Latest Blogs
Best Foods to Boost Your Immunity During Monsoon
Introduction Since monsoon showers hydrates the dried earth, it brings along a feeling of refreshment and joy. However, we cannot miss the fact that our immune system also receives a hit during this season. With infections and illnesses becoming more common, the need for a strong immune system is increasing, but how can you boost your body's natural defence mechanisms? The secret lies in healthy food to eat in rainy season. This blog post aims to provide you with a comprehensive rainy season food list and guide you on the foods that can boost your immunity during the monsoon. Let’s dive in! Turmeric Turmeric often tops the list of foods that boost the immune system, especially during the monsoon season. This golden spice is rich source of curcumin, which has powerful anti-inflammatory properties. Including turmeric intake in your monsoon food diet can help you to fight off infections and illnesses which are common during this season. You can add a pinch of turmeric to your meals or enjoy a warm glass of turmeric milk before bed. Probiotics and Fermented Food Probiotics play an essential role in maintaining a good gut health, directly linked to strong immunity. Fermented foods like yogurt are rich in probiotics and are considered as an excellent rainy season healthy food. You can also consume pickles and sourdough bread as they are fermented and promote good gut bacteria growth. Soups and Stews There is nothing more comforting than a hot bowl of soup or stew on a cold, rainy day. Soups and stews made from fresh vegetables such as carrots, beans and tomatoes are not only delicious but are also rich in essential vitamins and minerals. They support a healthy immune system, making them a excellent rainy season foods to boost immunity. Lemon Lemons are a powerhouse of Vitamin C - a vital nutrient that enhances the body's ability to fight off infections. Whether squeezed over salads or added to warm water, lemons can easily be included in your rainy season food list for an immunity boost. Masala Chai Masala Chai is a popular monsoon food in India. Spices used in Masala Chai, such as ginger, cardamom and cinnamon, contains immune-boosting properties. Enjoying a cup of hot masala chai on a rainy day not only improves your mood but also strengthens your immune system. Garlic Garlic is known for it's medicinal properties. It contains allicin, which increases the disease-fighting response of some types of white blood cells in the body when they encounter viruses. Including garlic in your diet, is an effective way to increase immunity during monsoon. Ginger The warming effect of ginger makes it perfect for consumption during monsoons. It has anti-inflammatory properties that help relieve sore throats and fight flu symptoms. Add ginger to your tea or meals for extra strength and protection against monsoon ailments. Nuts and Dry Fruits Nuts and dry fruits such as almonds and walnuts are rich in essential vitamins and fatty acids that strengthen our immune system. Include them in your rainy season food list for a power-packed immunity boost. Bitter Gourd Bitter gourd may not be everyone's favourite vegetable due to its bitter taste, but it is very beneficial during monsoons. Being a rich source of vitamins, it helps boost immunity and is a must during monsoon. Foods to Avoid During the Monsoon During the monsoon season, it is crucial to be mindful of the foods you consume to avoid health issues. Here are some foods to avoid: Leafy Vegetables: Exposed to dirt and bacteria because of high moisture, which can lead to possible stomach infections Seafood: More vulnerable to contamination during their breeding season, increase the risk of food poisoning Fried and Oily Foods: Difficulty in digesting due the humid weather, can cause indigestion and bloating Street Food: Often lacks proper hygiene, posing a risk of water-borne diseases like typhoid and diarrhoea Pre-cut Fruits and Salads: Possibility of easy contamination with bacteria, it is safer to consume freshly cut versions at home Dairy Products: Due to humid conditions these products can spoil quickly, can lead to stomach infections if consumed when spoiled Raw food: Can contain bacteria and pathogens, so thorough cooking is essential Mushrooms: Can create a breeding ground for harmful bacteria that can cause allergic reactions or food poisoning Spicy Food: Increases body heat and digestive problems, it is better to choose mild spices Sour Food: Causes water retention and bloating, which can aggravate conditions like arthritis and joint pain Conclusion Maintaining a strong immune system is crucial, especially during the monsoon season when our bodies are more vulnerable to infections. By incorporating healthy food to eat in rainy season, you can better equip your body to fight off diseases. However, if you notice persistent symptoms or prolonged fever, it may indicate a possibility of infection. In such cases, you must consult a healthcare professional immediately. At Metropolis Labs, we are dedicated to helping you stay in the best of health with our comprehensive health check-up services. Our expert technicians provide at-home blood sample collection for your convenience. All samples are processed at our advanced diagnostic labs, ensuring accurate results every time. At Metropolis Healthcare, we believe that prioritising your health is within reach with the right knowledge and medical care. Browse through our website for more information or book an at-home sample collection today!
Essential Monsoon Safety Tips for Families
Introduction As the much-awaited monsoon showers grace India, they brought not only relief from the summer heat but also potential health challenges, making it essential for us to follow certain monsoon safety precautions. Rainy weather, waterlogging and high humidity create favourable conditions for the outbreak of several diseases such as dengue, malaria and typhoid fever and others. Therefore, it is important to understand and implement these safety precautions during the rainy season to protect the health of your loved ones during the rainy season. In this article, we explore various monsoon safety tips for the monsoon season, including diet, personal hygiene, home safety and much more. By following these guidelines, you can ensure that your family enjoys the monsoons while staying fit and healthy. Take Care Of Your Skin During the monsoon season, it is important to follow a proper skin care routine as part of monsoon safety precautions. Humid weather can lead to skin infections. It is therefore essential to use an antibacterial soap, keep your skin dry and moisturize it regularly. These safety precautions during the rainy season can help you to prevent fungal infections, maintain healthy skin for your entire family. Avoid Getting Close To Sick People Monsoon often brings a spike in infectious diseases such as flu and colds. One of the critical monsoon safety tips is to avoid close contact with sick people. This precaution helps reduce the risk of infection and ensures that your family stays healthy and less susceptible to seasonal diseases during the rainy season. Keep Mosquitoes Away Keeping mosquitoes at bay is a crucial aspect of monsoon safety precautions. The rainy season provides an ideal breeding ground for mosquitoes, which can transmit diseases like dengue and malaria. Implementing monsoon safety tips such as using mosquito repellent, installing mosquito nets on windows and eliminating stagnant water can help protect your family from these health risks. Consume Healthy Foods Only Consuming healthy foods during the rainy season is among the most essential monsoon safety tips. The humidity in the weather can increase the risk of foodborne illnesses, making it crucial to prioritise food safety. Eating freshly cooked meals, avoiding street food, and drinking purified water are the key steps to prevent gastrointestinal infections. Incorporating immune-boosting foods like fruits, vegetables, and probiotics can further protect your family’s health. By following these dietary safety precautions during the rainy season, you can ensure that your family stays healthy and resists the common diseases of the season. Get The Right Kind Of Family Health Insurance Securing a comprehensive health insurance for your family is a wise monsoon safety precaution. The rainy season often brings a higher risk of medical emergencies. Having the right kind of insurance coverage ensures that your family is financially protected and can promptly access the necessary medical care, providing peace of mind during this unpredictable time. Drive Slowly And Carefully Driving slowly and carefully is one of the essential monsoon safety tips. During the rainy season, the roads are usually slippery and visibility is poor, which increases the risk of accidents. By following this safety precaution during the rainy season, you can ensure that your family stays safe while traveling, reducing the chance of accidents on wet and waterlogged roads. Don’t Touch Electrical Wires Avoiding contact with electrical wires is a basic monsoon safety precaution. Exposed or fallen wires can be extremely hazardous during the rainy season. Educating your family, especially little children, about the dangers and ensuring they stay away from electrical wires can help prevent electrocution accidents, keeping everyone safe from electrical hazards. Unplug Electronic Appliances Unplugging electronic appliances during the rainy season is a crucial monsoon safety precaution. The rainy season often brings thunderstorms and heavy rainfall, which can lead to power surges and electrical hazards. By unplugging appliances when not in use, you can protect them from potential damage caused by the voltage spikes and reduce the risk of fire hazards. This is a simple yet an effective practice to ensures your family's safety and helps in maintaining the longevity of your electronic devices, providing peace of mind during the unpredictable weather of the monsoon. Make Sure Your Windows Are Shut Properly Ensuring your windows are shut properly is a necessary monsoon safety precaution. Properly closed windows prevents the rainwater from entering your home, protecting your belongings and reducing the risk of water damage. This is a simple but an effective safety precaution during the rainy season which can help in maintaining a dry and safe internal environment for the family. Keep An Umbrella And Raincoat Handy Keeping umbrellas and raincoats handy is one of the most practical monsoon safety tips. The characteristic of the rainy season is sudden downpours and having these items readily available, can ensure that your family is dry and avoids diseases caused by soaked. This preparation is essential to maintain good health during monsoons. Prepare An Emergency Kit Preparing an emergency kit is a vital monsoon safety precaution for families. This kit should include essential items such as first aid supplies, necessary medications, flashlights, batteries, and non-perishable food. Additionally, consider including important documents in waterproof bags, portable phone chargers, and basic tools. Being equipped with an emergency kit ensures that your family is prepared for unexpected situations during the rainy season, such as power interrupt or being stranded due to flooding. This preparation enhances your family's safety and provides peace of mind amidst the unpredictability of the monsoon. Conclusion As a proverb says, "Prevention is better than cure." Implementing these monsoon safety precautions is crucial for the health and well-being of your family. For further peace of mind, consider regular health check-ups from trusted providers like Metropolis Labs. With their home sample collection service and accurate diagnostic tests, prioritising your family's health during the monsoon season becomes a breeze. Remember, a little caution can go a long way in ensuring an enjoyable and healthy monsoon for your family.
Top Health Tips for a Healthy Monsoon
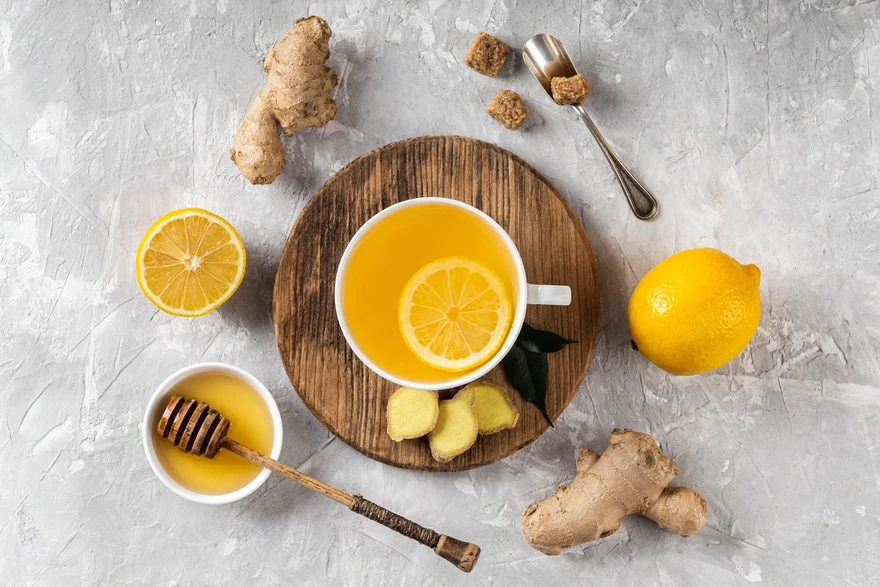
Introduction Apart from the cooling relief, monsoon also brings a wave of health concerns. While the smell of fresh soil after the rains is soothing, it is also the season when humidity increases and waterborne diseases also appear. So how can you stay healthy while enjoying this beautiful season? The answer lies in these health tips for monsoon season. This comprehensive guide will provide you with various monsoon health tips that will help you to enjoy the season without compromising your health. We will look at the dietary changes, lifestyle modifications, and preventive strategies that will help you safeguard your health during the monsoon season. Our aim is to provide you with monsoon safety tips to help you make informed decisions regarding your health. Drink Clean and Boiled Water During monsoons, water resources are at a higher risk of getting contaminated, resulting in an increase in the danger of waterborne diseases. One of the most important health tips for rainy season is to ensure that you drink clean water. Choose only filtered or boiled water always, as heat kills most bacteria, viruses and parasites. When traveling, carry your own water bottle or drink sealed and packaged water. Increase Your Vitamin C Intake Boosting immunity is one of the essential monsoon health tips. Consuming Vitamin C-rich fruits such as oranges and lemons can fortify your immune system, helping it combat infections more effectively. Example: Mrs Sharma makes sure to include a bowl of mixed fruit salad in her family's breakfast during monsoon. The salad contains a mix of papaya, oranges, pineapple, and kiwi - all rich in Vitamin C. This simple step helps her family enhance their immunity. Increase Probiotic Intake A good gut health plays a crucial role in maintaining overall well-being. And consuming probiotics such as yogurt can help in maintaining a healthy balance of good bacteria in your gut. A healthy gut goes a long way in strengthening your immune system, which is especially important during the monsoon season. Include Herbal Teas Herbal teas not only help soothe the throat but also boost immunity and aid digestion. Ginger Tea, Tulsi Tea, or Masala Chai are excellent choices during monsoons. They are packed with antioxidants that fortify your body's defence mechanism. Did you know? Studies suggest that by consuming green tea regularly can improve cardiovascular health and lower the risk of infections. Have Bitter Foods Incorporating bitter foods like bitter gourd, neem, and fenugreek in your diet can not only enhance digestion but can also boost immunity during the rainy season. These foods have natural antimicrobial properties which helps in cleansing the body and ward off infections. Including them in your meals can aid in maintaining good health and preventing common seasonal ailments. Avoid Junk Food One of the essential safety precautions during the rainy season is to avoid street food. Consuming junk food can lead to stomach upset due to potential contamination of the water or raw materials used. Stay Away from Spicy Food Spicy food tends to stimulate the secretion of acid in the stomach leading to digestive issues. During the monsoon season, it is better to reduce your very spicy foods intake as your digestion can be a bit compromised. This is one of the most essential health tips for monsoon season. Destroy Breeding Grounds for Mosquitoes Stagnant water serves as a perfect breeding ground for mosquitoes, which could result into the spread of diseases like dengue and malaria. Make sure you do not have any stagnant water around your house. Use insect repellents and mosquito nets for added protection. Avoid Walking in Dirty Water Walking in dirty water during monsoon season can expose you to various infections, so if it is unavoidable, make sure you wash your feet with clean water and apply antiseptic. Add a Disinfectant to the Bathwater During the rainy season, increased humidity and stagnant water can become a breeding ground for bacteria and fungi. To reduce the risk of infection and maintain good hygiene, it is recommended to add a disinfectant, such as a few drops of antiseptic liquid to the bath water. This can help to kill the microorganisms on the skin, keep you healthier and preventing common rainy season ailments like fungal infections. Iron Those Damp Clothes During the rainy season, clothes often do not dry completely due to high humidity, which leads to moisture that promotes mould growth and unpleasant odour. Ironing clothes not only helps prevent wrinkles, but also ensures that they are completely dry and moisture-free. Iron heat can also kill the remaining bacteria or mould spores. Dry Clothes and Shoes Properly After washing, hang the clothes to dry in a well-ventilated place or, if possible, use a dryer. Remove the insoles from your shoes and fill them with newspaper to absorb moisture. Then store them in a dry and ventilated place. Avoid wearing damp clothes and shoes as they can contain bacteria and mould and cause health problems. Wash Your Hands Maintaining hand hygiene is one of the most essential health tips for monsoon season, as this practice alone prevents most monsoon diseases. Make sure to scrub your hands with soap for at least 20 seconds and rinse thoroughly. Hand sanitisers with at least 60 percent alcohol can be a handy alternative when soap is not available. Get Enough Sleep Adequate sleep is vital during the rainy season to boost your immune system and help your body to fight off infections. Aim for 7-9 hours of restful sleep each night to stay healthy and maintain your energy levels. A good sleep can also improve your mood and overall well-being, making it easier to cope with the challenges that come along with the damp, cooler weather. Exercise Regularly Regular physical activity boosts the immune system and keeps you in good shape; but do remember to maintain good hygiene while working out, especially if you are using shared equipment in fitness centres. Conclusion As we embrace the monsoon season's refreshing drizzle, let's also equip ourselves with these health tips for a rainy season for enjoying an illness-free monsoon. Remember, prevention is always better than cure. From maintaining hand hygiene, consuming a balanced diet enriched with vitamins and probiotics, ensuring clean drinking water to regular exercise – every little effort counts towards safeguarding our health during this season. At Metropolis Labs, we believe that informed healthcare decisions are pivotal to achieving optimal health. Our advanced diagnostic labs and qualified technicians ensure timely and accurate pathology testing services. Furthermore, with our at-home blood sample collection service, you can now prioritise your health without compromising on comfort or safety. In conclusion, stay informed, stay protected, and enjoy the monsoon season with robust health and vitality. Your health is a priority, not an option - let's ensure it receives the attention it deserves!
Common Monsoon Illnesses and How to Prevent Them
Introduction The monsoon season brings much-needed relief from the summer heat, but it also brings its own set of health challenges. Increased humidity and stagnant water provide a perfect breeding ground for various pathogens, leading to an increase in monsoon diseases. In order to maintain good health at this time, it is important to understand these rainy season diseases and know how to prevent them for maintaining good health during this time. List Of Monsoon Diseases Dengue Dengue is a viral disease transmitted by the Aedes mosquito, which breeds in stagnant water. Dengue symptoms include high fever, severe headache, pain behind the eyes, joint and muscle pain, rash, and bleeding. Chikungunya Chikungunya is another viral disease transmitted by mosquitoes, which is characterized by high fever, severe joint pain, muscle pain, headache, fatigue and rash. The joint pain can be debilitating and last for weeks. Malaria Malaria is caused by the parasite Plasmodium, which is transmitted through the bite of an infected Anopheles mosquito. Symptoms include high fever, chills, sweating, headache, nausea and vomiting. Typhoid Typhoid is a bacterial infection spread through contaminated food and water. It is characterized by prolonged fever, weakness, abdominal pain, headache and loss of appetite. In severe cases, intestinal bleeding may occur. Viral Fever Viral fever is a common term for infections caused by various viruses. Symptoms include high fever, body aches, muscle aches, headache, fatigue, and sometimes a rash. These infections are typically self-limiting but can be uncomfortable. Influenza Influenza or Flu is a highly contagious respiratory disease caused by the influenza virus. Symptoms include fever, chills, cough, sore throat, runny or stuffy nose, body aches, headache, fatigue, sometimes vomiting and diarrhea. Cholera Cholera is a severe diarrhoeal infection caused by bacterium Vibrio cholerae. It is spread through contaminated water and food and causes severe dehydration, which can be fatal if not treated immediately. Jaundice Jaundice is a condition characterised by a yellowing of the skin and eyes due to high levels of bilirubin in the blood. It can be caused by various factors, including liver infections such as hepatitis. Hepatitis A & E Hepatitis A and E are viral liver infections spread by contaminated food and water. Symptoms include jaundice, fatigue, abdominal pain, loss of appetite and nausea. Hepatitis E is particularly dangerous for pregnant women. Cold and Flu Cold and flu are common during monsoons due to fluctuations in temperature and humidity. It's symptoms include runny or stuffy nose, sore throat, cough, body aches, headache and fever. Leptospirosis Leptospirosis is a bacterial infection spread by contact with water contaminated with the urine of infected animals. It can cause high fever, headache, chills, muscle aches, vomiting, jaundice and red eyes. Stomach Flu Stomach flu, or viral gastroenteritis, is an intestinal infection characterized by watery diarrhea, abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting, and sometimes fever. It is spread through contaminated food or water. Prevention tips to protect yourself from various monsoon diseases The combination of stagnant water, increased humidity, and the proliferation of insects creates an ideal breeding ground for various monsoon diseases. Here are some effective prevention tips to safeguard yourself from these rainy season diseases. Maintain Personal Hygiene Maintaining personal hygiene is of utmost important during the monsoon to prevent diseases like flu, cold, and respiratory infections. Wash your hands often with soap and water more often, especially after the contact with rainwater. Keep your nails trimmed and avoid touching your face with unclean hands. Drink Clean and Safe Water Waterborne diseases like cholera, typhoid, and gastroenteritis are common during the rainy season. Ensure that you drink only purified or boiled water. If you rely on tap water, using water purifiers can help in monsoon diseases prevention. Avoid consuming water from unreliable sources, such as roadside vendors. Eat Fresh and Home-Cooked Food During the rainy season, food can spoil due to high humidity levels. To prevent foodborne diseases such as diarrhoea and food poisoning, eat fresh, well-cooked meals. Avoid street food and wash fruits and vegetables thoroughly before eating them. Use Mosquito Repellents Diseases like dengue, malaria, and chikungunya are transmitted by mosquitoes, which breeds in stagnant water. Use mosquito repellents, nets, and wear long-sleeved clothing to minimize mosquito bites. Containers which can collect such as water flower pots and buckets, needs to be kept clean to reduce mosquito breeding sites. Keep Your Surroundings Clean Maintaining a clean environment is important in the prevention of monsoon diseases. Ensure that your surroundings are free of stagnant water, as it can become a breeding ground for mosquitoes. Dispose of garbage properly and ensure that drains and gutters are not clogged to prevent water accumulation. Protect Yourself from the Rain Getting drenched in rain can cause infections and illnesses such as the common cold, flu, and fungal infections. Carry an umbrella or wear a raincoat to protect yourself. If you get wet, change out of wet clothes immediately and dry yourself thoroughly to prevent fungal infections. Boost Your Immunity A strong immune system is vital for fighting off rainy season diseases. Include immune-boosting foods in your diet, such as fruits rich in vitamin C, vegetables, and probiotics like yogurt. Staying hydrated and getting an adequate amount of sleep can also contribute to a healthy immune system. Vaccinations and Medical Advice Consult your doctor about vaccinations that can protect you from certain monsoon diseases. Follow medical advice, especially if you have an underlying health condition that could make you more susceptible to infections during the rainy season. By following these prevention tips, you can enjoy the monsoon season while staying safe and healthy. Awareness and proactive measures is key to keeping monsoon diseases at bay. Conclusion Rainy season diseases and prevention should be the highest priority during the monsoon. Maintaining cleanliness and practical hygiene can help in reducing the risk of these monsoon diseases. Most importantly, if you experience any of the above symptoms, be sure to consult your doctor. For accurate diagnosis and effective treatment, it is important to get tested at a reliable diagnostic lab like Metropolis Labs. They offer at-home sample collection for a multitude of tests that help detect these monsoon diseases. Their experienced team and advanced labs ensure that you receive accurate results, enabling you to take timely action for your health. Remember, prevention is always better than cure, so let's stay safe this monsoon!
Understanding Kawasaki Disease: Diagnosis and Treatment
What Is Kawasaki Disease? Kawasaki disease is a rare but serious inflammatory condition that primarily affects children under the age of five. It targets blood vessels throughout the body, including the coronary arteries, which supply blood to the heart. Without timely Kawasaki disease treatment, Kawasaki disease can lead to significant heart complications. The exact Kawasaki disease causes remains unknown, and it does not spread from person to person. What Are The Symptoms Of Kawasaki Disease? Kawasaki disease symptoms generally appear in phases, with early signs often being more severe. Here are some key Kawasaki disease symptoms: High fever lasting for more than five days. Severe redness in the eyes (conjunctivitis) without pus. Rash on the torso and genital area. Swollen, red lips and strawberry tongue. Swollen, red palms and soles, often with peeling skin. Swollen lymph nodes, typically in the neck. Irritability in younger children is also common. What Causes Kawasaki Disease? The exact Kawasaki disease causes is still unknown. Researchers believe it could be triggered by an infection related to viruses or bacteria or an immune response to environmental factors such as chemicals or irritants. What Are The Risk Factors For Kawasaki Disease? Key risk factors for Kawasaki disease include: Age: The highest susceptibility is in children under five years old, Genetics: It appears more frequently in children of Asian descent. Gender : Being assigned male at birth . What Are The Complications Of Kawasaki Disease? If not treated promptly, Kawasaki disease causes serious cardiovascular complications, the most severe being coronary artery aneurysms, which increase the risk of heart attacks, blood clots, and heart vessel blockages. Other complications might include hepatitis in your child's liver, pancreatitis (inflammation) in your child's pancreas, heart attack, inflammation of heart muscles, valves, and the outer lining of the heart. In some cases, temporary arthritis or liver and gallbladder issues can occur. How Is Kawasaki Disease Diagnosed? Diagnosing Kawasaki disease involves ruling out other diseases with similar Kawasaki disease symptoms through a combination of clinical evaluation and laboratory tests. Doctors check for fever along with at least four of the primary symptoms of the disease. What Are The Three Stages Of Kawasaki Disease? Kawasaki disease progresses through three distinct stages: Acute Stage: High fever, eye redness, rash, swollen hands and feet, and swollen lymph nodes. This stage is the most intense and typically lasts 1-2 weeks. Subacute Stage: Symptoms of the acute stage may subside, but this stage brings peeling skin, joint pain, and liver abnormalities. It can last until the fourth week. Convalescent Stage: Symptoms continue to gradually fade during this final stage, which can last until all blood markers of inflammation have normalised. This phase may take up to eight weeks from the onset of symptoms. What Tests Will Be Done To Diagnose Kawasaki Disease? Kawasaki disease diagnosis typically involves several tests to support the clinical diagnosis including: Blood tests : These are used to detect high levels of inflammation and may include a complete blood count, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), and C-reactive protein (CRP). Urine tests : These are used to check for signs of inflammation and rule out urinary tract infections. Electrocardiogram (ECG) : These are used to assess heart function and detect irregularities. Chest X-ray : These are used to view the size and shape of the heart and check for lung infections. These tests help confirm the Kawasaki disease diagnosis and guide appropriate treatment plans. How Is Kawasaki Disease Treated? Kawasaki disease treatment aims to reduce inflammation and prevent heart complications. The standard Kawasaki disease treatment approach includes: Intravenous Immunoglobulin (IVIG): This is the primary treatment and is most effective when administered within the first ten days of illness. IVIG is a blood product that helps reduce inflammation and decrease the risk of coronary artery aneurysms. Aspirin: This can be used as a Kawasaki disease medication. Initially, high doses are used to reduce fever, pain, and joint swelling, and later, low doses help prevent blood clots. Corticosteroids: This may be used if symptoms are severe or if the response to IVIG is inadequate. Follow-up Echocardiograms: Regular heart monitoring is crucial, especially in the first few weeks after diagnosis to detect any changes in the heart. What Are The Complications Of The Treatment? Kawasaki disease treatment is generally safe, but it can have some complications, including: Hemolytic anaemia (red blood cells die faster than normal). Infusion reactions. Chest pain. Difficulty breathing. Upset stomach. Pain in muscles or joints. What Is The Outlook For Kawasaki Disease? The prognosis for Kawasaki disease in children is generally very good with early and effective treatment. Complications that affect the heart can be severe enough to be fatal within 15 to 45 days of the starting of the fever. Most children fully recover without any lasting effects. However, about 5% of cases develop coronary artery aneurysms, which can lead to long-term heart complications. Kawasaki Disease in adults can cause long-term damage to arteries and possible heart issues. Conclusion In conclusion, Kawasaki disease is a rare but serious condition that primarily affects young children. Prompt recognition of its symptoms, early diagnosis, and aggressive treatment, including IVIG and aspirin therapy, are crucial for minimising the risk of long-term complications, particularly coronary artery aneurysms. While the exact Kawasaki disease causes remains unknown, awareness among parents and healthcare providers is paramount for timely intervention. Metropolis Healthcare provides a comprehensive range of 4000+ clinical laboratory tests and profiles. Schedule your appointment with Metropolis Healthcare and protect your child from Kawasaki disease today.
Exploring Pheochromocytoma: Symptoms, Diagnosis, And Treatment
What Is Pheochromocytoma? Pheochromocytoma is a rare type of tumour that arises from the chromaffin cells or neuroendocrine cells (hormone-producing glands) of the adrenal gland, which is located on top of each kidney. These tumours predominantly produce excessive amounts of catecholamines (neurotransmitters), which include adrenaline and noradrenaline. The secretion of these hormones can lead to various symptoms. Pheochromocytomas are generally benign (non-cancerous) but can be malignant (cancerous) in a small percentage of cases. These tumours can occur at any age but are most commonly diagnosed in adults during their 30s to 50s. Pheochromocytomas may occur as part of hereditary syndromes such as multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 (MEN2), von Hippel-Lindau disease, and neurofibromatosis type 1. What Are The Symptoms Of Pheochromocytoma? Key pheochromocytoma symptoms include: High blood pressure (hypertension). Headache. Excessive sweating for no known reason. A pounding, fast or irregular heartbeat. Feeling shaky Pain in your chest and/or abdomen. Being much paler than usual. Nausea and/or vomiting. Diarrhea. Constipation. An extreme drop in blood pressure upon standing suddenly (orthostatic hypotension). Unexplained weight loss What Causes Pheochromocytoma? The exact pheochromocytoma causes are not well understood, but several genetic factors contribute to its development: Multiple endocrine neoplasia 2 syndrome (a rare condition caused by a genetic mutation that affects multiple glands in your endocrine system), types A and B (MEN2A and MEN2B). Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) disease (a rare genetic disorder that significantly increases the chance of having certain kinds of cancerous (malignant) tumours and noncancerous (benign) tumours and cysts). Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) (a condition that affects your skin and nervous system (brain, spinal cord and nerves)) Hereditary paraganglioma syndrome (a genetic condition that predisposes individuals to developing rare tumours called paragangliomas). Carney-Stratakis dyad [paraganglioma (rare tumours that arise from cells of the peripheral nervous system) and gastrointestinal stromal tumour (GIST) (tumours that develop in the walls of the stomach and intestines)]. How Is Pheochromocytoma Diagnosed? Pheochromocytoma diagnosis involves a combination of clinical assessment, biochemical tests, and imaging studies to confirm the presence of the tumour and its activity. The pheochromocytoma diagnosis typically includes: Clinical Evaluation: Review of symptoms and medical history. Biochemical Testing: Measurement of catecholamines and metanephrines in blood and urine. Imaging Studies: CT Scan: Often the first imaging technique used. MRI: Used for its superior soft tissue contrast. MIBG Scan: Detects extra-adrenal (outside adrenal glands) and metastatic (cancerous) tumours. Genetic Testing: Recommended for suspected hereditary cases. What Are The Risk Factors Of Pheochromocytoma? The risk factors for developing pheochromocytoma include: Genetic Disorders: Having a hereditary syndrome such as Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia type 2 (MEN2), von Hippel-Lindau disease, neurofibromatosis type 1, or hereditary paraganglioma-pheochromocytoma syndromes significantly increases the risk. Family History: A family history of pheochromocytoma or related genetic conditions elevates the likelihood of developing the tumour. Genetic Mutations: Specific mutations in genes like RET, VHL, NF1, and SDHx are linked to a higher risk of pheochromocytoma. What Are The Complications Of Pheochromocytoma? Pheochromocytoma causes several serious complications if not diagnosed and treated promptly: Severe Hypertension: Persistently high blood pressure or sudden severe spikes can lead to cardiovascular complications such as heart attack, stroke, or heart failure. Cardiac Arrhythmias: Abnormal heart rhythms, which can be life-threatening, may be triggered by excessive catecholamine levels. Heart Damage: Chronic high levels of catecholamines can lead to cardiomyopathy (disease of the heart muscle), impairing the heart's ability to pump blood effectively. Crisis with Multiorgan Failure: A pheochromocytoma crisis, often triggered by stress, surgery, or certain medications, can cause severe hypertension, leading to multiorgan failure or even death if not treated immediately. Metastatic Disease: Although rare, pheochromocytomas can metastasise (spread to other parts of the body), complicating pheochromocytoma treatment and worsening prognosis. Adverse Effects from Surgery: Surgical removal of the tumour, while often curative, carries risks of complications, especially if the tumour is not diagnosed preoperatively and managed appropriately. What Tests Are Used To Diagnose Pheochromocytoma? Diagnosing pheochromocytoma typically involves a combination of biochemical testing and imaging techniques to detect and locate the tumour. Commonly used tests are: Biochemical Tests Plasma-Free Metanephrines: This test measures the levels of metanephrines (metabolites of catecholamines) in the blood. It is highly sensitive and can detect tumours that secrete catecholamines episodically. 24-Hour Urinary Catecholamines and Metanephrines: This involves collecting urine for 24 hours to measure the levels of catecholamines and their metabolites. It helps confirm the production of excess hormones typical of pheochromocytomas. Pheochromocytomas Radiology (Imaging) Studies Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: A CT scan of the abdomen is typically the first imaging test performed to locate an adrenal tumour. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI is used for patients where radiation exposure is a concern or for better soft tissue contrast. It’s particularly useful in detecting small or extra-adrenal pheochromocytomas. Metaiodobenzylguanidine (MIBG) Scintigraphy: This nuclear medicine scan is used if CT or MRI results are inconclusive. Additional Diagnostic Tests Genetic Testing: Given the association with genetic syndromes, testing for mutations in genes such as RET, VHL, NF1, and SDHx is recommended for patients with a family history of pheochromocytoma or related conditions. Clonidine Suppression Test: Rarely used, but can be helpful in ambiguous cases. It measures plasma catecholamines before and after administration of clonidine, which should normally suppress norepinephrine in non-pheochromocytoma cases. How Is Pheochromocytoma Treated? Pheochromocytoma treatment varies depending on the specifics of the case, such as whether the tumour is benign or malignant, and if it has metastasised. Here are the main pheochromocytoma treatment options available: 1. Surgery Primary Treatment: Surgery is the primary pheochromocytoma treatment and is often curative, especially when the tumour is localised to the adrenal glands. Laparoscopic Adrenalectomy: This minimally invasive procedure is commonly used to remove single, small, benign tumours. Open Adrenalectomy: Required for larger or invasive tumors, or when malignancy is involved. 2. Radiation Therapy Palliative Care: Used mainly for pain relief in cases of bone metastasis from malignant pheochromocytoma. 3. Chemotherapy For Malignant Cases: Used if the tumour is malignant or has metastasised and is not amenable to complete surgical resection. Common chemotherapy agents include cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and dacarbazine. 4. Ablation Therapy Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA): Used for small or inoperable tumours to destroy cancer cells with heat. 5. Embolization Therapy Pre-Surgical or Palliative: This procedure involves blocking the blood supply to the tumour, often used preoperatively to shrink the tumour or palliatively to manage pheochromocytoma symptoms. 6. Targeted Therapy MIBG Therapy: Uses a radioactive iodine-labeled form of MIBG that targets catecholamine-producing cells, useful particularly in cases where traditional chemotherapy is less effective. Targeted Molecular Therapies: These are newer treatments that target specific pathways or mutations in tumour cells and are considered when other treatments fail or aren’t suitable. What Is The Outlook For Pheochromocytoma? The outlook for pheochromocytoma is generally positive when it receives proper treatment. Surgery successfully removes about 90% of these tumours. However, if pheochromocytomas are not treated, they can lead to severe, potentially fatal complications, including: Cardiomyopathy (heart muscle disease). Myocarditis (inflammation of the heart muscle). Cerebral haemorrhaging (uncontrolled bleeding in the brain). Pulmonary edema (fluid accumulation in the lungs). Additionally, untreated pheochromocytomas can increase the risk of experiencing a stroke or heart attack (myocardial infarction). Conclusion In conclusion, while pheochromocytoma can pose serious health risks if left untreated, the prognosis is typically very good when diagnosed early and managed effectively with surgical removal. Around 90% of these tumours can be successfully excised, significantly reducing the risk of complications of pheochromocytoma. However, it is crucial to recognise and address the potentially life-threatening complications associated with untreated pheochromocytomas, such as heart disease, stroke, and severe cardiovascular events. Metropolis Healthcare provides a comprehensive range of 4000+ clinical laboratory tests and profiles. Schedule your appointment with Metropolis Healthcare today and experience comprehensive care and expert diagnostics. Let's get started!
Monsoon Diet: What to Eat and Avoid During the Rainy Season
Introduction As the monsoon clouds gather over the Indian subcontinent, a wave of relief washes over us, bringing relief from the sweltering heat of summer. However, while we enjoy these cold showers, it's worth remembering that monsoon also comes with its own se of health concerns. Humidity during monsoons makes our body susceptible to several infections and diseases. Therefore, we must pay attention to what goes into our plates during this season - enter the concept of a well-planned monsoon diet. This blog aims to provide you with a comprehensive guide on which foods to embrace and which to avoid during the rainy season as part of your balanced monsoon diet plan. This guide is designed by keeping in mind that every bite you take should not only satisfy your hunger but also strengthen your immune system against monsoon-related illnesses. Eat Seasonal Fruits Seasonal fruits are rich in vitamins and minerals that help boost immunity and should be a part of your diet in rainy season. Choose apples, pears, pomegranates, lychees and bananas during monsoon. These fruits have a low water content, which reduces the risk of water-borne diseases. However, be careful when eating mangoes, which can cause skin problems like pimples. Hydrate with Warm Liquids Hydration is key to health, especially during the monsoons when the humidity can lead to dehydration. Go for warm or hot liquids like herbal teas with ginger, pepper, honey, mint and basil leaves. These not only keep you hydrated but also have antibacterial properties that enhances immunity. However, avoid excessive intake of coffee and tea as they dehydrate body fluids. Eat Light and Fresh A crucial aspect of your monsoon diet should be to eat light and fresh food. Heavy meals can be hard to digest while fresh food reduces the chances of infections. Go for foods which are a rich source in fibre like brown rice, oats, and barley which are excellent during monsoon. Add a dash of garlic to your soups or curries as it's a natural immunity booster. Steamed Vegetables During the monsoon season, raw vegetables can carry harmful bacteria and viruses that can cause various infections. Include steamed salad instead of raw salad in your monsoon diet plan. As steamed vegetables are easier to digest and the cooking process can also remove the bacteria effectively. Include Probiotics Including probiotic-rich foods like yogurt and almond milk will not only help in digestion but also boost our immune system. They are a healthy alternative to milk, which causes bloating and indigestion during monsoons. Bitter is Better Bitter vegetables like bitter gourd (karela) and herbs like neem, turmeric powder and fenugreek seeds (methi) help strengthen our immune system to prevent infections. Include them in your diet in rainy season. Don'ts of Monsoon Diet The monsoon season not only brings refreshing change in weather, but also an increases risk of waterborne diseases and digestive problems along. To stay healthy during this season, it is important to consider your monsoon diet plan and avoid certain foods and practices that can compromise your health. Here are some key "don'ts" to keep in mind for a safe and nutritious monsoon diet: Avoid Watery Foods During the monsoon season, it is recommended to avoid foods that contain water such as melons and cucumbers. These foods can increase the risk of waterborne diseases due to rainwater contamination. Additionally, foods containing water can cause bloating and indigestion, as the digestive system tends to be more sensitive during this time. Avoid Street Food Street food is a staple for many, but during the monsoon, it can be particularly hazardous. The humid conditions and exposure to rainwater make it easier for bacteria and other pathogens to contaminate these foods. To avoid gastrointestinal infections and food poisoning, it is best to avoid street food and go for home-cooked meals instead. Avoid Spicy Food Spicy foods can make digestive issues more worse, which is the most common condition during the monsoon season. The high humidity affects the body's digestive capacity, and consuming spicy foods can lead to acidity, indigestion, and discomfort. It is better to eat mild and easily digestible foods to keep your stomach settled. Avoid Eating Fried Foods While fried foods might be tempting during the cool, rainy weather, they can also be tough on the digestive system. The high fat content in fried foods slows down digestion and can lead to bloating and discomfort. It is beneficial to avoid these foods to maintain a healthy monsoon diet. Avoid Salt Excess salt can cause water retention and bloating, which is particularly uncomfortable during the humid monsoon season, and can also aggravate conditions like hypertension. Reducing salt intake as part of the monsoon diet helps maintain fluid balance and avoids unnecessary health complications during this time. Limit Seafood Monsoon is typically the breeding season for many types of fish and other seafood, which makes them more susceptible to contamination and infection. Consuming seafood during this season increases the risk of foodborne illnesses. It is safer to limit or avoid seafood and wait until the season passes. Avoid Raw Leafy Greens Raw leafy vegetables can contain dirt, bacteria and other pathogens that are difficult to wash away completely, especially during the rainy season. If consumed, these can lead to stomach infections and other health issues. Instead, cook leafy greens thoroughly to kill harmful microorganisms and make them safer to eat. Conclusion The monsoon season provides a refreshing relief from the summer heat, but certain precautions need to be taken with regards to diet. The above monsoon diet guide will give you information on which foods can help improve your health and which foods pose risk during the monsoon season. Staying healthy during monsoons is not just about the maintaining a right diet but also about maintaining cleanliness around us. Wash your hands before and after meals, ensure that your vegetables are washed well before cooking, and stay hydrated but with safe drinking water. Also, consider booking an at-home sample collection with Metropolis Labs for a comprehensive health check-up to ensure your health parameters are in check as you navigate through the monsoons.
 Home Visit
Home Visit Upload
Upload




















 WhatsApp
WhatsApp