Latest Blogs
Millet for Diabetes Management: Incorporating a Diabetes-Friendly Grain into Your Diet
If you're living with diabetes, you know that managing your blood sugar levels is crucial for maintaining good health. While there are many factors that influence blood glucose, your diet plays a significant role. Millets for diabetes have emerged as a nutritious and diabetes-friendly grain that can be a valuable addition to your meal plan. In this article, we'll explore what makes millet beneficial for people with diabetes and share practical tips on incorporating this versatile grain into your daily diet. What is a Millet? Millets are a group of small-seeded grasses that have been cultivated for thousands of years. This ancient grain is grown in many parts of the world, particularly in Asia and Africa. There are several types of millet, including pearl millet, finger millet, foxtail millet, and proso millet. Each variety has its own unique nutritional profile, but all share common characteristics that make them suitable for a diabetes-friendly diet. Nutritional Content Millets are nutrient-dense grains packed with essential vitamins, minerals, and fibre. A 100-gram serving of cooked millet has the following nutritional profile: 378 calories 73 grams of carbohydrates 6-11 grams of protein 4 grams of fibre Rich in vitamins A, E, and B6 High in magnesium, phosphorus, and potassium This impressive nutritional profile makes millet a wholesome choice for overall health, especially for those managing diabetes. Can People with Diabetes Eat Millet? If you are wondering, is millet good for diabetes? The answer is yes. Millet and diabetes make a great pair. This nutritious grain offers several benefits that can help people with diabetes better manage their blood sugar levels and overall health. Let's dive into the specific ways millet can be advantageous for those living with diabetes. How Does Millet Benefit People with Diabetes? Here are some of the benefits of millets for diabetes: Low Glycaemic Index One of the key factors that make millet good for diabetes is its low glycaemic index (GI). GI is a measure of how quickly a food raises blood sugar levels. Foods with a high GI cause rapid spikes in blood glucose, while low GI foods lead to a slower, more gradual rise. Studies have shown that millet has a mean GI of 52.7, which is significantly lower than other common grains like white rice and wheat. This low GI helps prevent sudden spikes in blood sugar, making it easier for people with diabetes to manage their glucose levels. Rich in Fibre Millet's high fibre content is another reason why it's an excellent choice for diabetes management. A single serving of millet provides around 4 grams of fibre, which is substantial for digestive health and blood sugar control. Fibre slows down the digestion process, allowing sugar to enter the bloodstream gradually. This helps prevent sharp rises in blood glucose and keeps you feeling full and satisfied for longer. Including fibre-rich foods like millet in your diet is a simple yet effective strategy for managing diabetes. Nutrient-Dense In addition to its low GI and high fibre content, millets are packed with essential nutrients that support overall health and can help manage diabetes-related comorbidities. This gluten-free grain is a good source of: Magnesium: Helps regulate blood sugar and supports heart health Chromium: Enhances insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism Phospholipids: Beneficial for cell membrane function and insulin signalling Potassium: Crucial for maintaining healthy blood pressure levels Incorporating nutrient-dense foods like millet into your diet can help you meet your nutritional needs while managing diabetes effectively. Types of Millet for Diabetes Management While all types of millets offer similar benefits for diabetes management, some varieties are more commonly used and easier to incorporate into various dishes. Here are some of the best millets for diabetes to consider: Pearl Millet: This is the most widely cultivated type of millet, known for its slightly sweet and nutty flavour. Pearl millet is versatile and can be used in a range of recipes, from porridge to salads. Finger Millet: Also known as ragi, finger millet is a nutrient-dense variety that's particularly high in calcium and iron. It has a slightly earthy taste and can be used to make rotis, porridges, and even desserts. Foxtail Millet: This type of millet has a mild, slightly sweet flavour and a texture similar to rice. Foxtail millet is often used as a rice substitute in dishes like pulao and khichdi. Proso Millet: With its light, fluffy texture and mild flavour, proso millet is a great option for making porridges, pilafs, and even baked goods. Incorporating Millet into a Diabetes-Friendly Diet Now that you know which millets are good for diabetes, let's explore some practical ways to include this nutritious grain in your daily meal plan. Here are some millet recipes for diabetics: Breakfast Ideas Millet Porridge: Cook millet with milk or water and add your favourite fruits, nuts, or seeds for a wholesome and filling breakfast. Millet Pancakes: Mix millet flour with other whole-grain flour to create delicious and diabetes-friendly pancakes. Lunch and Dinner Recipes Millet Salad: Toss cooked millet with fresh vegetables, herbs, and a light vinaigrette for a refreshing and nutritious salad. Millet Risotto: Replace rice with millet in your favourite risotto recipe for a healthier twist on this classic dish. Snacks and Desserts Millet Energy Balls: Combine cooked millet with nuts, seeds, and a touch of honey to make tasty and portable energy balls. Millet Pudding: Cook millet with milk and sweeten it with natural options like stevia or honey for a comforting and diabetes-friendly dessert. FAQs 1. Can I eat millet every day if I have diabetes? Yes, you can include millet in your daily diet, but it's important to maintain a balanced intake. While millet is nutritious, it also contains phytic acid, which can inhibit nutrient absorption if consumed in excess. 2. Which type of millet is best for lowering blood sugar? All types of millet have a low glycaemic index and high fibre content, making them beneficial for blood sugar management. However, pearl millet and finger millet are often highlighted for their additional nutritional benefits and versatility in recipes. 3. Is millet better than rice or wheat for diabetics? Yes, millet is generally considered a better choice than rice or wheat for people with diabetes. Its lower glycaemic index, higher fibre content, and richer nutrient profile make it a superior option for managing blood sugar levels effectively. Conclusion Millets for diabetes offer a nutritious and delicious way to manage blood sugar levels and support overall health. By incorporating this diabetes-friendly grain into your diet through various recipes and meal ideas, you can enjoy the benefits of its low glycaemic index, high fibre content, and rich nutrient profile. Remember, managing diabetes is a journey that requires consistent effort and the right tools. If you're looking for reliable diagnostic services and health check-ups to support your diabetes management, Metropolis Healthcare is here to help. With a network of advanced diagnostic labs across India and a team of skilled blood collection technicians, Metropolis offers convenient at-home sample collection and quick, accurate test results. Take charge of your health today by booking a diabetes screening or health check-up with Metropolis Healthcare.
Natural Ways to Boost AMH Levels and Enhance Fertility
Anti-Müllerian Hormone (AMH) is a key indicator of a woman's ovarian reserve and fertility potential. Produced by the granulosa cells in the ovarian follicles, AMH levels provide valuable insights into the quantity of remaining eggs. For women hoping to conceive, understanding how to increase AMH levels naturally is crucial. While AMH levels naturally decline with age, certain lifestyle modifications and natural remedies for AMH levels may help support overall reproductive health and potentially influence AMH. In this article, we'll explore the connection between AMH and fertility, and share practical tips to optimise your AMH levels. What is AMH (Anti-Müllerian Hormone)? AMH is a hormone secreted by the small, immature follicles in the ovaries. It serves as an indirect measure of the number of eggs remaining in a woman's ovarian reserve. AMH levels can be assessed through a simple blood test, providing a snapshot of a woman's fertility potential. However, it's important to note that while AMH indicates the quantity of eggs, it does not reflect their quality. Understanding AMH and Fertility AMH and fertility are closely interlinked. Higher AMH levels generally suggest a more abundant ovarian reserve, which can be advantageous for fertility treatments like in-vitro fertilization (IVF). Women with higher AMH often respond better to ovarian stimulation and may have higher success rates with assisted reproductive techniques. Conversely, lower AMH levels may indicate a diminished egg supply and potentially reduced fertility. Why are AMH Levels Important? Assessing AMH levels is a critical component of fertility evaluations. It helps healthcare providers estimate a woman's ovarian reserve and tailor fertility treatment plans accordingly. For women considering IVF or other assisted reproductive technologies, AMH levels can provide valuable prognostic information and guide expectations. Additionally, monitoring AMH levels over time can offer insights into the rate of ovarian reserve depletion. Causes of Low AMH Levels Several factors can contribute to low AMH levels: Advanced age: AMH levels naturally decline with age as the ovarian reserve diminishes. Ovarian surgery: Procedures like ovarian cystectomy or endometriosis surgery may impact AMH levels. Chemotherapy: Certain cancer treatments can damage the ovaries and lower AMH. Premature ovarian insufficiency: This condition, characterised by early menopause, can result in low AMH. Can AMH Levels Be Increased Naturally? While there is limited scientific evidence to suggest that AMH levels can be dramatically increased through natural means, adopting healthy lifestyle practices and making dietary adjustments may support overall reproductive health and potentially influence AMH levels. Let's explore some natural remedies for AMH levels. Natural Ways to Improve AMH Levels 1. Balanced Diet for Hormonal Health Nourishing your body with a well-balanced diet rich in essential nutrients is key for optimal hormonal health. Focus on consuming: Antioxidant-rich fruits and vegetables to combat oxidative stress Whole grains and fiber-rich foods to regulate hormone levels Lean proteins to support cellular repair and growth Healthy fats like omega-3s to reduce inflammation Staying well-hydrated is also crucial for overall health and hormone balance. 2. Importance of Regular Exercise Engaging in regular physical activity can benefit reproductive health in several ways: Improves insulin sensitivity and regulates blood sugar levels Reduces stress and promotes hormonal balance Maintains a healthy body weight, which is important for fertility Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week. However, avoid excessive or intense exercise, which may negatively impact hormone levels. 3. Stress Management Techniques Chronic stress can wreak havoc on hormonal balance. Implementing stress-reducing practices into your daily routine may help support overall reproductive health: Practice relaxation techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga Engage in hobbies and activities that bring you joy and relaxation Prioritise self-care and create a balanced lifestyle While the direct impact of stress reduction on AMH levels is not well-established, managing stress is beneficial for overall well-being. 4. Supplements for Low AMH Certain supplements have been studied for their potential to support ovarian function and egg quality: DHEA: This hormone precursor has shown promise in some studies, but more research is needed to confirm its effectiveness in increasing AMH levels. CoQ10: This antioxidant may help protect egg cells from oxidative damage and improve fertility outcomes. Myo-inositol: This B-vitamin-like substance may enhance egg quality and support ovarian function. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any supplement regimen to ensure safety and appropriateness for your individual needs. 5. Minimizing Environmental Toxins Exposure to environmental toxins like BPA, phthalates, and pesticides has been linked to hormonal disruption and potential fertility issues. To minimise your exposure: Choose organic produce when possible Avoid plastic food containers and opt for glass or stainless steel Use natural, fragrance-free personal care and cleaning products Filter your drinking water to remove contaminants FAQs Which foods increase AMH levels? While no single food has been proven to directly increase AMH levels, a nutrient-dense, well-balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats may support overall reproductive health and hormonal balance. Can low AMH be reversed? Low AMH levels, especially those related to age, are generally not reversible. However, adopting healthy lifestyle practices and exploring fertility treatment options with a healthcare provider can help optimise your chances of conceiving despite low AMH. How to Test AMH Levels? If you're concerned about your fertility or interested in assessing your ovarian reserve, a simple blood test can measure your AMH levels. Consult with your healthcare provider to determine if AMH testing is appropriate for you and to interpret the results in the context of your overall reproductive health. Metropolis Healthcare, a leading chain of diagnostic labs across India, offers convenient at-home blood sample collection for AMH testing. Their team of skilled phlebotomists ensures a comfortable and hassle-free experience, while their state-of-the-art labs deliver accurate results. With online report access via email and the user-friendly Metropolis TruHealth app, you can easily monitor your AMH levels and take proactive steps towards enhancing your fertility. Conclusion Understanding the link between AMH and fertility is a crucial step in your journey towards conceiving. While there's no guaranteed way to increase AMH levels naturally, adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, stress management, and minimizing toxin exposure may support overall reproductive health. If you're concerned about your AMH levels or fertility potential, don't hesitate to consult with a healthcare provider. They can guide you through fertility testing, interpret your results, and recommend personalized strategies to optimise your chances of achieving pregnancy. Remember, knowledge is power when it comes to your reproductive health. By staying informed, making proactive choices, and seeking the right medical guidance, you can take control of your fertility journey. With the support of trusted diagnostic partners like Metropolis Healthcare, you can gain valuable insights into your AMH levels and work towards your dream of building a family.
Mouth Larvae: Types, Causes, Symptoms & Treatment
What is mouth larva? Mouth larva, or oral myiasis, is a parasitic infestation of the oral cavity caused by fly larvae. Though rare, it can result in severe discomfort and tissue damage if left untreated. This condition is more common in tropical and subtropical regions, where certain fly species thrive. The larvae feed on oral tissues, causing inflammation, pain, and potential destruction of affected areas. Factors such as poor oral hygiene, open wounds, and underlying health conditions increase the risk of infestation. Individuals with compromised immunity or untreated oral injuries are particularly vulnerable. Mouth larva symptoms may include swelling, foul odour, excessive salivation, and visible larvae within the mouth. If untreated, the condition can lead to severe infections and tissue necrosis. Recognising the early signs of mouth larva or oral myiasis and seeking prompt medical attention are crucial to preventing complications. Proper oral care, wound management, and hygiene can reduce the risk of developing mouth larva infestations. Types of mouth larva There are several mouth larva types that can infest oral tissues, leading to severe medical complications. Cochliomyia hominivorax, also known as the New World screwworm fly, is a dangerous species that requires living tissue to complete its life cycle. It aggressively invades the mouth, causing extensive tissue damage and obligatory myiasis. Chrysomya bezziana, the Old World screwworm fly, is another significant species responsible for mouth larva or oral myiasis, particularly in tropical regions. Like C. hominivorax, it infests living tissue and can lead to serious complications if untreated. Secondary myiasis occurs when larvae infest pre-existing oral wounds or necrotic tissue, exacerbating infections. Unlike primary infestations, this type arises from an already compromised oral environment. Understanding different oral myiasis or mouth larva types is crucial for timely intervention and treatment, as infestations can lead to extreme discomfort, infection, and, in severe cases, life-threatening conditions. What are the early signs of mouth larva? Recognising the early signs of oral myiasis or a mouth larva infestation is essential for quick medical intervention. The condition often starts with mild symptoms that can quickly escalate if left untreated. One of the most alarming mouth larva symptoms is a crawling or wriggling sensation in the mouth, which can be highly distressing. Other signs include: Swelling and redness: The affected area may become inflamed, leading to discomfort. Foul odour: A strong, unpleasant smell can develop due to tissue damage. Pain or discomfort: Ranging from mild irritation to severe pain Excessive salivation: The body’s response to the foreign larvae in the oral cavity Visible larvae: In advanced cases, small larvae may be seen in the infected area. One of the primary mouth larva causes is the presence of fly larvae in the mouth, often due to poor oral hygiene, open wounds, or underlying health issues. Those in tropical regions face a higher risk due to the prevalence of parasitic flies. If symptoms appear, prompt mouth larva treatment is crucial. This usually involves manual removal of larvae, wound care, and medications to prevent infection. Seeking early medical attention significantly improves recovery and prevents complications. What are the symptoms of mouth larva? As mouth larva or oral myiasis progresses, symptoms become increasingly severe and distressing. Early recognition is essential to prevent serious complications. The condition often begins with mild discomfort but can rapidly worsen if left untreated. Early Mouth Larva Symptoms: Swelling and redness: Initial inflammation of the oral tissues, often leading to mild discomfort Mild pain or irritation: A dull ache or sensitivity in the affected area Foul breath or bad taste: An unusual odour or unpleasant taste due to tissue irritation Excessive salivation: The body’s response to the infestation, leading to increased drooling Advanced Mouth Larva Symptoms: Intense pain and discomfort: As the larvae burrow deeper, eating, drinking, and speaking become increasingly difficult. Severe swelling: The affected area may become significantly enlarged, sometimes causing difficulty in opening the mouth. Foul odour: A strong, putrid smell develops due to tissue destruction and larval activity. Tissue destruction: Ulcers, open sores, or lesions may appear in the oral cavity. Necrosis of gum tissue: In severe cases, parts of the gum tissue may die, turning black or discoloured. Sensation of movement: Some patients report a crawling or pulsating sensation inside their wounds, especially after tooth extraction. Visible larvae: In extreme cases, small worm-like larvae may be seen wriggling inside infected areas. If you suspect an infestation, seeking urgent medical care is essential. A healthcare provider will examine your mouth, identify the larvae, and determine an appropriate mouth larva treatment plan. This may involve: Manual removal of visible larvae using forceps Irrigation of the affected area with antiseptic or saline solutions Antibiotic therapy to prevent or treat bacterial infections Pain management through medication and proper wound care Surgical debridement in severe cases to remove necrotic tissue and promote healing Follow-up care is critical to ensure the complete eradication of larvae and full recovery of oral tissues. Causes of mouth larva Several factors can contribute to the development of mouth larva. One of the primary mouth larva causes is poor oral hygiene, which creates an environment conducive to fly infestations. When food particles and debris accumulate in the mouth, they attract flies that lay eggs, leading to larval growth. Open wounds or lesions in the mouth, such as those caused by dental procedures or injuries, can also serve as entry points for larvae. Flies are attracted to these wounds, where they deposit their eggs, which then hatch into larvae. Certain underlying health conditions, such as diabetes, malnutrition, or immunodeficiency, can increase an individual's susceptibility to oral myiasis. These conditions weaken the body's natural defenses, making it easier for larvae to establish themselves in the mouth. Exposure to fly-infested areas, particularly in tropical and subtropical regions with poor sanitation, is another risk factor. Mouth breathing, especially during sleep, can also attract flies. When the mouth is open for extended periods, it provides an opportunity for flies to enter and lay eggs. What are the risks and complications of mouth larvae? Untreated mouth larva infestations can lead to severe complications. Severe Tissue Damage: The larvae feed on oral tissues, leading to ulcers, necrosis, and potential disfigurement. Spread of Infestation: In advanced cases, larvae can migrate to the nose, eyes, or other body parts, worsening the condition. Secondary Bacterial Infections: Open wounds caused by the larvae increase the risk of infections, which can complicate treatment. Sepsis or Blood Poisoning: If bacteria enter the bloodstream, the infection can become life-threatening. Pain and Functional Impairment: Severe swelling and tissue destruction may make eating, speaking, and swallowing difficult. Systemic Health Issues: If untreated, the infestation can weaken the immune system and cause further health complications. Immediate medical intervention is crucial to prevent these serious risks. How to prevent mouth larva? Preventing mouth larva involves a combination of good oral hygiene practices and awareness of risk factors. Some preventive measures include: Brushing and flossing regularly to maintain a clean oral environment Promptly treating open wounds or sores in the mouth Avoiding exposure to fly-infested areas, especially in regions with poor sanitation Keeping the mouth closed while sleeping to prevent fly entry Seeking regular dental check-ups to identify and address any oral health issues How to diagnose mouth larva? Diagnosing mouth larva or oral myiasis typically involves a physical examination of the oral cavity. A healthcare provider will carefully inspect the mouth for signs of infestation, such as the presence of larvae or tissue damage. In some cases, the provider may extract a larva from the mouth for microscopic examination. This helps identify the specific species involved, which can guide treatment decisions. Imaging tests, such as X-rays or CT scans, may be performed to assess the extent of the infestation and any damage to the oral structures. What are the medications for mouth larva? Mouth larva treatment typically involves a combination of medications to eliminate the infestation, prevent infections, and promote healing. Antiparasitic drugs like ivermectin or albendazole are often prescribed to kill the larvae. Antibiotics are essential to prevent or treat secondary bacterial infections caused by tissue damage. Anti-inflammatory medications help reduce swelling and discomfort, while pain relievers provide relief from severe irritation. Additionally, antiseptic solutions are used to irrigate and cleanse the affected area, preventing further complications. Prompt medical intervention and proper medication management are crucial to ensuring effective treatment and full recovery from mouth larva infestations. FAQs Is mouth larva dangerous? Yes, mouth larva can be dangerous if left untreated. It can lead to severe tissue damage, systemic infections, and potentially life-threatening complications. How do you get rid of mouth larvae? Getting rid of mouth larvae involves professional medical intervention. Treatment typically includes mechanical removal of the larvae, antibiotics for secondary infections, and anti-parasitic medications to eliminate the infestation. How do you treat myiasis in the mouth? Treating oral myiasis involves a combination of mechanical removal of the larvae, antibiotics to manage secondary infections, and antiseptic mouth rinses to promote healing and prevent further infestation. Why do people get mouth larvae? People get mouth larvae when flies lay eggs in open oral wounds, decayed teeth, or infected tissues. Poor oral hygiene, weakened immunity, and exposure to unsanitary conditions increase the risk. The condition is more common in tropical regions where parasitic flies thrive. Can mouth larva be cured? Yes, mouth larva can be cured with proper treatment. This includes removing the larvae manually, using antiparasitic medications, antibiotics to prevent infection, and wound care. Conclusion Mouth larva, or oral myiasis, is a distressing infestation that requires prompt medical attention. By understanding the types, causes, early signs, and symptoms of this condition, you can take proactive steps to protect your oral health. If you suspect mouth larva or notice any unusual symptoms, don't hesitate to consult a healthcare provider. At Metropolis Healthcare, we offer comprehensive diagnostic services, including pathology testing, to help identify oral myiasis and other health concerns. Our team of skilled technicians provides convenient at-home sample collection, ensuring your comfort and safety. With our state-of-the-art labs and commitment to delivering reliable results, we're here to support you on your journey to optimal oral health.
Claustrophobia (Fear of Enclosed Spaces)
What is claustrophobia? Claustrophobia is an anxiety disorder classified as a specific phobia in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5). It involves an intense, irrational fear of being confined in small or enclosed spaces, even when no real danger exists. Individuals with claustrophobia often experience feelings of being trapped, suffocated, or unable to escape, leading to severe distress. Common triggers include elevators, crowded rooms, tunnels, and airplanes. Claustrophobia symptoms can range from mild anxiety to full-blown panic attacks, with physical reactions such as sweating, rapid heartbeat, dizziness, and shortness of breath. Proper diagnosis and treatment, including therapy and relaxation techniques, can help manage and reduce symptoms effectively. What situations can trigger claustrophobia? Various situations can trigger claustrophobic reactions, such as: Elevators and small rooms without windows Airplanes, trains, and tunnels MRI machines and other medical procedures Crowded places like packed concerts or subways Even the mere thought of these situations can provoke anxiety in individuals with claustrophobia. The fear is often disproportionate to the actual risk involved. What does claustrophobia feel like? People with claustrophobia often experience a subjective sense of being trapped, even when there is no actual danger. They may fear running out of air, suffocating, or not being able to breathe properly when in confined spaces. These feelings can be so intense that they lead to panic attacks. How common is claustrophobia? Claustrophobia is a relatively common anxiety disorder, affecting approximately 12.5% of the population at some point in their lives. Studies have shown that women are more likely to experience claustrophobia compared to men. However, it's important to note that anyone can develop this phobia, regardless of age, gender, or background. Who gets claustrophobia? Claustrophobia can affect anyone, but it tends to develop during childhood or adolescence. Environmental factors, such as a traumatic experience in a confined space, can contribute to the onset of this phobia. Additionally, genetics may play a role with some individuals. What are the symptoms of claustrophobia? Claustrophobia symptoms can vary in intensity, ranging from mild discomfort to severe panic attacks. Common physical symptoms include difficulty breathing, a sensation of suffocation, rapid heartbeat, chest pain, trembling, excessive sweating, dizziness, and lightheadedness. These reactions are triggered by the fear of being trapped, even when no real danger is present. Psychological symptoms often involve overwhelming anxiety, a fear of losing control, and an intense urge to escape the confined space. In severe cases, these symptoms can escalate into full-blown panic attacks, which may include nausea, a sense of impending doom, or detachment from reality. Situations that commonly trigger claustrophobia include elevators, crowded rooms, airplanes, tunnels, or MRI machines. The severity of symptoms varies among individuals, but for some, claustrophobia causes significant daily life impact. Therapy, relaxation techniques, and gradual exposure therapy can help manage symptoms effectively. What causes claustrophobia? Claustrophobia causes intense fear of confined spaces, though its exact origins are not fully understood. Researchers believe it results from a combination of genetic and environmental factors. The amygdala, the brain’s fear-processing centre, may be overactive in individuals with claustrophobia, heightening anxiety in enclosed spaces. Other factors that may contribute include: Traumatic experiences, such as being trapped in a small space Learned behavior, where individuals develop fear by observing others with claustrophobia Anxiety disorders, which can increase susceptibility to claustrophobia Since claustrophobia causes distress, therapy and exposure techniques can help individuals manage their fears effectively. How is claustrophobia diagnosed? Claustrophobia is typically diagnosed through a combination of clinical evaluation and psychological assessments conducted by a mental health professional, such as a psychologist or psychiatrist. The diagnostic process involves: Symptom Assessment: The clinician will inquire about the frequency and severity of your claustrophobia symptoms when exposed to confined spaces. They will assess whether you experience panic attacks, intense anxiety, or avoidance behaviours in triggering situations. Health History Review: Your healthcare provider will review your medical history to identify any past experiences or traumas that may have contributed to the development of your claustrophobia. This may include incidents of being trapped, confined, or experiencing a panic attack in a small space. Psychological Tests and Questionnaires: You may be asked to complete standardised questionnaires or undergo psychological tests to evaluate your fear levels and the impact of claustrophobia on your daily functioning. These assessments help determine the severity of your phobia. Physical Examination: A physical exam may be performed to rule out any underlying medical conditions that could be causing or exacerbating your claustrophobic symptoms. This ensures that your fear is not a result of a physical health issue. Differential Diagnosis: The mental health professional will differentiate claustrophobia from other anxiety disorders, such as panic disorder, agoraphobia, or specific phobias. They will ensure that your symptoms are not better explained by another mental health condition. How is claustrophobia treated? Claustrophobia treatment typically involves a combination of psychological therapies and, in some cases, claustrophobia medicine to manage acute anxiety symptoms. The primary treatment approaches for claustrophobia include: Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT) CBT is a widely used and highly effective therapy for treating phobias, including claustrophobia. This type of therapy helps you: Identify and challenge the negative thoughts and beliefs associated with confined spaces Learn coping strategies to manage anxiety symptoms Gradually expose yourself to feared situations in a controlled and safe manner Through CBT, you'll work with a therapist to understand and modify your thought patterns and reactions to triggers, ultimately reducing your fear response. Exposure Therapy Exposure therapy is a specific type of CBT that involves gradual and systematic exposure to the feared situation or object. The goal is to help you become more comfortable with confined spaces by: Starting with mildly frightening situations and progressively increasing the intensity Remaining in the feared situation until your anxiety subsides Learning that the feared consequences do not occur, leading to a reduction in anxiety over time Your therapist will guide you through the exposure process, providing support and teaching you relaxation techniques to manage your anxiety. Relaxation Techniques Relaxation techniques are often used in conjunction with CBT and exposure therapy to help you cope with anxiety symptoms during exposure to triggers. These techniques may include: Deep breathing exercises Progressive muscle relaxation Guided imagery or visualisation By practicing these techniques regularly, you can learn to control your body's stress response and reduce the intensity of your claustrophobia symptoms. Medication In some cases, claustrophobia treatment may include medication to help manage severe anxiety or panic symptoms. Common medications used include: Benzodiazepines: Fast-acting anti-anxiety medications that can provide relief during acute panic attacks Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs): Antidepressants that can help reduce anxiety over time However, it's important to note that medication should be used in combination with therapy and under the guidance of a healthcare professional. Self-Help Strategies In addition to professional treatment, there are several self-help strategies you can use to manage your claustrophobia: Educate yourself about the phobia and its triggers Practice relaxation techniques regularly Challenge negative thoughts and beliefs Gradually expose yourself to feared situations Seek support from friends, family, or support groups Are medications used to treat claustrophobia? While therapy is the primary treatment for claustrophobia, medications may be prescribed to help manage symptoms. Claustrophobia medicine typically falls into two categories: Antidepressants: Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) like fluoxetine (Prozac) and sertraline (Zoloft) can help reduce anxiety by increasing serotonin levels in the brain. Anti-anxiety medications: Benzodiazepines, such as alprazolam (Xanax) and lorazepam (Ativan), provide short-term relief from anxiety symptoms. However, these should be used cautiously due to their potential for dependence. It's essential to consult a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate claustrophobia treatment plan for your individual needs. What can we do to better cope with claustrophobia? Coping with claustrophobia types involves a combination of lifestyle changes, relaxation techniques, and therapy to help manage anxiety in confined spaces. One helpful technique is deep breathing exercises. When feelings of anxiety arise, focusing on slow, controlled breaths can help calm the mind and reduce physical symptoms. Similarly, visualisation techniques, such as imagining yourself in a safe, open space, can provide a sense of comfort during stressful situations. Exercise helps lower overall stress and anxiety levels, making it easier to manage fears. Additionally, challenging negative thoughts by questioning irrational fears and replacing them with more positive beliefs can reduce anxiety responses. Gradual exposure therapy is also beneficial. By slowly introducing yourself to feared situations—starting with mild exposure and progressing to more challenging environments—you can desensitize anxiety over time. For those struggling with severe claustrophobia, professional therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), can be highly effective. What can we expect if we have a diagnosis of claustrophobia? If you've been diagnosed with claustrophobia, you can expect to experience intense fear and anxiety when confronted with enclosed spaces. Common claustrophobia symptoms include rapid heartbeat, sweating, trembling, shortness of breath, nausea, dizziness, and panic attacks. Treatment for claustrophobia typically involves cognitive-behavioural therapy (CBT), which helps you identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviours. Your therapist may also use systematic desensitisation, gradually exposing you to feared situations while practising relaxation techniques. Having claustrophobia, what can we do to better prepare ourselves for an MRI imaging test? MRI scans can be particularly challenging for individuals with claustrophobia due to the enclosed space of the machine. However, several strategies can help you prepare and manage anxiety during the procedure. Communicate your concerns with your healthcare provider and the MRI technician before the scan. Informing them about your claustrophobia allows them to take necessary measures, such as explaining the procedure in detail or offering additional support to ensure your comfort. Inquire about open MRI machines, as some facilities offer open or wide-bore MRI scanners that provide more space and can feel less confining. If an open MRI is available, it may be a better option for those with severe claustrophobia. Consider sedation if necessary. A doctor may prescribe short-term sedatives to help you stay calm and reduce anxiety during the procedure. Practice relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and visualisation exercises. These methods can help you stay focused and maintain a sense of control throughout the scan. How do we know at what point we need to see a doctor for our claustrophobia? If your claustrophobia significantly impacts your daily life or causes severe distress, it's time to seek professional help. Consider seeing a doctor if: Your fear prevents you from engaging in essential activities, such as using lifts or public transportation You experience frequent panic attacks or intense anxiety when faced with enclosed spaces Your phobia persists despite your attempts to cope on your own Conclusion Living with claustrophobia can be challenging, but with the right knowledge and support, you can learn to manage your anxiety and lead a fulfilling life. Remember, you're not alone in this journey—millions of people worldwide experience claustrophobia, and many have found relief through therapy and medication. If you suspect that you or a loved one may have claustrophobia, consider reaching out to Metropolis Healthcare for reliable diagnostic services and health check-ups. With a team of qualified professionals and state-of-the-art facilities, Metropolis Labs can help you prioritise your mental and physical well-being.
Five Sense Organs: How They Work Together
Have you ever marveled at how you experience the vibrant sights, melodious sounds, tantalizing smells, delightful tastes, and soothing touches that make life so rich? It's all thanks to the intricate workings of your five sense organs. The eyes, ears, nose, tongue, and skin are the gateways through which you perceive and interact with the world around you. These remarkable human sense organs not only enrich your daily experiences but also play a vital role in keeping you safe and healthy. So how exactly do the five sense organs work together to help you navigate and enjoy your environment? Let's take a closer look. What are the sense organs? The human body has five sense organs that allow us to perceive and interact with the environment. These include the eyes (sight), ears (hearing), nose (smell), tongue (taste), and skin (touch). Each of these organs plays a crucial role in gathering information and sending signals to the brain for processing. Sense organ functions vary based on the stimuli they detect. The eyes capture light and colour, helping us see. The ears process sound waves and maintain balance. The nose detects different odours, while the tongue identifies sweet, sour, salty, bitter, and umami tastes. The functions of the skin are to respond to temperature, pressure, and pain, allowing us to feel sensations. Together, these five types of sense organs help us navigate daily life and stay aware of our surroundings. Functions of the Five Sense Organs Now that we know what the main human sense organs are, let's explore in more detail how each one works to provide a specific sense. Sense organ functions are essential for perceiving the world, as each organ detects different types of stimuli and transmits signals to the brain. While they have distinct roles, the five sense organs often work together, sending integrated information to the brain to create a unified perceptual experience. This coordination allows us to respond effectively to our surroundings and enhances our ability to interact with the environment. Eyes: Sense of Sight Your eyes are your windows to the visual world. But have you ever wondered how they transform light into the colourful, detailed images you see? It all starts when light enters the eye through the clear, dome-shaped cornea. The light then passes through your pupil, the opening in the centre of the coloured iris, and is focused by the lens onto the retina at the back of the eye. The retina is lined with millions of light-sensitive cells called rods and cones. Rods enable you to see in dim light, while cones allow you to perceive colors and fine details. These photoreceptors convert the light into electrical signals, which then travel along the optic nerve to the visual cortex in the brain, where the image is processed and interpreted. Incredibly, the sense organs of sight—the eyes—are capable of distinguishing about 10 million different colours! However, many eye conditions can impair this vital sense, such as nearsightedness, farsightedness, and astigmatism. Regular eye check-ups can help detect and manage such issues early, preserving your precious gift of sight. Ears: Sense of Hearing From the chirping of birds to the laughter of loved ones, your ears open up the world of sound. But the process of hearing is a fascinating sequence of events. It begins when sound waves enter the ear canal and cause the eardrum to vibrate. These vibrations are then amplified by the three smallest bones in the body: the malleus (hammer), incus (anvil), and stapes (stirrup) in the middle ear. The stapes transfer the amplified vibrations to the cochlea, a fluid-filled, snail-shaped structure in the inner ear. Rippling through the cochlear fluid, the vibrations bend tiny hair cells, triggering electrical signals that travel via the auditory nerve to the brain. The brain then processes these signals, allowing you to perceive sounds and their direction, volume, and pitch. Remarkably, the sense organs responsible for hearing—the ears—can discern about 400,000 distinct sounds! However, exposure to loud noises, infections, aging, and certain medications can damage the delicate hair cells in the cochlea, leading to hearing loss. Nose: Sense of Smell From the aroma of freshly brewed coffee to the fragrance of blooming roses, your nose lets you experience the world of scents. Olfaction, or the sense of smell, begins when odour molecules enter the nostrils and dissolve in the mucus lining the roof of each nasal cavity. Embedded in this lining are millions of olfactory receptor cells, each with hair-like cilia that bind to specific odor molecules. This binding triggers receptor cells to send electrical impulses via the olfactory nerve to the olfactory bulbs, which relay the signals to the brain's olfactory cortex. The brain then identifies the smell by matching the pattern of activated receptors with previously learned odor patterns. Interestingly, your sense of smell is closely linked with your memory and emotions, which is why certain scents can vividly evoke past experiences and feelings. Did you know that the nose—one of the five sense organs—can detect over 1 trillion distinct smells? However, smoking, aging, head injuries, and certain illnesses like Parkinson's disease and Alzheimer's can impair this sensory superpower. Tongue: Sense of Taste The tantalising world of taste is brought to you by the thousands of taste buds dotting your tongue's surface. Each bud consists of 50–100 specialised gustatory receptor cells that detect the five basic tastes: sweet, salty, sour, bitter, and umami (savory). When food chemicals dissolve in saliva and interact with these receptors, electrical signals are generated and transmitted via facial nerves to the brain's gustatory cortex for identification. However, what you perceive as the "flavour" of food is actually a combination of tastes detected by your tongue and aromas detected by your nose. This is why your sense of taste may seem diminished when you have a stuffy nose. In fact, the tongue is much more limited in its taste perception compared to the nose's smell capacity, distinguishing only about 5–6 taste categories. Some factors that can affect your sense of taste include smoking, nutritional deficiencies, oral infections, and certain medications. If you experience persistent changes in how food tastes, consult your doctor to rule out any underlying issues. Skin: Sense of Touch As the body's largest sensory organ, your skin allows you to experience a wide range of tactile sensations, from the warmth of the sun to the softness of a fluffy blanket. Sense organ functions are vital for detecting and interpreting different stimuli, and the skin achieves this through a complex network of nerve endings and specialised receptors that detect touch, pressure, vibration, temperature, and pain. For example, Meissner's corpuscles respond to light touch, Pacinian corpuscles detect pressure and vibration, Merkel's discs perceive sustained pressure, and Ruffini endings sense skin stretching. When these receptors are stimulated, they send electrical signals through sensory nerves to the brain's somatosensory cortex, which processes the information and generates the appropriate touch perception. While incredibly sensitive, the skin's sensory acuity varies across different body parts. For instance, fingertips and lips are much more touch-sensitive than the back or legs, which is why using fingers to explore objects provides the most detailed tactile information. Other Sense Organs While we often focus on the traditional five senses, there are additional sensory systems that play crucial roles in our perception and interaction with the environment. Two of these lesser-known sense organs are the vestibular system, responsible for balance and coordination, and the proprioception system, which provides body awareness. The vestibular system, located in the inner ear, helps us maintain stability and spatial orientation. Proprioception, often called the "sixth sense," allows us to perceive the position and movement of our body parts without looking. These sense organs' functions are essential for smooth movement, posture control, and overall physical coordination. Vestibular System (Balance and Coordination) The vestibular system, located in the inner ear, is essential for maintaining balance and spatial orientation. It consists of the otolith organs (utricle and saccule) and the semicircular canals, which detect changes in head position and movement. When you tilt your head, spin around, or suddenly stop, the vestibular system helps you maintain equilibrium and prevents dizziness. It works closely with the visual and proprioceptive systems to ensure smooth movement and coordination. An interesting fact: The vestibular system is so sensitive that it can detect head movements as small as 0.004 degrees! This incredible precision allows us to stay steady while walking, running, or even standing still in a moving environment. Proprioception System (Body Awareness) Have you ever wondered how you can touch your nose with your eyes closed or walk without looking at your feet? This is thanks to the proprioception system, which allows us to sense the position and movement of our body parts without visual input. Proprioceptors, located in muscles, tendons, and joints, constantly send information to the brain about the relative positioning of our limbs. Proprioception enables us to perform complex tasks, like playing musical instruments or typing on a keyboard, with incredible precision and coordination. It's like having a sixth sense that keeps track of our body's movements and adjusts muscle tension and joint positions accordingly. How to Keep Sense Organs Healthy? Maintaining the health of our sense organs is crucial for ensuring optimal sensory function throughout our lives. Our eyes, ears, nose, skin, and tongue help us perceive the world, and taking proper care of them ensures their longevity and efficiency. Here are essential tips for keeping each of the five sense organs healthy: Eye Care Tips The eyes are one of the most vital sense organs, allowing us to see and interpret the world around us. Keeping them healthy ensures good vision and prevents eye-related diseases. Schedule Regular Eye Exams: Visit an eye specialist at least once a year to detect and address any vision problems early on. Early diagnosis of conditions like cataracts, glaucoma, and macular degeneration can prevent severe damage. Wear Protective Eyewear: Use safety goggles or protective glasses when working with chemicals, sharp objects, or engaging in sports to prevent injuries. Maintain a Nutritious Diet: Consume foods rich in vitamins A and C, as well as omega-3 fatty acids, to support eye health. Carrots, spinach, citrus fruits, and fish are excellent choices. Reduce Screen Time: Prolonged exposure to screens can cause eye strain and fatigue. Follow the 20-20-20 rule: Every 20 minutes, look at something 20 feet away for 20 seconds. Ear Care Tips Our ears help us hear and maintain balance. Taking care of them can prevent hearing loss and other ear-related problems. Protect Against Loud Noises: Avoid prolonged exposure to loud music or noise. Use earplugs or noise-canceling headphones in noisy environments. Avoid Inserting Objects in the Ear: Refrain from using cotton swabs or any sharp objects inside your ears, as they can damage the eardrum or push wax deeper. Get Regular Hearing Tests: Hearing tests can help detect early signs of hearing loss. Consult an audiologist if you experience ringing in the ears (tinnitus) or difficulty hearing. Limit Use of Earphones: Using earphones at high volumes can damage your hearing. Keep the volume at 60% or lower and take breaks. Nose and Smell Care Tips The nose plays a crucial role in breathing and detecting scents. Keeping it healthy ensures a strong sense of smell and clear nasal passages. Keep Nasal Passages Moisturised: Use saline sprays or a humidifier, especially in dry environments, to prevent nasal dryness. Avoid Strong Chemicals and Pollutants: Exposure to harsh chemicals, smoke, or strong odors can damage olfactory receptors. Wear a mask if necessary. Quit Smoking: Smoking can dull your sense of smell and lead to respiratory problems. Practice Good Hygiene: Regularly clean your hands and avoid touching your nose to prevent infections like colds and sinusitis. Skin Care Tips The skin is the largest sense organ and is responsible for touch, temperature detection, and protection from external elements. Use Sunscreen: Apply sunscreen with an adequate SPF to protect against harmful UV rays that can cause premature aging and skin cancer. Keep Skin Moisturised: Dry skin can become irritated and lose sensitivity. Use a good-quality moisturiser to keep your skin healthy and hydrated. Be Gentle When Cleansing: Avoid harsh soaps and scrubbing too hard, as this can damage the skin barrier and reduce tactile sensitivity. Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to maintain skin elasticity and overall health. Eat a Balanced Diet: Consume foods rich in vitamins E and C to promote healthy skin. Tongue and Taste Care Tips The tongue helps us taste and digest food. Keeping it clean and healthy ensures an optimal sense of taste and prevents infections. Maintain Good Oral Hygiene: Brush your teeth twice daily, floss regularly, and clean your tongue to prevent bacterial buildup. Stay Hydrated: A dry mouth can reduce your ability to taste. Drinking enough water keeps the tongue moist and functioning properly. Consume a Balanced Diet: Zinc, iron, and vitamin B12 are essential for maintaining taste bud health. Include nuts, lean meat, and dairy in your diet. Avoid Excessive Sugar and Spicy Foods: Too much sugar can cause oral infections, while very spicy foods can irritate taste buds. Avoid Smoking and Alcohol: These substances can dull your sense of taste over time. Frequently Asked Questions What is the function of sense organs? Sense organs are specialised structures that allow us to perceive and interact with the world around us. They gather information about our environment, such as sights, sounds, smells, tastes, and tactile sensations, and transmit this information to the brain for interpretation. Sense organs functions are essential for our survival, safety, and enjoyment of life. Which is the largest sense organ? The skin is the largest sense organ in the human body. It is responsible for the sense of touch, allowing us to perceive temperature, pressure, pain, and texture. The skin covers an impressive surface area of approximately 2 square meters in adults, making it the most extensive of the five sense organs. Can a person have no sense of touch? While extremely rare, there are conditions that can impair or eliminate a person's sense of touch. For example, individuals with certain neurological disorders or nerve damage may experience reduced or absent tactile sensation. However, a complete lack of touch sensation is highly uncommon and would significantly impact an individual's ability to interact with their environment safely. What are olfactory organs? Olfactory organs refer to the structures in the nose responsible for the sense of smell. The primary olfactory organ is the olfactory epithelium, which contains millions of olfactory receptors. These receptors detect odor molecules in the air and send signals to the brain, allowing us to perceive and distinguish between different scents. Which part of the human ear maintains body balance? The vestibular apparatus, located in the inner ear, is responsible for maintaining body balance and spatial orientation. It consists of the otolith organs (utricle and saccule) and the semicircular canals, which detect changes in head position and movement. The vestibular system works in conjunction with other sense organs, such as the eyes and proprioceptors, to keep us balanced and coordinated. Conclusion The five sense organs - eyes, ears, nose, tongue, and skin - along with the vestibular and proprioception systems, form an incredible network that allows us to perceive, interact with, and enjoy the world around us. By understanding how these sense organs work together and taking steps to maintain their health, we can ensure a more complete and fulfilling sensory experience throughout our lives. At Metropolis Healthcare, we understand the importance of maintaining healthy sense organs. Our team of expert pathologists and technicians provide accurate and reliable diagnostic services, including tests related to sensory health. With our convenient at-home sample collection and user-friendly online reporting system, prioritising your well-being has never been easier.
Erythema Toxicum Neonatorum: Should Parents Be Concerned?
What is erythema toxicum neonatorum? Erythema toxicum neonatorum (ETN) is a common, benign, and self-limiting skin condition that affects newborns, typically within the first few days of life. It presents as red blotchy patches, often accompanied by small papules or pustules, which may resemble an allergic reaction. Despite its name, ETN is not caused by toxins, infections, or any harmful substances. This condition is temporary and harmless, resolving on its own within a few days to a couple of weeks without requiring treatment. ETN does not cause discomfort to the baby, and affected infants continue to feed, sleep, and behave normally. Understanding ETN can help parents avoid unnecessary worry when they notice these skin changes in their newborn. Who might get erythema toxicum neonatorum? Erythema toxicum neonatorum (ETN) is a common skin condition that can affect any newborn, but certain factors may increase the likelihood of its occurrence. Erythema toxicum neonatorum causes are not fully understood, but some patterns have been observed. Full-term infants are more likely to develop ETN than premature babies. Studies suggest that 70-80% of full-term infants experience ETN, while only 5-25% of preterm babies are affected. The reason for this difference is not entirely clear but may be linked to immune system maturity. Infants with higher birth weights also have a slightly increased risk of ETN compared to those with lower birth weights. Additionally, vaginally delivered babies are more prone to ETN than those born via C-section, possibly due to exposure to maternal bacteria during birth. Some research suggests that male infants develop ETN more frequently than females, though the exact erythema toxicum neonatorum causes behind this trend remain unknown. Despite these patterns, ETN is a random and harmless condition that can appear in any newborn, regardless of sex, birth weight, or delivery method. Parents should remember that ETN is temporary, painless, and does not indicate any underlying health issues. Where does the name ‘erythema toxicum neonatorum’ come from? The term erythema toxicum neonatorum originates from medical terminology that describes the characteristics of the condition: "Erythema" refers to redness of the skin. "Toxicum" suggests a reaction, but ETN is not caused by toxins or infections. The term may have been historically used because the rash resembles toxic or allergic reactions. "Neonatorum" means that the condition occurs in newborn babies. Though the name may sound concerning, ETN is completely harmless and requires no medical intervention. How common is erythema toxicum neonatorum? Erythema toxicum neonatorum (ETN) is one of the most common skin conditions in healthy newborns. Studies suggest that it affects 40–70% of all newborns, with a higher prevalence in full-term infants (70–80%) compared to premature babies (5-25%). While the exact reason for this variation is unclear, gestational age appears to play a role in ETN occurrence. Despite its alarming appearance, ETN is a harmless and temporary condition, making it a normal part of newborn development. What causes erythema toxicum neonatorum? Exact erythema toxicum neonatorum causes are unknown, but researchers have proposed several theories: Immune System Development: Some studies suggest that ETN is an inflammatory response triggered by the baby’s immune system adapting to life outside the womb. The activation of certain immune cells in the skin may contribute to the rash. Bacterial Exposure: Another theory is that ETN results from the baby’s first exposure to bacteria entering the hair follicles after birth. This reaction may be part of the natural process of skin adaptation. Hormonal Changes: The withdrawal of maternal hormones after birth may also play a role in the development of ETN. Newborns undergo hormonal adjustments in the first few days of life, which might contribute to temporary skin changes. Despite these theories, no specific external factor has been definitively linked to causing ETN. What are the symptoms of erythema toxicum neonatorum? Erythema toxicum neonatorum symptoms typically include red patches or blotches on the skin, often accompanied by small papules or pustules that appear yellowish-white and are surrounded by a red halo. The rash commonly affects the face, chest, arms, and legs, and in some cases, it may also appear on the palms and soles. One of the key characteristics of erythema toxicum neonatorum symptoms is that the lesions can appear and disappear within hours or days. Some bumps may resemble tiny fluid-filled blisters, but they do not cause pain or discomfort. Importantly, ETN does not lead to fever, itching, or irritability, and babies with this condition continue to feed, sleep, and behave normally. Although the rash may look concerning, it is entirely harmless and temporary. How is erythema toxicum neonatorum diagnosed? ETN is easily diagnosed by a visual examination by a healthcare provider. The characteristic rash, combined with the baby’s age and overall health, is usually enough to confirm the diagnosis. In rare cases, if there is any doubt, a doctor may: Take a small sample from a pustule to examine under a microscope. Rule out other skin conditions, such as neonatal acne, milia, or infections. However, additional tests are usually unnecessary unless symptoms are unusual or persistent. Your pediatrician may also observe your baby for a few days to determine erythema toxicum neonatorum vs. neonatal acne symptoms. How is erythema toxicum neonatorum treated? Erythema toxicum neonatorum treatment is not required, as the condition resolves naturally within a few days to two weeks. Parents can maintain a gentle skincare routine by keeping the baby’s skin clean and dry, using mild, fragrance-free cleansers during baths, and avoiding harsh or irritating skincare products. Since ETN is harmless and does not cause discomfort, medications or special creams are unnecessary. The rash will fade on its own without leaving any marks or long-term effects, allowing parents to focus on their baby’s overall well-being. How can we prevent erythema toxicum neonatorum? Currently, there are no known methods to prevent erythema toxicum neonatorum from occurring, as the exact causes are still not fully understood. ETN is considered a normal and harmless part of a newborn's development, and it does not reflect any underlying health issues or require any specific preventive measures. What can we expect if our baby has erythema toxicum neonatorum? If your newborn develops erythema toxicum neonatorum, you can expect: The rash to appear within the first few days of life, often on the second or third day The lesions to come and go, sometimes appearing in crops over several days No pain, itching, or discomfort for your baby Complete resolution of the rash within 1-2 weeks without any treatment No long-term effects on your baby's skin or overall health As a parent, it's understandable to feel worried when you see any rash on your newborn's delicate skin. However, rest assured that ETN is a common and benign condition that will clear up on its own without causing any harm to your baby. Does erythema toxicum neonatorum return after treatment? Since erythema toxicum neonatorum does not require any treatment and resolves spontaneously, it typically does not recur after the initial episode. In rare cases, new crops of lesions may appear in different areas during the first week or two, but they will also clear up on their own. Once the rash has completely disappeared, it is unlikely to come back. When to see a doctor? While erythema toxicum neonatorum is a harmless condition, it's always a good idea to bring any skin changes to your pediatrician's attention. You should consult your baby's doctor if: You are unsure about the diagnosis or concerned about the appearance of the rash The rash persists beyond 2 weeks or seems to be getting worse Your baby develops a fever, appears irritable, or shows signs of illness You notice any signs of skin infection, such as pus, increasing redness, or swelling Conclusion As a new parent, seeing a rash on your baby’s skin can be alarming, but understanding ETN can help ease concerns. Since no specific erythema toxicum neonatorum treatment is needed, parents can focus on gentle skincare and monitoring. If you have any doubts or questions about erythema toxicum in newborn babies or overall health, don't hesitate to consult your pediatrician or a trusted healthcare provider. At Metropolis Healthcare, we understand the importance of your baby's well-being and are committed to providing reliable diagnostic services to support your family's health journey.
Adjustment Disorder
What is an adjustment disorder? An adjustment disorder is an unhealthy emotional or behavioural response to a stressful event or major life change. It occurs when the reaction is out of proportion to the stressor’s severity but not as extreme as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Adjustment disorders in adults and children typically develop within three months of the triggering event, affecting daily functioning at home, work, school, or in social situations. While it's natural for children to experience some distress when faced with difficult situations, an adjustment disorder is characterised by symptoms that are disproportionate to the triggering event and cause significant impairment in social, academic, or other areas of functioning. What are the types of adjustment disorders? There are six main types of adjustment disorders, each presenting with distinct symptoms: Adjustment Disorder with Depressed Mood: Individuals experience persistent sadness, tearfulness, and feelings of hopelessness. Adjustment Disorder with Anxiety: Symptoms include excessive worry, nervousness, jitteriness, and, in children, fear of separation from major attachment figures. Adjustment Disorder with Mixed Anxiety and Depressed Mood: A combination of anxiety and depressive symptoms, such as excessive worry and persistent sadness. Adjustment Disorder with Disturbance of Conduct: Marked by significant behavioural problems, including violating societal norms, engaging in destructive behaviour, truancy, or aggression. Adjustment Disorder with Mixed Disturbance of Emotions and Conduct: Individuals exhibit both emotional symptoms (such as sadness and anxiety) and behavioural issues (such as defiance or aggression). Unspecified Adjustment Disorder: Characterised by maladaptive reactions that do not fit within the other categories, such as social withdrawal, avoidance, or emotional inhibition. These types of adjustment disorders help clinicians tailor treatment approaches based on specific symptom patterns. While adjustment disorders can be distressing, they are typically short-term and manageable with therapy, coping strategies, and social support. Early intervention is key to preventing long-term emotional or behavioural difficulties. How common are adjustment disorders? While specific prevalence rates for children are less documented, adjustment disorders are relatively common reactions to stressors. A study conducted in a community sample of children aged 9-16 years found that 3.7% met the criteria for an adjustment disorder. However, the occurrence can vary widely based on individual circumstances and the nature of the stressor. Also, since symptoms of adjustment disorders often overlap with other conditions, adjustment disorders may be underdiagnosed or misdiagnosed in clinical settings. What are the symptoms of adjustment disorders? Symptoms of adjustment disorders vary by subtype but generally include emotional, behavioural, and physical signs. Common symptoms include: Persistent sadness, hopelessness, or loss of interest in usual activities Excessive crying spells and emotional distress Nervousness, excessive worry, or separation anxiety Difficulty sleeping or frequent nightmares Trouble concentrating or making decisions Social withdrawal from friends, family, or activities Avoidance of school, work, or other responsibilities Increased irritability, frustration, or angry outbursts Defiant, reckless, or impulsive behaviors, such as fighting or property destruction These symptoms significantly impact daily life but are typically temporary. With proper support, therapy, and coping strategies, individuals can manage and overcome adjustment disorders effectively. What causes adjustment disorders? Adjustment disorders causes can primarily be attributed to significant stressors that feel overwhelming and difficult to manage. These can be single events or a series of accumulated stressors. Common triggers include: Divorce or separation of parents Loss of a loved one, such as a family member or pet Moving to a new home, school, or unfamiliar environment Chronic illness or disability, either personally or within the family Family conflicts or domestic violence, creating emotional distress Bullying or social rejection, leading to feelings of isolation Academic struggles or school-related pressure, impacting self-esteem Traumatic experiences, including abuse, accidents, or natural disasters Each child perceives and responds to stress differently. Their temperament, coping skills, and support system influence how they process challenging events. Early recognition and intervention, such as counseling and emotional support, can help children develop healthy coping mechanisms and resilience. What are the triggers for adjustment disorders? Adjustment disorder causes stem from significant life changes or stressful events, particularly when a child perceives them as overwhelming or faces multiple stressors simultaneously. Common triggers include: Divorce or parental separation, disrupting family stability Loss of a loved one or pet, leading to grief and emotional distress Moving homes or changing schools, causing feelings of uncertainty Breaking up with a close friend or romantic partner, impacting emotional well-being Major disappointments, such as failing to make a sports team or achieve a goal Serious illness or accident in the family, creating stress and anxiety Children’s responses vary based on their coping skills, resilience, and support system. Early intervention helps manage symptoms effectively. What are the risk factors for adjustment disorders? While any child can develop an adjustment disorder, certain factors may increase the risk: Exposure to frequent or severe stressors Lack of social support or close relationships Pre-existing mental health conditions like anxiety or depression Family history of mental health disorders Poor coping skills or problem-solving abilities Identifying and addressing these risk factors early on can help prevent or mitigate the impact of adjustment disorders. What are the complications of adjustment disorders? If left untreated, adjustment disorders can lead to more serious mental health issues over time. Potential complications include: Development of chronic depression or anxiety disorders Substance abuse or addiction Self-harm or suicidal thoughts or behaviours Academic failure or school dropout Social isolation and relationship problems Seeking prompt professional treatment can help prevent these negative outcomes and promote healthy adjustment. How are adjustment disorders diagnosed? Adjustment disorders are diagnosed through a comprehensive clinical evaluation by a mental health professional, such as a child psychologist or psychiatrist. The diagnosis is based on identifying an emotional or behavioural response to a clear stressor, which significantly affects daily life. Key diagnostic features include: Symptoms emerging within three months of an identifiable stressor Marked distress or significant impairment in social, academic, or family functioning Reactions that are out of proportion to the severity or nature of the stressor Symptoms not better explained by another mental health disorder To diagnose adjustment disorders, clinicians use interviews, psychological assessments, and reports from parents, teachers, or caregivers to understand the child’s emotional state and coping abilities. The diagnostic process also involves ruling out other conditions such as depression, anxiety disorders, or post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Early diagnosis is crucial because delayed adjustment disorders treatment may lead to more serious mental health issues. With proper support, including therapy and coping strategies, children can learn to manage stress and build resilience. Adjustment Disorders DSM-5 Criteria The DSM-5 (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition) provides specific criteria to diagnose adjustment disorders: The development of emotional or behavioural symptoms in response to an identifiable stressor, occurring within three months of its onset. The symptoms must be clinically significant, demonstrated by one or both of the following: Marked distress that is out of proportion to the stressor’s severity or intensity, considering cultural and contextual factors. Significant impairment in social, academic, occupational, or other important areas of daily functioning. The disturbance does not meet the criteria for another mental disorder and is not just an exacerbation of a pre-existing condition. The symptoms are not part of normal bereavement following a loss. Once the stressor has ended, symptoms do not persist beyond six months after its resolution. Clinicians use these criteria to ensure the diagnosis is accurate and not confused with other mental health conditions like depression or generalized anxiety disorder. Additionally, adjustment disorders may be categorised into subtypes, such as those with depressed mood, anxiety, mixed emotions, or behavioural disturbances. The specific subtype helps guide treatment approaches. Mental health professionals often assess the severity and duration of symptoms to determine the best course of action. Therapy, counseling, and support systems play a crucial role in helping individuals recover. Cognitive-behavioural therapy (CBT) is often effective in teaching coping skills, stress management, and emotional regulation. Since adjustment disorders are temporary, most individuals improve with the right intervention and support. However, without adjustment disorders treatment, symptoms may persist, leading to further emotional difficulties. Seeking help early can prevent long-term challenges and promote overall well-being. How are adjustment disorders treated? Adjustment disorders treatment typically involves a combination of psychotherapy and supportive interventions. The primary treatment modalities include: Cognitive-behavioural therapy (CBT): Helps the child identify and change negative thought patterns and develop coping skills. Family therapy: Addresses family dynamics and communication patterns that may be contributing to or maintaining the child's distress. Supportive therapy: Provides a safe space for the child to process emotions and experiences related to the stressor. School-based interventions: May include accommodations, counselling, or support groups to help the child succeed academically and socially. Medication: In some cases, short-term use of medications like antidepressants or anti-anxiety drugs may be recommended to alleviate severe symptoms. Treatment plans are tailored to the individual child's needs and may involve a multidisciplinary team of mental health professionals, educators, and family members. What medications treat adjustment disorders? In most cases, psychotherapy is the first-line treatment for adjustment disorders in children. However, if symptoms are severe or not improving with counselling, medications may be prescribed on a short-term basis: Anti-anxiety medications like benzodiazepines may help alleviate acute anxiety symptoms. Antidepressants like SSRIs may be used to treat persistent depressive or anxiety symptoms. Medications should always be taken under the supervision of a qualified psychiatrist or physician. How soon after treatment will we feel better? The timeline for improvement after starting adjustment disorders treatment varies from child to child. Some factors that can influence progress include severity and duration of symptoms, type and intensity of treatment, and the child's engagement and response to therapy. In general, most children start to show improvement within a few weeks to a few months of starting treatment. However, it's important to continue treatment even after symptoms subside to prevent relapse and promote long-term coping skills. Can adjustment disorders be prevented? While it may not be possible to prevent all cases of adjustment disorders, parents can take proactive steps to build resilience and help their children manage stress more effectively. Creating a supportive home environment plays a crucial role in how children respond to life’s challenges. Encouraging open communication and emotional expression allows children to feel heard and understood. Teaching healthy coping skills and problem-solving strategies helps them navigate difficulties with confidence. Strong social connections, including friendships and supportive family relationships, provide a crucial buffer against stress. Parents can also model adaptive responses to change, showing children how to handle transitions and setbacks in a positive way. If signs of distress emerge, seeking professional help early can prevent symptoms from worsening. What can we expect if we have an adjustment disorder? If your child is diagnosed with an adjustment disorder, treatment will focus on emotional support, coping strategies, and gradual recovery. The first step is a comprehensive evaluation, where a mental health professional will assess your child’s symptoms and create an individualized treatment plan tailored to their needs. Therapy plays a key role in recovery. Regular sessions with a therapist will help your child process emotions, manage stress, and develop effective coping skills. In some cases, professionals may collaborate with teachers and school personnel to ensure academic and social support. For children experiencing severe distress, short-term medication may be considered to manage symptoms. Over time, with consistent treatment, you can expect gradual improvements in mood, behaviour, and daily functioning. Recovery is a process, and setbacks are normal. However, with ongoing monitoring, follow-ups, and a strong support system, most children can achieve remission and build lifelong resilience. How long does an adjustment disorder last? By definition, symptoms of an adjustment disorder arise within 3 months of the stressor and do not last longer than 6 months after the stressor has ended. If symptoms persist beyond this timeline, it's possible that the child has developed another mental health condition like major depression or an anxiety disorder, which may require additional treatment. When to see a doctor? It's important to seek professional help for your child if: Their emotional or behavioural symptoms are severe and interfering with daily life. Symptoms are not improving a few weeks after the stressful event has ended. Your child is showing signs of suicidal thoughts or self-harming behaviours. You are concerned about your child's mental health for any reason. A good place to start is with your child's paediatrician, who can assess symptoms, provide guidance, and refer to a child mental health specialist if needed. Adjustment disorder vs. PTSD: What's the difference? While adjustment disorders and PTSD both involve emotional and behavioural symptoms following a stressful event, there are some key differences: PTSD is triggered by exposure to actual or threatened death, serious injury, or sexual violence. Adjustment disorders can be triggered by a wider range of stressful events. Symptoms of PTSD are more severe and include re-experiencing the trauma, avoidance of trauma-related reminders, negative changes in thinking and mood, and increased arousal and reactivity. PTSD can arise more than 3 months after the trauma and often lasts longer than 6 months. Adjustment disorders have a more limited timeline. Conclusion Facing new challenges is a natural part of life, but for some children, the emotional toll can lead to such disorders. In fact, adjustment disorder in adults can also be challenging, highlighting the importance of mental health awareness at every stage of life. If you are concerned about your child or loved one's mental health, don't hesitate to reach out to your doctor or a psychologist for guidance. And if you need a stress-free way to check on your child's physical health, consider Metropolis Healthcare's at-home diagnostic and health check-up services.









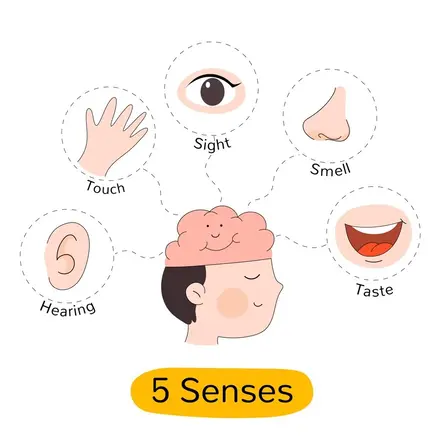







 WhatsApp
WhatsApp