभिन्न प्रकार के रिपेलेंट्स (DEET, पैरामीथेन डायल, पिकारिडिन, IR3535 और नींबू युकलिप्टस ऑयल) का उपयोग करें। ये सभी प्रभावी होते हैं, लेकिन उत्पाद की पैकेजिंग पर दिए गए निर्देशों का पालन करें। यात्रा के दौरान मच्छरदानी वाले कमरे या एयर कंडीशनिंग वाली जगहों को प्राथमिकता दें। आप खिड़कियों, दरवाजों और बिस्तर के ऊपर मच्छरदानी भी लगा सकते हैं। लंबे कपड़े पहनें ताकि त्वचा ढकी रहे और मच्छर काट न सकें। मच्छरों की सूंड कपड़ों को पार करने में कठिनाई महसूस करती है। यात्रा से पहले चिकनगुनिया के बारे में जानकारी लें। यह जानना महत्वपूर्ण है कि कहां और कब विशेष सावधानी बरतनी चाहिए। सेंटर्स फॉर डिजीज कंट्रोल एंड प्रिवेंशन (CDC) जैसी संस्थाओं की वेबसाइट से इस संक्रमण और उसके फैलाव की जानकारी प्राप्त करें। अगर आप चिकनगुनिया प्रभावित क्षेत्र में हैं, तो मच्छर भगाने के लिए अतिरिक्त उपाय अपनाएं। होटल में मच्छरदानी, एयर कंडीशनर, क्वालिटी रिपेलेंट्स का इस्तेमाल करें। अगर बाहर जा रहे हैं तो मच्छर भगाने वाली अगरबत्ती, स्प्रे, सिट्रोनेला कैंडल और ट्रैप्स का उपयोग करें। दिन के समय विशेष सतर्कता बरतें, क्योंकि चिकनगुनिया फैलाने वाले एडीज एजिप्टी (Aedes aegypti) और एडीज एल्बोपिक्टस (Aedes albopictus) मच्छर दिन के दौरान ज्यादा सक्रिय होते हैं। छोटे बच्चों की सुरक्षा पर ध्यान दें। अगर आप बच्चों के साथ बाहर जा रहे हैं, तो मच्छरों के काटने से बचाने के लिए अतिरिक्त उपाय करें। डिहाइड्रेशन से बचाव करें क्योंकि चिकनगुनिया के दौरान शरीर में पानी की कमी हो सकती है। बुखार होने पर पर्याप्त मात्रा में पानी, जूस, सूप और इलेक्ट्रोलाइट ड्रिंक्स का सेवन करें। अगर आपको हृदय रोग, मधुमेह या हाई ब्लड प्रेशर जैसी कोई स्वास्थ्य समस्या है, तो चिकनगुनिया के दौरान डॉक्टर के निर्देशों का सख्ती से पालन करें, क्योंकि ये बीमारियां चिकनगुनिया को और जटिल बना सकती हैं। क्या चिकनगुनिया का कोई टीका है? अभी तक चिकनगुनिया के लिए कोई वैक्सीन नहीं है, और न ही कोई खास इलाज उपलब्ध है। लेकिन अगर आपको चिकनगुनिया जैसे लक्षण महसूस हों, तो तुरंत डॉक्टर से संपर्क करें। अस्पताल में आपका सही तरीके से इलाज किया जाएगा और लक्षणों को कंट्रोल किया जा सकेगा। अगर आपको पहले से कोई गंभीर बीमारी है, तो आपको अस्पताल में भर्ती होने की जरूरत भी पड़ सकती है। मच्छरों पर नियंत्रण से चिकनगुनिया की रोकथाम इस संक्रमण से बचने का सबसे असरदार तरीका है मच्छरों की संख्या कम करना और उनके काटने से बचना। इसके लिए आप ये उपाय अपना सकते हैं: ठहरे हुए पानी को खत्म करें। छोटी-छोटी जगहों पर जमा पानी, जैसे कि गड्ढे, बाल्टी, पुराने टायर, गमलों में रुका पानी – ये सब मच्छरों के लिए परफेक्ट ब्रीडिंग ग्राउंड होते हैं। अगर कहीं भी पानी जमा हो गया हो, यहां तक कि बोतल के ढक्कन में भी, तो उसे तुरंत फेंक दें ताकि मच्छरों को पनपने का मौका न मिले। हल्के रंग के कपड़े पहनें। गहरे रंग के कपड़ों की तुलना में हल्के रंग मच्छरों को कम आकर्षित करते हैं। साथ ही, हल्के रंग गर्मी को भी कम सोखते हैं, जिससे आपको ठंडक भी मिलेगी और अगर कोई मच्छर कपड़े पर बैठा हो तो उसे जल्दी से देखा जा सकेगा। घर के आसपास पानी जमा होने से बचें। अगर आपके घर में पक्षियों के पानी पीने के बर्तन, स्विमिंग पूल या पानी की टंकियां हैं, तो ध्यान रखें कि पानी हमेशा साफ रहे। फाउंटेन का बहता पानी मच्छरों को आकर्षित नहीं करता, लेकिन बारिश का पानी जमा होने वाले बैरल, जानवरों के पानी के कटोरे और खुले टब मच्छरों के लिए परफेक्ट होते हैं। इसलिए, पानी को नियमित रूप से बदलें और बैरल को ढककर रखें ताकि मच्छर उसमें अंडे न दे सकें। मच्छर पकड़ने वाले ट्रैप्स का इस्तेमाल करें। चिकनगुनिया से लड़ने में सबसे अहम कदम मच्छरों की संख्या और उनके काटने की घटनाओं को कम करना है। इस लड़ाई में मच्छर पकड़ने वाले ट्रैप्स एक अच्छा विकल्प हो सकते हैं। सभी ट्रैप अलग-अलग तरह से काम करते हैं। मॉस्किटो मैगनेट जैसे मच्छरमार उपकरण खून चूसने वाले कीड़ों को आकर्षित करने के लिए गर्म और नम कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड छोड़ते हैं और फिर इन मच्छरों को अंदर खींचकर जाल में फंसा लेते हैं, जहां वे सूखकर मर जाते हैं। ये ट्रैप इस तरह डिज़ाइन किए गए हैं कि वे इंसानी सांस लेने की प्रक्रिया की नकल करते हैं, जिससे मादा मच्छर उनकी ओर आकर्षित होती हैं। जितनी ज्यादा मादा मच्छर मारी जाएंगी, उतने ही कम खून चूसने वाले मच्छर प्रजनन कर पाएंगे। आपकी जगह पर मच्छरों की संख्या काफी हद तक कम हो जाएगी, खासकर अगर आपके आंगन के चारों ओर एक ऊँची और अभेद्य बाड़ लगी हो। स्प्रे और रिपेलेंट्स के विपरीत, ट्रैप्स सभी मौसमों में 24/7 प्रभावी रूप से काम कर सकते हैं। चिकनगुनिया एक गंभीर बीमारी है जो किसी व्यक्ति के स्वास्थ्य को दिनों, महीनों या यहां तक कि वर्षों तक प्रभावित कर सकती है। इस वायरस के कारण होने वाला दर्द इतना तीव्र हो सकता है कि यह गंभीर स्थितियों को जन्म दे सकता है, जो जीवन के लिए खतरा बन सकती हैं। यात्रा करने से पहले, चिकनगुनिया महामारी के बारे में अधिक जानें और समय पर रोकथाम के उपाय अपनाएं। चिकनगुनिया और अन्य मच्छरजनित बीमारियों से बचाव का सबसे प्रभावी तरीका है कि अपने घर के आसपास मच्छरों की संख्या कम की जाए। इस समस्या का एक समाधान मच्छर पकड़ने वाले ट्रैप्स हैं, जैसे कि मॉस्किटो मैगनेट, जो 24/7 काम करके आपके क्षेत्र में मच्छरों की संख्या को कम करते हैं और आपको बीमारियों से बचाते हैं। निष्कर्ष इस लेख को पढ़ने के बाद, अब आपको पता चल गया होगा कि चिकनगुनिया क्या है, यह कैसे फैलता है और इससे बचाव के लिए किन तरीकों का इस्तेमाल किया जा सकता है। खुद को इस बीमारी से बचाने के लिए सभी जरूरी उपाय जरूर अपनाएँ, और अगर आपको चिकनगुनिया जैसे कोई भी लक्षण महसूस हों, तो तुरंत डॉक्टर से सलाह लें। हमने आपको मच्छर जाल (मॉस्किटो ट्रैप्स) के बारे में भी बताया है, जो चिकनगुनिया से लड़ने में मदद कर सकते हैं। कुछ स्थितियों में, मच्छर जाल ही एकमात्र प्रभावी तरीका होता है जिससे घर के आस-पास मच्छरों की संख्या कम की जा सकती है और बीमारी से बचाव किया जा सकता है। कुछ लोग कह सकते हैं कि मच्छर जाल महंगे होते हैं, लेकिन जब आप इसकी तुलना चिकनगुनिया के इलाज के खर्च से करते हैं, तो यह एक किफायती विकल्प साबित होता है। तो देर मत कीजिए, एक अच्छा मच्छर जाल खरीदें और इस लेख में बताए गए सभी उपायों का पालन करें ताकि आप खुद को चिकनगुनिया से सुरक्षित रख सकें।
एम्पाइमा: फेफड़ों के आसपास पस जमा होना और इसके उपचार के उपाय
एम्पाइमा क्या होता है? एम्पाइमा का मतलब है कि फेफड़ों और छाती की दीवार के बीच की पतली झिल्ली (प्लूरा) में पस जमा हो जाता है।आम तौर पर, इस स्थान पर थोड़ी मात्रा में द्रव (fluid) होता है, जो फेफड़ों को आसानी से फैलने और सिकुड़ने में मदद करता है। लेकिन जब इंफेक्शन हो जाता है, तो यहां पस भरने लगता है, जिससे फेफड़ों पर दबाव पड़ता है और सांस लेने में दिक्कत हो सकती है। क्या एम्पाइमा COPD है? नहीं, एम्पाइमा क्रॉनिक ऑब्स्ट्रक्टिव पल्मोनरी डिजीज (COPD) नहीं है। COPD एक दीर्घकालिक फेफड़ों की बीमारी है, जिसमें एम्फीसेमा और क्रॉनिक ब्रोंकाइटिस जैसी समस्याएं शामिल होती हैं, जो सांस लेने में रुकावट पैदा करती हैं। इसके विपरीत, एम्पाइमा एक अचानक होने वाली (acute) स्थिति है, जिसमें किसी इंफेक्शन की वजह से फेफड़ों के चारों तरफ पस जमा हो जाता है। एम्पाइमा किसे प्रभावित करता है? एम्पाइमा किसी भी उम्र के लोगों को हो सकता है, लेकिन कुछ लोगों में इसका खतरा ज्यादा होता है: बच्चे, खासकर 5 साल से छोटे 65 साल से ज्यादा उम्र के बुजुर्ग कमज़ोर इम्यून सिस्टम वाले लोग जिन्हें पहले से कोई फेफड़ों की बीमारी हो, जैसे निमोनिया या टीबी जिनकी हाल ही में छाती की सर्जरी हुई हो या छाती में चोट लगी हो एम्पाइमा कितनी आम बीमारी है? एम्पाइमा ज्यादा आम नहीं है, यह हर साल करीब 1 लाख में 1 व्यक्ति को प्रभावित करता है। हालांकि, यह निमोनिया की एक गंभीर जटिलता है और करीब 5% निमोनिया मरीजों में देखा जाता है। एम्पाइमा के लक्षण क्या हैं? एम्पाइमा के लक्षण निमोनिया या किसी अन्य इंफेक्शन के कुछ दिनों या हफ्तों बाद दिख सकते हैं। इसके लक्षणों में शामिल हैं: बुखार और ठंड लगना सीने में दर्द, जो सांस लेने या खांसने पर बढ़ जाता है सांस फूलना खांसी, जिसमें बदबूदार, हरा-पीला बलगम आ सकता है बिना वजह वजन कम होना थकान और कमजोरी महसूस होना एम्पाइमा होने के कारण क्या हैं? एम्पाइमा का सबसे सामान्य कारण बैक्टीरियल निमोनिया है। अगर निमोनिया का सही इलाज न किया जाए या एंटीबायोटिक दवाएं असर न करें, तो इंफेक्शन फेफड़ों से प्लूरल स्पेस में फैल सकता है, जिससे वहां पस जमा हो जाता है। समय के साथ, यह पस बहुत गाढ़ा हो सकता है। अन्य कारणों में शामिल हैं: फेफड़ों की सर्जरी के बाद जटिलताएं फटे हुए फेफड़ों में मवाद (लंग एब्सेस या फेफड़ों का ऐब्सेस) सीने में चोट या किसी दुर्घटना के कारण संक्रमण IV ड्रग यूज़ से होने वाले इंफेक्शन कमज़ोर इम्यून सिस्टम वाले लोगों में फंगल इंफेक्शन एम्पाइमा कितनी जल्दी विकसित होता है? एम्पाइमा आमतौर पर कुछ दिनों से लेकर हफ्तों में विकसित होता है। यह तीन चरणों में आगे बढ़ता है: एक्सुडेटिव स्टेज, फाइब्रिनोप्यूरुलेंट स्टेज और ऑर्गेनाइजिंग स्टेज। क्या एम्पाइमा संक्रामक (छूने से फैलने वाली) बीमारी है? नहीं, एम्पाइमा खुद संक्रामक नहीं होता। लेकिन जो इंफेक्शन इसे पैदा करते हैं, जैसे बैक्टीरियल निमोनिया या टीबी, वे एक व्यक्ति से दूसरे व्यक्ति में फैल सकते हैं। एम्पाइमा का निदान कैसे किया जाता है? अगर डॉक्टर आपके लक्षणों और शारीरिक जांच के आधार पर एम्पाइमा का शक करते हैं, तो वे इसकी पुष्टि के लिए कुछ टेस्ट करवाने की सलाह दे सकते हैं: सीने का एक्स-रे – प्लूरल स्पेस में जमा तरल (फ्लूइड) को दिखाने के लिए। सीटी स्कैन – फेफड़ों और प्लूरा की अधिक स्पष्ट और विस्तृत इमेज प्राप्त करने के लिए। अल्ट्रासाउंड – थोरासेंटीसिस (फ्लूइड निकालने की प्रक्रिया) के लिए सही जगह तय करने में मदद करता है। थोरासेंटीसिस – एक सुई के जरिए प्लूरल स्पेस से फ्लूइड निकालकर उसकी जांच की जाती है, जिससे इंफेक्शन की पुष्टि होती है। एम्पाइमा का पता लगाने के लिए कौन-कौन से टेस्ट किए जाते हैं? एम्पाइमा की पुष्टि करने और संक्रमण की गंभीरता जानने के लिए डॉक्टर कई टेस्ट कर सकते हैं: CBC (कंप्लीट ब्लड काउंट) – सफेद रक्त कोशिकाओं (WBC) की बढ़ी हुई संख्या को दिखाता है, जो इंफेक्शन का संकेत देती है। ब्लड कल्चर – खून में बैक्टीरिया की मौजूदगी का पता लगाने के लिए। प्लूरल फ्लूइड कल्चर और ग्राम स्टेनिंग – प्लूरल स्पेस से निकाले गए द्रव में मौजूद बैक्टीरिया की पहचान करने के लिए। प्लूरल फ्लूइड टेस्ट (pH और ग्लूकोज़ स्तर) – एम्पाइमा में pH और ग्लूकोज़ का स्तर आमतौर पर कम होता है, जिससे इसका निदान करने में मदद मिलती है। इमेजिंग टेस्ट (X-ray, CT स्कैन, अल्ट्रासाउंड) – फेफड़ों के चारों ओर जमा फ्लूइड को देखने और उसकी मात्रा का आकलन करने के लिए। क्या एम्पाइमा का इलाज संभव है? जी हां, एम्पाइमा का इलाज किया जा सकता है अगर समय पर और सही उपचार किया जाए। इलाज का मुख्य उद्देश्य संक्रमित फ्लूइड को बाहर निकालना, मूल इंफेक्शन को खत्म करना, और फेफड़ों को फिर से सामान्य रूप से फैलने का अवसर देना है। अधिकांश लोग पूरी तरह से ठीक हो जाते हैं, लेकिन इलाज की सफलता उम्र, समग्र स्वास्थ्य और एम्पाइमा की गंभीरता जैसे कारकों पर निर्भर करती है। अगर इलाज में देरी होती है, तो इससे सेप्सिस, फेफड़ों में मवाद (एब्सेस), या प्लूरल मोटाई जैसी जटिलताएं हो सकती हैं, जिनके लिए सर्जरी की आवश्यकता हो सकती है। एम्पाइमा का इलाज करने के लिए कौन सी दवाएं दी जाती हैं? एम्पाइमा का इलाज आमतौर पर एंटीबायोटिक्स से किया जाता है, जो इंफेक्शन को खत्म करने में मदद करती हैं। शुरुआत में ब्रॉड-स्पेक्ट्रम एंटीबायोटिक्स दी जाती हैं, जो विभिन्न प्रकार के बैक्टीरिया के खिलाफ काम करती हैं। फिर, प्लूरल फ्लूइड में पाए गए विशेष बैक्टीरिया के आधार पर दवाइयों को कस्टमाइज (अनुकूलित) किया जाता है। इलाज शुरू करने के बाद मुझे अच्छा महसूस होने में कितनी जल्दी समय लगेगा? कई लोग एम्पाइमा के इलाज शुरू करने के कुछ ही दिनों में बेहतर महसूस करने लगते हैं। जब संक्रमित फ्लूइड बाहर निकाला जाता है, तो सीने का दर्द और सांस फूलने की समस्या अक्सर बेहतर हो जाती है। हालांकि, थकान और खांसी कुछ हफ्तों तक बनी रह सकती है। ज्यादातर लोग 2-4 हफ्तों में अपनी सामान्य गतिविधियों में वापस लौट सकते हैं, लेकिन पूर्ण स्वस्थ होने में कुछ महीने लग सकते हैं। एम्पाइमा को कैसे रोका जा सकता है? एम्पाइमा के होने का जोखिम कम करने के लिए आप निम्नलिखित कदम उठा सकते हैं: न्युमोकोकल और फ्लू के वैक्सीनेशन को समय पर लें सांस की इंफेक्शंस का इलाज तुरंत करवाएं धूम्रपान न करें और सेकंडहैंड स्मोक से बचें अच्छी ओरल हाइजीन बनाए रखें क्रॉनिक बीमारियों जैसे डायबिटीज का सही तरीके से प्रबंधन करें स्वस्थ जीवनशैली अपनाएं, जिसमें पर्याप्त आराम, अच्छा पोषण और नियमित व्यायाम शामिल हो। अगर हमें एम्पाइमा हो जाए तो क्या अपेक्षित हो सकता है? अगर आपको एम्पाइमा का निदान हुआ है, तो आप निम्नलिखित चीजों की उम्मीद कर सकते हैं: 7-10 दिन या उससे ज्यादा समय के लिए आईवी एंटीबायोटिक्स और चेस्ट ट्यूब ड्रेनेज के लिए अस्पताल में भर्ती रहना। वाइटल साइन, फ्लूइड आउटपुट, और फेफड़ों की कार्यक्षमता की दैनिक निगरानी। प्रगति ट्रैक करने के लिए पुनः इमेजिंग। अगर एंटीबायोटिक्स से इंफेक्शन ठीक नहीं होता, तो सर्जिकल इंटरवेंशन की संभावना। कई हफ्तों तक एंटीबायोटिक थेरेपी और कम गतिविधि स्तर। पूर्ण ठीक होने के लिए नियमित फॉलो-अप विज़िट्स। निमोनिया और एम्पाइमा में क्या अंतर है? निमोनिया फेफड़ों के ऊतकों में संक्रमण है, जबकि एम्पाइमा फेफड़ों के चारों ओर स्थित प्लूरल स्पेस (फेफड़ों के आसपास की झिल्ली) में संक्रमण है। निमोनिया कहीं ज्यादा आम है, जो करीब 1% आबादी को प्रभावित करता है, जबकि एम्पाइमा सिर्फ 0.001% लोगों में होता है। निमोनिया में उत्पादक खांसी, बुखार और सांस लेने में कठिनाई होती है। एम्पाइमा अक्सर निमोनिया के फैलने के कारण प्लूरल स्पेस में पस जमा होने से होता है, जिससे लक्षण और ज्यादा गंभीर हो सकते हैं। दोनों बीमारियों का इलाज एंटीबायोटिक्स से किया जाता है, लेकिन एम्पाइमा में संक्रमित फ्लूइड को बाहर निकालने के लिए ड्रेनेज की जरूरत होती है। एम्पाइमा और एब्सेस में क्या अंतर है? एब्सेस एक स्थानीय (localised) पस का जमा होता है जो फेफड़ों के ऊतकों में इंफेक्शन के कारण बनता है, जबकि एम्पाइमा फेफड़ों के चारों ओर के प्लूरल स्पेस में पस का जमा है। एब्सेस आमतौर पर अच्छी तरह से सीमित होता है और सिर्फ एंटीबायोटिक्स से ठीक हो सकता है। एम्पाइमा ज्यादा फैलाव वाला होता है और लगभग हमेशा पस निकालने के लिए ड्रेनेज की जरूरत होती है। कभी-कभी, एक बड़ा एब्सेस प्लूरल स्पेस में फट सकता है, जिससे एम्पाइमा हो सकता है। दोनों ही स्थितियां निमोनिया की जटिलताओं के रूप में हो सकती हैं। एम्पाइमा और प्लूरल इफ्यूजन में क्या अंतर है? प्लूरल इफ्यूजन एक सामान्य शब्द है, जो प्लूरल स्पेस (फेफड़ों के चारों ओर की जगह) में अधिक तरल का जमा होने को दर्शाता है। यह तरल सिरस (स्पष्ट), रक्तमय, या प्यूरुलेंट (पस से भरा) हो सकता है। एम्पाइमा विशेष रूप से संक्रमित तरल या पस को संदर्भित करता है, जो प्लूरल स्पेस में जमा होता है, और यह प्लूरल इफ्यूजन का एक प्रकार है। प्लूरल इफ्यूजन के अन्य कारणों में हृदय विफलता, गुर्दे की बीमारी, जिगर का सिरोसिस, और कैंसर शामिल हैं। एम्पाइमा हमेशा संक्रमण के कारण होता है और एंटीबायोटिक इलाज की आवश्यकता होती है। एम्पाइमा और पैराप्न्युमोनिक इफ्यूजन में क्या अंतर है? पैराप्न्युमोनिक इफ्यूजन एक प्रकार का प्लूरल इफ्यूजन है जो निमोनिया के कारण दूसरी बार विकसित होता है। यह असर न होने वाला (clear fluid) या जटिल (पस जैसा तरल) हो सकता है। एम्पाइमा एक जटिल पैराप्न्युमोनिक इफ्यूजन है, जिसमें तरल स्पष्ट रूप से पस से भरा होता है। पैराप्न्युमोनिक इफ्यूजन बहुत सामान्य है, जो निमोनिया के मामलों के 20-40% में होता है, जबकि एम्पाइमा बहुत कम होता है। निष्कर्ष एम्पाइमा एक गंभीर स्थिति है, जो तत्काल चिकित्सा ध्यान की आवश्यकता होती है। यदि आपको एम्पाइमा के लक्षण हैं, खासकर निमोनिया के बाद, तो उपचार में देरी न करें। मेट्रोपोलिस हेल्थकेयर में, हम आपके लक्षणों के मूल कारण की पहचान करने में मदद करने के लिए व्यापक डायग्नोस्टिक सेवाएं प्रदान करते हैं। हमारी कुशल फ्लेबोटोमिस्ट टीम आपके घर के आराम से रक्त और प्लूरल फ्लूइड नमूने एकत्र कर सकती है। आज ही अपनी सेहत की देखभाल शुरू करें!
ऑस्टियोपीनिया: कमजोर हड्डियों के शुरुआती संकेत और उन्हें मजबूत करने के असरदार तरीके
ऑस्टियोपीनिया क्या है? ऑस्टियोपीनिया एक ऐसी स्थिति है जिसमें हड्डियों की मिनरल डेंसिटी (BMD) सामान्य से कम हो जाती है। यह ऑस्टियोपोरोसिस से पहले की स्टेज होती है, जिसमें हड्डियों का नुकसान और ज्यादा हो जाता है। ऑस्टियोपीनिया में हड्डियां थोड़ी कमजोर हो जाती हैं, लेकिन ऑस्टियोपोरोसिस जितनी नाजुक नहीं होतीं। इसे ऐसे समझें कि आपकी हड्डियां आपको पहले ही संकेत दे रही हैं कि अब उन्हें ज्यादा देखभाल और मजबूती की जरूरत है। ऑस्टियोपीनिया और ऑस्टियोपोरोसिस में क्या फर्क है? दोनों ही स्थितियों में हड्डियों की मजबूती कम होती है, लेकिन इनके गंभीरता स्तर अलग-अलग होते हैं: ऑस्टियोपीनिया में बोन मिनरल डेंसिटी (BMD) स्कोर -1 से -2.5 के बीच होता है। इसका मतलब है कि हड्डियां सामान्य से कमजोर हैं, लेकिन इतनी नाजुक नहीं हुई हैं कि हल्के झटकों से टूट जाएं। ऑस्टियोपोरोसिस इससे ज्यादा गंभीर होता है, जिसमें BMD स्कोर -2.5 से भी कम हो जाता है। इस स्थिति में हड्डियां बहुत ज्यादा खोखली हो जाती हैं और हल्की सी चोट या गिरने से भी फ्रैक्चर का खतरा बढ़ जाता है। यानी, ऑस्टियोपीनिया हड्डियों की सेहत के लिए "येलो अलर्ट" है, जबकि ऑस्टियोपोरोसिस "रेड अलर्ट" है, जो बताता है कि फ्रैक्चर का खतरा ज्यादा बढ़ गया है। अगर ऑस्टियोपीनिया के लक्षण समय रहते पकड़ लिए जाएं, तो सही ट्रीटमेंट और लाइफस्टाइल से हड्डियों को मजबूत बनाया जा सकता है, ताकि वे और ज्यादा कमजोर न हों। ऑस्टियोपीनिया कितना आम है? ऑस्टियोपीनिया काफी आम है, खासतौर पर उम्र बढ़ने के साथ। नेशनल ऑस्टियोपोरोसिस फाउंडेशन के मुताबिक, 4.3 करोड़ से ज्यादा अमेरिकी वयस्कों की हड्डियों की मिनरल डेंसिटी कम है या उन्हें ऑस्टियोपीनिया है। अंदाजा लगाया जाता है कि 50 साल से ज्यादा उम्र के लगभग आधे लोगों में किसी न किसी स्तर पर हड्डियों का नुकसान होता है। खासतौर पर महिलाओं में, खासकर मेनोपॉज के बाद, इसका खतरा ज्यादा होता है, क्योंकि हार्मोनल बदलाव हड्डियों के नुकसान को तेज कर देते हैं। ऑस्टियोपीनिया के लक्षण क्या हैं? ऑस्टियोपीनिया की चालाकी ये है कि इसके सीधे-सीधे लक्षण आमतौर पर नजर नहीं आते। आपको ये महसूस नहीं होता कि आपकी हड्डियां कमजोर हो रही हैं। लेकिन फिर भी कुछ संकेत होते हैं, जिन पर ध्यान देना जरूरी है: बार-बार स्ट्रेस फ्रैक्चर होना या हल्की चोट से हड्डी टूट जाना समय के साथ कद का कम होना पीठ दर्द या शरीर की मुद्रा (पोश्चर) में बदलाव, खासतौर पर रीढ़ की हड्डी में कॉम्प्रेशन फ्रैक्चर की वजह से ऑस्टियोपीनिया होने की वजह क्या है? ऑस्टियोपीनिया के कारण मुख्य रूप से दो तरह के होते हैं: 1. उम्र के साथ हड्डियों का प्राकृतिक कमजोर होना हमारी हड्डियां लगातार टूटती और बनती रहती हैं। लेकिन 30 साल की उम्र के बाद हड्डियों का टूटना, बनने की प्रक्रिया से ज्यादा तेज हो जाता है, जिससे धीरे-धीरे बोन डेंसिटी कम होने लगती है। महिलाओं में मेनोपॉज के बाद यह प्रक्रिया और तेजी से होती है, जिससे हड्डियां ज्यादा कमजोर हो सकती हैं। 2. कुछ बीमारियां और दवाइयां कुछ स्वास्थ्य समस्याएं और ट्रीटमेंट भी हड्डियों को कमजोर कर सकते हैं, जैसे: रूमेटॉइड आर्थराइटिस और दूसरी सूजन वाली बीमारियां थायरॉइड और पैराथायरॉइड से जुड़ी गड़बड़ियां सीलिएक डिजीजv और इंफ्लेमेटरी बाउल डिजीज (IBD) कीमोथेरेपी और रेडिएशन थेरेपी लंबे समय तक कॉर्टिकोस्टेरॉइड या कुछ एंटी-सीज़र (मिर्गी की) दवाइयां लेना ऑस्टियोपीनिया का खतरा किन लोगों को ज्यादा होता है? उम्र और जेंडर के अलावा, कुछ और फैक्टर्स भी हैं जो ऑस्टियोपीनिया होने का खतरा बढ़ा सकते हैं: परिवार में ऑस्टियोपोरोसिस या हड्डी टूटने का इतिहास बैठे-बैठे ज्यादा समय बिताना और वेट-बेयरिंग एक्सरसाइज न करना गलत खान-पान, खासकर कैल्शियम और विटामिन D की कमी धूम्रपान और ज्यादा शराब पीना कम बॉडी वेट या बहुत पतला हड्डियों का स्ट्रक्चर कुछ खास नस्लें, जैसे कि कोकेशियन और एशियाई महिलाएं अगर आपको इनमें से कोई भी रिस्क फैक्टर है, तो आपको अपनी हड्डियों की सेहत को लेकर और ज्यादा सतर्क रहने की जरूरत है। जैसे, अगर परिवार में किसी को ऑस्टियोपोरोसिस रहा है, तो 65 साल की उम्र से पहले ही बोन डेंसिटी टेस्ट करवाना एक समझदारी भरा कदम हो सकता है। ऑस्टियोपीनिया से होने वाली जटिलताएं क्या हैं? ऑस्टियोपीनिया का सबसे बड़ा खतरा हड्डियों के फ्रैक्चर का बढ़ा हुआ रिस्क होता है। हड्डियां कमजोर और नाजुक हो जाती हैं, जिससे मामूली गिरावट या हल्के झटके से भी फ्रैक्चर हो सकता है। ये फ्रैक्चर दर्द, चलने-फिरने में दिक्कत, और गंभीर मामलों में ब्लड क्लॉट्स या इन्फेक्शन जैसी समस्याएं पैदा कर सकते हैं। रीढ़ की हड्डी (स्पाइन) में कंप्रेशन फ्रैक्चर एक बड़ी चिंता होती है। इनमें कशेरुकाओं (वर्टिब्रे) में छोटे-छोटे क्रैक आ जाते हैं, जिससे पीठ दर्द, कद का छोटा होना और झुकी हुई मुद्रा (stooped posture) हो सकती है। अगर बार-बार ऐसे फ्रैक्चर हों, तो काइफोसिस (kyphosis) या "डॉवेगर हंप" जैसी स्थिति बन सकती है। अगर ऑस्टियोपीनिया को नजरअंदाज किया जाए, तो यह धीरे-धीरे ऑस्टियोपोरोसिस में बदल सकता है। इसलिए, हड्डियों की सेहत बनाए रखने और फ्रैक्चर से बचने के लिए जल्दी पहचान और सही इलाज बेहद जरूरी है। ऑस्टियोपीनिया की पहचान कैसे होती है? ऑस्टियोपीनिया का पता लगाने के लिए बोन मिनरल डेंसिटी (BMD) टेस्ट किया जाता है। इसके लिए डुअल-एनर्जी एक्स-रे एब्सॉर्प्शियोमेट्री (DEXA) स्कैन नामक एक खास तरह का एक्स-रे किया जाता है। ये टेस्ट बिना दर्द के होता है और आमतौर पर कूल्हों (hip) और रीढ़ (spine) की हड्डियों की डेंसिटी मापने के लिए किया जाता है। DEXA स्कैन के नतीजे T-स्कोर के रूप में आते हैं, जो आपकी हड्डियों की मजबूती की तुलना एक 30 साल के स्वस्थ व्यक्ति की हड्डियों से करता है: T-स्कोर -1 से -2.5 के बीच हो तो इसका मतलब है कि आपको ऑस्टियोपीनिया है। T-स्कोर -2.5 से कम हो तो ये ऑस्टियोपोरोसिस की ओर इशारा करता है। DEXA स्कैन आपकी हड्डियों की सेहत का एक स्पष्ट आंकलन देता है और डॉक्टर को सही इलाज तय करने में मदद करता है। इसके अलावा, डॉक्टर ब्लड टेस्ट भी करा सकते हैं, ताकि यह देखा जा सके कि कहीं कोई दूसरी बीमारी हड्डियों के नुकसान की वजह तो नहीं बन रही। ऑस्टियोपीनिया का इलाज क्या है? ऑस्टियोपीनिया के इलाज का मकसद हड्डियों की और कमजोरी रोकना और फ्रैक्चर के खतरे को कम करना होता है। इसके लिए आमतौर पर दो तरह के उपाय अपनाए जाते हैं: 1. लाइफस्टाइल में बदलाव कैल्शियम (1000-1200 mg/दिन) और विटामिन D (600-800 IU/दिन) सही मात्रा में लें – इसे डाइट या सप्लीमेंट्स के जरिए पूरा किया जा सकता है। वेट-बेयरिंग और रेजिस्टेंस एक्सरसाइज करें – जैसे वॉकिंग, जॉगिंग, वेट ट्रेनिंग, और योग, जो हड्डियों को मजबूत बनाने में मदद करते हैं। स्मोकिंग छोड़ें और शराब का सेवन कम करें, क्योंकि ये हड्डियों को नुकसान पहुंचाते हैं। संतुलित डाइट लें और स्वस्थ वजन बनाए रखें, क्योंकि बहुत ज्यादा दुबला शरीर भी हड्डियों के नुकसान का खतरा बढ़ा सकता है। 2. दवाइयां बिस्फॉस्फोनेट्स – ये दवाइयां हड्डियों के टूटने की गति को कम करके उनकी मजबूती बनाए रखने में मदद करती हैं और फ्रैक्चर के खतरे को कम करती हैं। इन्हें आमतौर पर उन लोगों को दिया जाता है जिनकी हड्डियों में ज्यादा कमजोरी होती है या जिनमें अन्य जोखिम फैक्टर होते हैं। हॉर्मोन थेरेपी – मेनोपॉज के शुरुआती दौर में एस्ट्रोजन थेरेपी हड्डियों को कमजोर होने से बचा सकती है, लेकिन इसके कुछ साइड इफेक्ट्स भी हो सकते हैं, इसलिए इसे केवल बोन हेल्थ के लिए रूटीन में नहीं दिया जाता। अन्य दवाइयां – आपकी स्थिति के आधार पर डॉक्टर रालॉक्सिफीन, डेनोसुमैब, या टेरीपराटाइड जैसी दवाइयों की सलाह दे सकते हैं, जो हड्डियों को मजबूत करने में मदद करती हैं। सही इलाज के लिए डॉक्टर से सलाह लें और अपनी हड्डियों की सेहत के हिसाब से पर्सनलाइज़्ड ट्रीटमेंट प्लान बनवाएं। बोन डेंसिटी की नियमित जांच से यह पता लगाया जा सकता है कि इलाज कितना असरदार हो रहा है और जरूरत के अनुसार इसमें बदलाव किए जा सकते हैं। क्या ऑस्टियोपीनिया को रोका जा सकता है? उम्र बढ़ने के साथ कुछ हद तक हड्डियों का कमजोर होना तो स्वाभाविक है, लेकिन आप अपनी हड्डियों को मजबूत बनाए रखने के लिए कई कदम उठा सकते हैं: कैल्शियम और विटामिन D भरपूर लें - 1000-1200 mg कैल्शियम रोज़ाना लें, जिसे दूध, दही, पनीर, हरी पत्तेदार सब्जियों और फोर्टिफाइड फूड्स से पाया जा सकता है। विटामिन D के लिए धूप में समय बिताएं, फैटी फिश, अंडे की जर्दी खाएं, और जरूरत पड़ने पर सप्लीमेंट लें। नियमित एक्सरसाइज करें - वेट-बेयरिंग एक्सरसाइज जैसे वॉकिंग, जॉगिंग, डांसिंग और रेजिस्टेंस ट्रेनिंग (वेट लिफ्टिंग या रेजिस्टेंस बैंड के साथ वर्कआउट) से हड्डियों को मजबूत किया जा सकता है। हफ्ते में कम से कम 5 दिन, 30 मिनट एक्सरसाइज का लक्ष्य रखें। धूम्रपान छोड़ें और शराब सीमित करें - स्मोकिंग और ज्यादा शराब हड्डियों को कमजोर करती हैं और फ्रैक्चर का खतरा बढ़ाती हैं। बोन-डेंसिटी की जांच करवाएं - अगर आप 65+ साल की महिला, 70+ साल के पुरुष हैं, या आपके अंदर ऑस्टियोपीनिया के रिस्क फैक्टर हैं, तो डॉक्टर से DEXA स्कैन कराने की सलाह लें ताकि समय रहते हड्डियों की सेहत का पता लगाया जा सके। अगर ऑस्टियोपीनिया हो जाए तो क्या उम्मीद करें? अगर आपको ऑस्टियोपीनिया है, तो हड्डियों की घनत्व (बोन डेंसिटी) कम हो सकती है, जिससे फ्रैक्चर का खतरा बढ़ जाता है, लेकिन इसका मतलब यह नहीं कि आपको ऑस्टियोपोरोसिस हो ही जाएगा। नियमित एक्सरसाइज, कैल्शियम और विटामिन D का सही मात्रा में सेवन हड्डियों के नुकसान को धीमा कर सकता है। आपका डॉक्टर हड्डियों की सेहत बनाए रखने और फ्रैक्चर के खतरे को कम करने के लिए लाइफस्टाइल में बदलाव या कुछ दवाइयां लेने की सलाह दे सकता है। क्या ऑस्टियोपीनिया को ठीक किया जा सकता है? ऑस्टियोपीनिया का कोई पक्का इलाज नहीं है, लेकिन हड्डियों के नुकसान की रफ्तार को धीमा किया जा सकता है और कुछ हद तक इसे रीवर्स भी किया जा सकता है। सही लाइफस्टाइल और मेडिकल ट्रीटमेंट अपनाने से समय के साथ DEXA स्कैन पर आपका T-स्कोर सुधार सकता है। कुछ शोधों में पाया गया है कि बिस्फॉस्फोनेट दवाओं का लगातार इस्तेमाल करने से 3-4 साल में हड्डियों की डेंसिटी लगभग 5% तक बढ़ सकती है। इसके अलावा, नियमित एक्सरसाइज, सही मात्रा में कैल्शियम और विटामिन D लेने से भी हड्डियों की मजबूती पर सकारात्मक असर पड़ता है। डॉक्टर को कब दिखाना चाहिए? अगर आपके अंदर ऑस्टियोपीनिया या ऑस्टियोपोरोसिस के जोखिम फैक्टर मौजूद हैं, तो अपनी हड्डियों की सेहत को लेकर डॉक्टर से सलाह लेना अच्छा रहेगा। कुछ खास कारण जिनकी वजह से आपको मेडिकल सलाह लेनी चाहिए: आप 65 साल से अधिक उम्र की महिला या 70 साल से अधिक उम्र के पुरुष हैं। आपके परिवार में ऑस्टियोपोरोसिस या हड्डियों में फ्रैक्चर का इतिहास है। आपको मामूली गिरावट या चोट से फ्रैक्चर हो चुका है। आपको कोई ऐसी मेडिकल कंडीशन है या आप ऐसी दवाइयां ले रहे हैं जो हड्डियों की सेहत को प्रभावित कर सकती हैं। आपको पीठ दर्द, कद में कमी, या शरीर के पोस्चर में बदलाव जैसे लक्षण महसूस हो रहे हैं। निष्कर्ष ऑस्टियोपीनिया भले ही बिना किसी स्पष्ट लक्षणों के हो, लेकिन यह आपकी हड्डियों की सेहत के लिए एक महत्वपूर्ण चेतावनी संकेत है। अगर आप अपनी हड्डियों की सेहत को लेकर चिंतित हैं, तो मेट्रोपोलिस हेल्थकेयर से संपर्क करें और बोन डेंसिटी स्कैन करवाएं, ताकि आपको व्यक्तिगत जरूरतों के अनुसार सही सलाह मिल सके। भारतभर में अत्याधुनिक डायग्नोस्टिक लैब्स के नेटवर्क और घर पर सैंपल कलेक्शन की सुविधा देने वाले अनुभवी फ्लेबोटोमिस्ट्स की टीम के साथ, मेट्रोपोलिस हेल्थकेयर आपकी हड्डियों की सेहत की जांच और निगरानी में भरोसेमंद साथी बन सकता है। आज ही अपनी हड्डियों की सेहत को प्राथमिकता दें, ताकि भविष्य में आपको इसका फायदा मिले!















 WhatsApp
WhatsApp