Latest Blogs
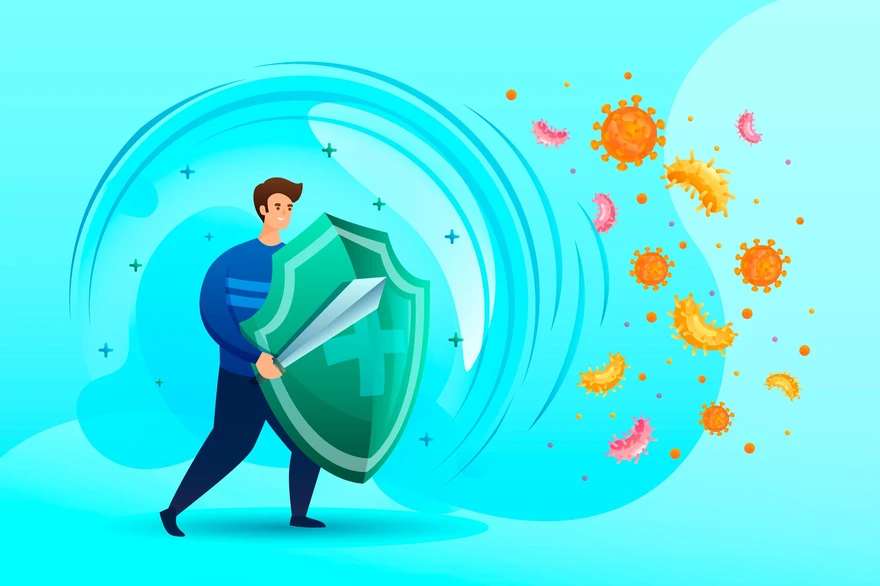
Top 10 Myths About Immunity: Separating Fact from Fiction
Introduction Immunity myths abound, leaving many confused about what really helps or harms the immune system. Separating facts about immunity from fiction is crucial for making informed choices to support your health. In this article, we bust myths about the immune system and share evidence-based tips to strengthen your body's natural defences. Understanding how the immune system works can empower you to make informed choices that support your overall health. Myth 1: You Can Boost Your Immunity Overnight Fact: Building a strong foundation of overall health is key to a robust immune system. While certain habits, like getting enough sleep and eating a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients, are important, no single action will magically boost immunity instantly. Myth 2: Vitamin C Prevents All Illnesses Fact: Although vitamin C supports immune function, it doesn't make you invincible against every bug. Eating a variety of fruits and vegetables is key for getting the spectrum of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants needed for a well-functioning immune system. Myth 3: Cold Weather Causes Weak Immunity Fact: It's a common belief that exposure to cold temperatures weakens immunity. However, the real culprit is the increased indoor contact during winter, which allows viruses to spread more easily. Dressing appropriately for the weather and maintaining hygiene helps more than avoiding the cold itself. Myth 4: Antibiotics Help with Viral Infections Fact: Antibiotics only work against bacterial infections, not viruses. Taking antibiotics unnecessarily can disrupt the gut microbiome, which plays a vital role in immune health. If you have a viral illness, focus on rest, hydration, and symptom relief as recommended by your doctor. Myth 5: Children Need More Immunity Boosters Than Adults Fact: A child's developing immune system does need support, but the same principles apply across ages: a nutritious diet, an active lifestyle, and good sleep. Ensuring kids get recommended vaccines is important, but loading up on supplements and "kid-friendly" immunity boosters is often unnecessary. Myth 6: Stress Doesn't Impact Immunity Fact: Chronic stress takes a heavy toll on immune function over time. Persistently high cortisol levels hamper the body's inflammatory response and ability to fight invading pathogens. Finding healthy ways to relieve stress is one of the top immunity facts to remember. Myth 7: Immunity Weakens Only with Age Fact: While immune responses aren't as robust in later life, your daily habits matter more than the number of candles on your birthday cake. Older adults who exercise regularly, eat well, and get adequate sleep often have stronger immunity than younger people with poor lifestyle habits. Myth 8: More Supplements Mean Better Immunity Fact: Supplements can fill dietary gaps, but they aren't meant to replace a balanced diet. Foods contain immune-supportive compounds that work together in ways that can't be replicated by pills. Focus first on eating wholesome foods and consult your doctor about whether specific supplements might help. Myth 9: Exercise Has No Impact on Immunity Fact: Regular moderate exercise is one of the pillars of healthy immunity. It promotes good circulation, allowing immune cells to move through the body more efficiently. In contrast, being sedentary can increase inflammation and impair immune regulation. Myth 10: Vaccination Makes You Completely Immune Fact: Vaccines significantly reduce the risk of contracting certain diseases, but none are 100% effective. Factors like age, health status, and waning immunity mean that sometimes a vaccinated person can still get sick. However, vaccination often makes the illness much milder compared to not being vaccinated. Tips for Building a Strong Immune System Eat a rainbow: colourful fruits and veggies provide a range of immunity-supporting nutrients. Stay hydrated to promote cellular function and flush out toxins. Get moving with moderate exercise like brisk walking most days of the week. Prioritise sleep, aiming for 7-9 hours per night to allow the immune system to recharge. Manage stress through relaxation practices and social connection. Follow recommended vaccine schedules to train your immune system against serious diseases. Limit alcohol consumption Conclusion Lifelong habits have the greatest impact on immune health—not crash diets, mega-doses of supplements, or obsessive avoidance of germs. When searching for credible immunity facts, focus on the fundamentals: good nutrition, consistent activity, quality sleep, and stress relief. If you need help assessing or improving your immune function, Metropolis Healthcare offers advanced diagnostic testing and health check services with the convenience of at-home sample collection. Our team of experts is committed to providing the insights you need to make informed decisions about your well-being. FAQs Do immunity boosters work? While some supplements may support immunity, the most effective "booster" is consistently practicing healthy lifestyle habits over time. A nutrient-dense diet, regular physical activity, and restorative sleep should be the foundation of your immune-strengthening plan. How long does it take to build strong immunity? Building robust immunity is an ongoing process. While some positive changes, like getting more sleep, can yield benefits quickly, it generally takes several weeks to notice lasting improvements in immune function after implementing healthier habits. Can I improve immunity after falling ill frequently? Yes! Having a history of frequent infections doesn't mean you're destined to always get sick easily. By adopting the immunity-building practices discussed above and working with your doctor to address any underlying health issues, you can strengthen your resilience season by season.
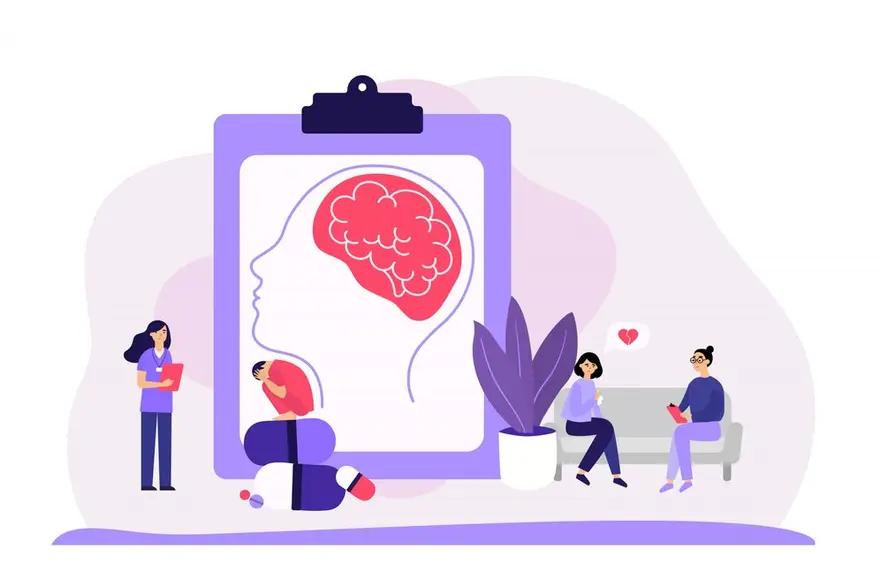
The Link Between Vitamin Deficiency and Depression: Understanding the Impact on Mental Health
Introduction Mental health is a critical aspect of overall well-being, and various factors can influence it, including nutrition. While the connection between diet and mental health may not always be apparent, research has shown that vitamin deficiency and depression are closely linked. Vitamins play a vital role in brain function, and deficiencies can contribute to the development or exacerbation of mental health issues such as depression and anxiety. In this article, we'll explore the connection between vitamin deficiencies and mental health, focusing on the key vitamins involved and how to identify and address these deficiencies. Understanding the Role of Vitamins in Mental Health Vitamins are essential nutrients that play crucial roles in maintaining physical and mental health. They are involved in various biological processes, including neurotransmitter synthesis, energy production, and the regulation of mood. A diet rich in essential vitamins for mental health helps ensure proper brain function and can mitigate the risk of mental health issues. Vitamins act as cofactors in metabolic pathways, influence gene expression, and protect against oxidative stress, all of which are critical for mental well-being. For instance, vitamins B6, B12, and folate are involved in the metabolism of homocysteine, which, when elevated, is associated with depression and anxiety. Key Vitamin Deficiencies Linked to Mental Health Issues Several vitamin deficiencies have been linked to mental health issues, particularly depression and anxiety. Let's take a closer look at some of the most significant ones: Vitamin D Deficiency Vitamin D deficiency has been strongly linked to both depression and anxiety and vitamin deficiency. Low levels of vitamin D are associated with increased symptoms of these conditions. Studies have shown that vitamin D supplementation can significantly reduce anxiety levels in individuals with deficiencies. Vitamin D plays a crucial role in the health of the brain and nervous system, and its deficiency can impact calcium channels in the hippocampus, a region of the brain involved in mood regulation. Vitamin A Deficiency While less commonly discussed in the context of mental health, vitamin A is essential for overall health and can indirectly affect mental well-being. Vitamin A deficiency can lead to impaired cognitive function and may contribute to broader health issues that can impact mental health. However, direct links between vitamin A deficiency and depression or anxiety are not as well-documented as those for other vitamins. B-Vitamins (B6, B12, Folate) B vitamins, particularly B6, B12, and folate, are crucial for mood regulation and cognitive function. These vitamins are involved in the synthesis of neurotransmitters and the metabolism of homocysteine. Elevated homocysteine levels, often resulting from deficiencies in these B vitamins, are associated with depression, anxiety, and other mental health issues. These vitamins also play roles in energy production and the maintenance of healthy neurons. Omega-3 Fatty Acids (Not a Vitamin but Vital) Although not vitamins, omega-3 fatty acids are essential for brain health and have been shown to have anti-depressive and anti-anxiety effects. These fatty acids, particularly EPA and DHA, support brain function by reducing inflammation, promoting neurogenesis, and modulating neurotransmitter systems. Supplementation with omega-3 fatty acids has been found to improve mood, cognition, and overall mental health. Magnesium and Vitamin C Deficiency Magnesium and vitamin C are also important for mental health, though they are often overlooked. Magnesium deficiency can lead to symptoms of depression and anxiety, as magnesium is involved in neurotransmitter function and neuronal health. Vitamin C is an antioxidant that protects against oxidative stress, which is implicated in various mental health conditions. While less research focuses specifically on these nutrients in mental health, they are part of a broader nutritional approach to maintaining good mental well-being. How Vitamin Deficiencies Affect Depression Vitamin deficiencies can significantly contribute to the development and exacerbation of depression. For instance, deficiencies in vitamins B6, B12, and folate can lead to elevated homocysteine levels, which are associated with depression. Vitamin deficiency and depression are closely linked, as vitamin D deficiency impacts calcium channels in the hippocampus, a region critical for mood regulation. Omega-3 fatty acid deficiencies can result in reduced neurogenesis and increased inflammation in the brain, contributing to depressive symptoms. Additionally, antioxidant pathways, such as the NRF2 pathway, which can be affected by various vitamin deficiencies, play a role in protecting against oxidative stress that can lead to depression-like symptoms. How Vitamin Deficiencies Affect Anxiety Vitamin deficiencies can also contribute to anxiety. Anxiety and vitamin deficiency have been linked, particularly with vitamin D deficiency, which has been associated with increased anxiety levels. Supplementation with vitamin D has been shown to reduce these symptoms. B-vitamin deficiencies can affect neurotransmitter synthesis, leading to anxiety. Omega-3 fatty acid deficiencies can result in increased inflammation and reduced neuroplasticity, which can exacerbate anxiety. Furthermore, magnesium and vitamin C deficiencies can disrupt neurotransmitter function and increase oxidative stress, both of which can contribute to anxiety. Identifying and Addressing Vitamin Deficiencies If you suspect that vitamin deficiencies may be contributing to your mental health issues, it's essential to take steps to identify and address these deficiencies. Here are some ways to do so: Consult with a healthcare professional: Talk to your doctor or a registered dietitian about your concerns. They can help assess your nutritional status and recommend appropriate tests or interventions. Get tested: Blood tests can help identify specific vitamin deficiencies. Your healthcare provider can order these tests and interpret the results. Improve your diet: Focus on consuming a balanced diet rich in foods for mental health support. Include a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats to ensure you're getting a wide range of essential nutrients. Consider supplementation: If deficiencies are identified or if you struggle to meet your nutritional needs through diet alone, your healthcare provider may recommend specific vitamin supplements. It's crucial to follow their guidance and not self-diagnose or self-medicate. Address underlying health issues: Certain health conditions, such as digestive disorders or autoimmune diseases, can interfere with nutrient absorption. Work with your healthcare team to manage these conditions and optimise your nutritional status. FAQs Can vitamin deficiency cause depression and anxiety? Yes, vitamin deficiencies, particularly in vitamins D, B6, B12, and folate, can contribute to the development or worsening of depression and anxiety symptoms. Can taking vitamin supplements cure depression? While addressing vitamin deficiencies can help alleviate symptoms of depression, supplements alone are not a cure. Depression is a complex condition that often requires a multi-faceted approach, including therapy, medication, and lifestyle changes. Which vitamins are most effective for anxiety? Best vitamins to combat depression and anxiety include vitamin D, B-vitamins (B6, B12, and folate), and omega-3 fatty acids. However, it's essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplement regimen. How long does it take to see improvements in mood after addressing deficiencies? The time it takes to see improvements in mood after addressing vitamin deficiencies can vary depending on the individual and the severity of the deficiency. Some people may notice improvements within a few weeks, while others may take longer. How does vitamin A affect mental health? While vitamin A is essential for overall health, its direct impact on mental health is less well-established compared to other vitamins. Vitamin A deficiency can lead to impaired cognitive function and may indirectly affect mental well-being. Conclusion Understanding the link between vitamin deficiency and depression is crucial for maintaining optimal mental health. By recognising the key vitamins involved and taking steps to identify and address deficiencies, you can support your brain function and reduce the risk of depression and anxiety. If you suspect that vitamin deficiencies may be impacting your mental well-being, consider reaching out to Metropolis Healthcare for their expert diagnostic services. With a team of skilled professionals and state-of-the-art facilities, Metropolis Healthcare can help you assess your nutritional status through comprehensive blood tests. Their convenient at-home sample collection service ensures that prioritising your health is easy and accessible.
How Does Vitamin D Deficiency Affect Your Sleep? Understanding the Connection
Introduction Did you know that a lack of the "sunshine vitamin" could be robbing you of restful sleep? Surprisingly, vitamin D deficiency and sleep disturbances often go hand in hand. This article explores the link between low vitamin D and sleep problems, including the symptoms and strategies to improve your vitamin D levels. The Role of Vitamin D in the Body Vitamin D is a crucial nutrient that supports multiple functions in your body, from maintaining strong bones to regulating your immune system. But its influence extends even further—vitamin D also plays a key role in regulating your sleep-wake cycles. In fact, vitamin D receptors are found in areas of the brain that control your circadian rhythms and sleep processes. How Vitamin D Deficiency Impacts Sleep When your body lacks sufficient vitamin D, it can wreak havoc on your sleep patterns. Research shows that individuals with low vitamin D often experience: Difficulty falling asleep at night Frequent awakenings during the night Decreased total sleep time Poor overall sleep quality Vitamin D deficiency disrupts sleep primarily due to its role in melatonin production. Without enough vitamin D, your melatonin levels can plummet, making it harder to drift off and stay asleep. Additionally, vitamin D helps regulate your circadian rhythms—the internal "clock" that signals when it's time to sleep and wake up. Which Symptoms of Vitamin D Deficiency Affect Sleep So how can you tell if low vitamin D might be behind your sleep woes? Watch out for these common symptoms: Excessive daytime fatigue and sleepiness Insomnia or difficulty falling and staying asleep Restless or non-restorative sleep Sleep disturbances like sleep paralysis If you find yourself constantly battling exhaustion despite spending enough time in bed, it's worth getting your vitamin D levels checked. A simple blood test can reveal whether a deficiency is at the root of your sleep struggles. How to Improve Sleep Through Vitamin D The good news is that boosting your vitamin D intake can work wonders for your sleep quality. Here are some effective ways to up your levels: Soak up some sunshine: Spend time outdoors during the day to naturally produce vitamin D in your skin. Aim for 10–30 minutes of direct sunlight exposure, a few times per week. Eat vitamin D-rich foods: Incorporate fatty fish, egg yolks and fortified dairy products into your diet. These foods are among the best natural sources of vitamin D. Consider supplements: If your levels are very low, your doctor may recommend taking a daily vitamin D supplement. Be sure to follow the dosage instructions carefully. Making these simple changes can have a profound impact on regulating your sleep-wake cycles and improving the quality of your rest. In one study, participants who took vitamin D supplements daily for 2 months fell asleep 13 minutes faster and slept 20 minutes longer on average. FAQ's Can Vitamin D Deficiency Really Cause Sleep Problems? Yes, research shows a strong link between vitamin D deficiency and sleep disturbances. Low vitamin D can make it harder to fall asleep, cause nighttime awakenings, and decrease overall sleep quality. How Does Vitamin D Help Improve Sleep? Vitamin D supports sleep by helping produce melatonin, your sleep hormone. It also regulates your circadian rhythms, which control your sleep-wake cycles. Optimal vitamin D levels promote more restful, restorative sleep. What Are the Common Symptoms of Vitamin D Deficiency Related to Sleep? If you have low vitamin D and sleep issues, you may experience daytime fatigue, difficulty falling asleep, frequent awakenings during the night, and unrefreshing sleep. Some people also report sleep paralysis, a temporary inability to move upon falling asleep or waking. Can Vitamin D Supplements Help with Sleep Issues? Studies suggest that vitamin D supplements can indeed improve sleep quality, especially in people with a deficiency. Supplementing may help you fall asleep faster, sleep longer, and wake up feeling more rested. However, it's important to work with your doctor to determine the right dosage for your needs. Are Vitamin D Deficiency and Sleep Apnoea Connected? While more research is needed, some studies have found a potential link between vitamin D deficiency and sleep apnea. Low vitamin D levels may increase the risk and severity of this sleep-breathing disorder. Correcting a deficiency might help improve apnoea symptoms in certain cases. When to See a Doctor? If you suspect low vitamin D is disrupting your sleep, don't hesitate to talk to your healthcare provider. Persistent insomnia, daytime sleepiness, and unrefreshing sleep warrant further evaluation. Your doctor can order a blood test to check your vitamin D levels and recommend the appropriate treatment plan, which may include dietary changes, sunlight exposure, or supplementation. Conclusion The connection between vitamin D deficiency and sleep problems is undeniable. By understanding this link and taking proactive steps to maintain healthy vitamin D levels, you can set the stage for more restful, rejuvenating sleep. If you need help assessing your vitamin D status, consider Metropolis Healthcare's convenient at-home blood testing services. With a commitment to delivering reliable results and personalised care, Metropolis empowers you to prioritise your health and well-being, one night of blissful sleep at a time.
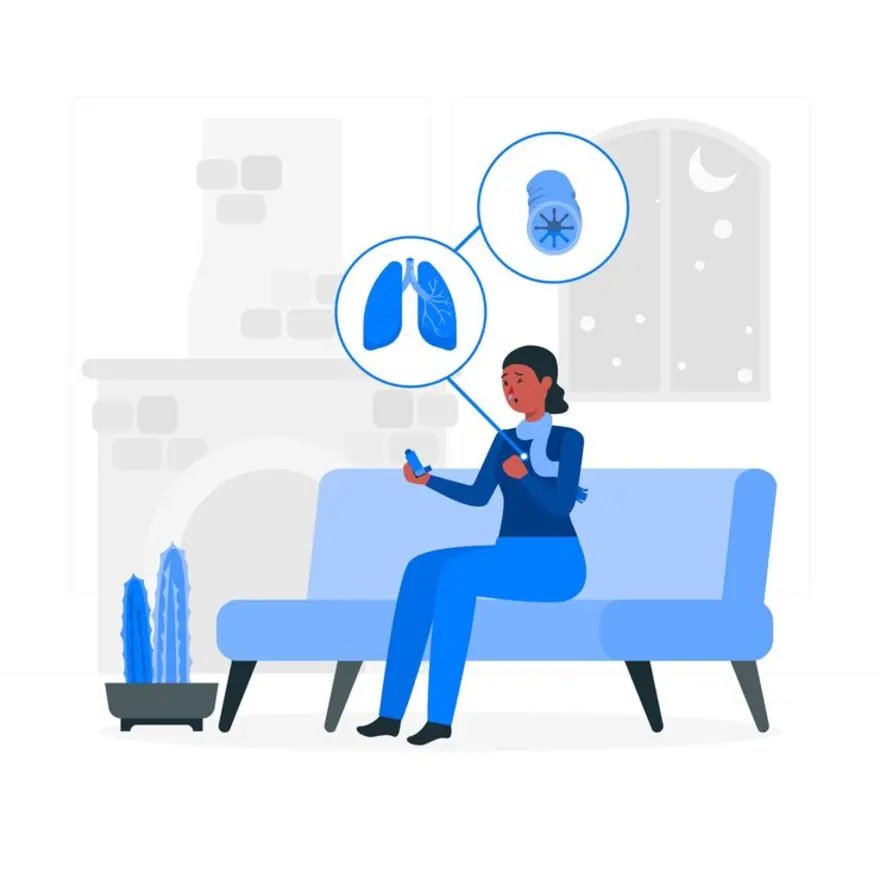
Asthma Attack vs. Anaphylaxis: Understanding the Key Differences
Introduction Asthma attacks and anaphylaxis are two serious medical emergencies that can cause difficulty breathing and be life-threatening if not treated promptly. While they share some similar symptoms, it's crucial to understand the key differences between an asthma attack vs anaphylaxis. Knowing how to recognise the signs and respond appropriately can make all the difference in a critical situation. In this article, we'll explore the specifics of each condition, including causes, symptoms, treatment, and prevention, to empower you with the knowledge to keep yourself and your loved ones safe. What is an asthma attack? An asthma attack, also known as an asthma exacerbation, occurs when the airways become inflamed and constricted, making it hard to breathe. During an attack, the bronchial tubes tighten and produce excess mucus, narrowing the air passages. Common symptoms of an asthma attack include: Wheezing or whistling sound when breathing Shortness of breath Chest tightness or pressure Coughing, especially at night or early in the morning Asthma attacks can be triggered by various factors such as allergens (pollen, dust mites, pet dander), irritants (smoke, strong odours), respiratory infections, exercise, cold air, and even emotional stress. The severity of an attack can range from mild to life-threatening, requiring immediate medical attention. What is anaphylaxis? Anaphylaxis is a severe, potentially fatal allergic reaction that can occur within seconds or minutes of exposure to an allergen. It is a medical emergency that requires immediate treatment with epinephrine. Common triggers of anaphylaxis include: Foods (peanuts, tree nuts, shellfish, milk, eggs) Insect stings (bees, wasps, hornets) Medications (penicillin, aspirin) Latex During anaphylaxis, the immune system releases a flood of chemicals, including histamine, causing the airways to narrow, blood pressure to drop, and the tongue and throat to swell. Symptoms typically involve more than one system of the body and may include: Skin reactions (hives, itching, swelling) Low blood pressure (dizziness, fainting) Constricted airways (difficulty breathing, wheezing) Swollen tongue or throat (trouble swallowing, hoarse voice) Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea Weak and rapid pulse Anaphylaxis can be life-threatening if not treated right away with an injection of epinephrine and expert medical care. Key Symptoms: Asthma Attack vs. Anaphylaxis While both an asthma attack and anaphylaxis can cause respiratory distress, there are important differences in their symptom profiles. Here's a breakdown of the key distinguishing features: Category Asthma Attack Anaphylaxis Onset of Symptoms Gradual, developing over hours or days Sudden, progressing rapidly (often within minutes) Main Symptoms Wheezing, coughing, shortness of breath, chest tightness Respiratory symptoms plus hives, swelling, dizziness, vomiting, etc. If you're unsure whether someone is having an asthma attack vs. anaphylaxis, it's always best to err on the side of caution and treat it like anaphylaxis with epinephrine first, then follow up with asthma medication if needed. Anaphylaxis can be fatal without prompt epinephrine. Causes and Triggers Comparison For Asthma Attack and Anaphylaxis While some triggers like allergens can overlap, there are notable differences in the underlying causes and onset of asthma attacks and anaphylaxis. This table breaks it down: Feature Asthma Attack Anaphylaxis Triggers Allergens, irritants, infections, exercise, weather changes Foods, insect stings, medications, latex Onset Gradual, builds up over hours or days Sudden, within seconds to minutes of exposure Systems Involved Mainly respiratory Multiple: respiratory, skin, GI, cardiovascular Mechanism Inflammation and constriction of airways Massive allergic immune system reaction It's possible for the conditions to overlap. For example, someone with asthma can also have anaphylaxis to a food or insect sting. In those cases, the priority is to treat the anaphylaxis with epinephrine first and foremost. Emergency Treatment for Asthma Attack and Anaphylaxis Prompt treatment is essential for both asthma attacks and anaphylaxis, but the approach differs. Here's what to do: Asthma Attack: Use a quick-relief inhaler (albuterol) as directed, usually 2-6 puffs Stay calm and take slow, deep breaths Sit upright; don't lie down If no improvement, take more puffs of the inhaler as directed If symptoms worsen or don't improve after using inhaler, call 911 Anaphylaxis: Immediately inject the epinephrine auto-injector (EpiPen) into the outer thigh Call 911 right away, even if symptoms start to improve Lie down with legs elevated, if possible If available and needed, use an asthma inhaler after epinephrine A second dose of epinephrine may be needed if symptoms persist Always err on the side of caution and seek emergency medical care if an asthma attack is severe or not responding to medication and for any suspected anaphylaxis. Risk Factors and Prevention Knowing your triggers and risk factors is key to preventing asthma attacks and anaphylaxis. Here are some proactive steps: Asthma: Identify and avoid your asthma triggers (allergens, irritants, etc.) Take controller medications as prescribed to reduce airway inflammation Follow your Asthma Action Plan Get a flu shot yearly Anaphylaxis: Know your allergens and avoid them strictly Read food labels vigilantly every time Tell restaurants about your food allergies Carry your epinephrine auto-injectors at all times Wear a medical ID bracelet noting your allergies Have a written Anaphylaxis Action Plan Conclusion Understanding the difference between an asthma attack and anaphylaxis is critical for getting the right treatment quickly. While both can affect breathing, anaphylaxis is a sudden, multi-system allergic reaction that can be fatal without prompt epinephrine. Knowing your triggers, having an action plan, and carrying your medications can help you stay one step ahead. If you need help identifying your triggers or developing a management plan, consider Metropolis Healthcare's comprehensive health check-up and diagnostic testing services. With a nationwide presence, skilled phlebotomists for home sample collection, and user-friendly online reports, Metropolis is committed to providing reliable, convenient, and personalised care to help you navigate your health with confidence. Remember, when faced with a breathing emergency, stay calm, act fast, and get help. You've got this! FAQs How can I tell the difference between an asthma attack and anaphylaxis? The key is to look at the onset and range of symptoms. Anaphylaxis comes on suddenly with symptoms like hives, swelling, and dizziness in addition to respiratory problems. Asthma attacks are usually more gradual and involve mainly coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath. When in doubt, treat for anaphylaxis and use epinephrine first. Can an asthma attack lead to anaphylaxis? While a severe asthma attack itself doesn't typically lead to anaphylaxis, it's possible for an allergic reaction to trigger both an asthma attack and anaphylaxis at the same time. For example, someone severely allergic to peanuts might experience both asthma symptoms and anaphylaxis after eating peanuts. The priority is to treat the anaphylaxis with epinephrine. What should you do if you have asthma and anaphylaxis? Having both conditions means being extra vigilant. Know your asthma and anaphylaxis action plans. Carry your asthma inhaler and epinephrine auto-injectors with you at all times. Strictly avoid your allergens. If exposed, use epinephrine first, then your asthma inhaler. Always seek emergency care for anaphylaxis. When to See a Doctor? If you suspect you or your child may have asthma or a serious allergy, see your doctor. They can help diagnose the condition, identify triggers, and create a personalised management plan. If you've had an asthma attack or anaphylactic reaction, follow up with your doctor to help prevent future episodes. Remember, the best offence is a good defence.
Vitamin D and Diabetes: The Surprising Connection and Importance of Testing
Introduction Vitamin D, the "sunshine vitamin," has been making headlines in recent years for its potential role in a variety of health conditions, including diabetes. Vitamin D and diabetes share a complex relationship that researchers are still unraveling. Low vitamin D levels have been linked to an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes, while maintaining healthy levels may help prevent or manage the condition. In this article, we'll explore the emerging connection between vitamin D and diabetes, the benefits of maintaining optimal vitamin D status, and why testing your levels is crucial, especially if you have or are at risk for diabetes. Understanding Vitamin D: The Basics Before diving into the link between vitamin D and diabetes, let's cover some vitamin D basics. This fat-soluble vitamin is essential for strong bones, a healthy immune system, and overall well-being. Our bodies produce vitamin D when exposed to sunlight, but it can also be obtained through certain foods (fatty fish, egg yolks, fortified dairy) and supplements. Vitamin D exists in two main forms: D2 (ergocalciferol) and D3 (cholecalciferol). D3 is more effective at raising blood levels of the active form of vitamin D, called 25-hydroxyvitamin D or 25(OH)D. This is the form that is measured in blood tests to assess vitamin D status. The Link Between Vitamin D and Diabetes A growing body of research suggests a significant association between vitamin D and diabetes risk. Studies have found that: Low vitamin D levels are linked to both the initial development of insulin resistance and the subsequent onset of type 2 diabetes due to the death of insulin-producing beta cells. Vitamin D supplementation may improve insulin sensitivity and beta-cell function, two key factors in the development and progression of type 2 diabetes. Recent trials indicate that vitamin D supplementation may reduce the risk of developing diabetes by 10–13% in people with prediabetes, especially those who start out with sufficient vitamin D levels. How does vitamin D influence diabetes risk? Several mechanisms have been proposed to explain how vitamin D influences diabetes risk: Vitamin D helps maintain normal calcium levels and reactive oxygen species (ROS) in beta cells, which is important for their survival and function. It reduces inflammation and prevents certain epigenetic changes that contribute to insulin resistance and beta-cell dysfunction Vitamin D affects blood sugar levels by enhancing the expression of insulin receptors and improving insulin sensitivity. Benefits of Maintaining Healthy Vitamin D Levels for Diabetics If you have diabetes or are at risk for developing it, maintaining optimal vitamin D levels offers several benefits: Better insulin sensitivity: Higher vitamin D levels are associated with improved insulin sensitivity, helping your body use insulin more effectively to manage blood glucose. Enhanced beta-cell function: Vitamin D supports the health and function of the pancreatic beta cells that produce insulin. Reduced inflammation: With its anti-inflammatory properties, vitamin D may help counteract the chronic low-grade inflammation associated with type 2 diabetes. Symptoms of Vitamin D Deficiency in Diabetic Patients Vitamin D deficiency is common, affecting an estimated 1 billion people worldwide. In people with diabetes, low vitamin D can manifest in various ways: Muscle weakness, aches, or cramps Bone pain and increased susceptibility to fractures Fatigue and tiredness Mood changes, such as depression If you experience any of these symptoms, it's important to talk to your doctor and have your vitamin D levels checked. Why Testing for Vitamin D Levels is Crucial in Diabetes Regular vitamin D testing is important for several reasons, especially if you have diabetes or prediabetes: Identifying deficiency: Testing can detect vitamin D deficiency or insufficiency, allowing for timely correction through supplementation. Personalising treatment: Knowing your vitamin D status helps your healthcare provider develop a personalised plan to optimise your levels and potentially improve diabetes management. Assessing diabetes risk: In people with prediabetes, vitamin D testing can help evaluate the risk of progressing to type 2 diabetes and guide prevention strategies. How to Maintain Healthy Vitamin D Levels in Diabetes If you have diabetes, aim to maintain vitamin D levels in the sufficient range, typically 30-50 ng/mL (75-125 nmol/L). Here are some ways to achieve and sustain healthy levels: Get some sun: Spending 10-30 minutes in the sun a few times a week can help your body produce vitamin D. Just remember to practice safe sun exposure and protect your skin from burning. Eat vitamin D-rich foods: Incorporate foods like fatty fish (salmon, tuna, mackerel), egg yolks, mushrooms, and fortified milk or cereals into your diet. Consider supplements: For many people, especially those with deficiency or insufficiency, vitamin D supplements are necessary to achieve optimal levels. Work with your doctor to determine the right dose for you. Monitor your levels: Get your vitamin D levels checked regularly, at least once a year or as often as your healthcare provider recommends, to ensure you're maintaining healthy levels. FAQ's Can vitamin D reverse diabetes? While vitamin D supplementation cannot cure diabetes, it may help improve blood sugar control and prevent or delay the onset of type 2 diabetes in people with prediabetes by enhancing insulin sensitivity and beta-cell function. How often should diabetics check vitamin D levels? People with diabetes should have their vitamin D levels tested at least annually or more frequently if recommended by their healthcare provider, especially if they have risk factors for deficiency or are taking supplements. Can vitamin D affect insulin? Yes, vitamin D has been shown to influence insulin sensitivity and secretion. Adequate vitamin D levels are associated with better insulin sensitivity, while deficiency may contribute to insulin resistance. Conclusion The connection between vitamin D and diabetes is becoming increasingly clear, with mounting evidence suggesting that maintaining healthy vitamin D levels may help prevent or manage type 2 diabetes. If you have diabetes or are at risk, getting your vitamin D levels tested regularly is a simple yet important step in managing your health. At Metropolis Healthcare, we understand the vital role that accurate testing plays in diabetes management. Our team of skilled phlebotomists offers convenient at-home blood sample collection for vitamin D testing. With our state-of-the-art laboratories and commitment to delivering reliable results, you can trust Metropolis to be your partner in monitoring and optimising your vitamin D status. Take charge of your health today—book a vitamin D test with Metropolis Healthcare and take a proactive step towards diabetes prevention and better overall well-being.
Understanding Vitamin A Deficiency: Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention
What is vitamin A deficiency? Vitamin A deficiency occurs when the body does not receive adequate amounts of vitamin A, leading to various health issues, particularly night blindness and other eye problems. This deficiency is prevalent in low- and middle-income countries where diets lack sufficient vitamin A-rich foods. Who does vitamin A deficiency affect? Vitamin A deficiency primarily affects vulnerable populations such as: Infants and young children Pregnant women Breastfeeding mothers These groups have higher nutritional demands and may have limited access to vitamin A-rich foods. In developing countries, vitamin A deficiency is a significant public health concern, causing preventable blindness and increased susceptibility to infections in children. What is vitamin A? Vitamin A is an essential nutrient crucial for maintaining: Healthy eyes and vision Proper immune function Skin health Growth and development Vitamin A plays a vital role in the formation of rhodopsin, a pigment in the retina that allows the eye to adjust to changes in light, enabling night vision. It also supports the development and maintenance of epithelial cells, which form the lining of many bodily structures, and aids in the body's defence against infections. Imagine a child struggling to see in dim light or a pregnant woman dealing with frequent infections. These are just a few examples of how vitamin A deficiency can impact health and quality of life. What are the different forms of vitamin A? Vitamin A exists in two main forms: Preformed vitamin A (retinol and retinal): found in animal products like liver, beef, oily fish, chicken, eggs, and fortified milk. Provitamin A (beta-carotene): Found in plant-based foods such as carrots, mangoes, sweet potatoes, and leafy green vegetables. The body converts beta-carotene into active vitamin A. What complications can occur due to vitamin A deficiency? Vitamin A deficiency can lead to severe complications, including: Night blindness Xerophthalmia (dry eyes) Corneal ulcers and scarring Permanent blindness Increased susceptibility to infections, particularly gastrointestinal and respiratory infections Stunted growth in children Anemia In severe cases, death Vitamin A deficiency is the leading cause of preventable childhood blindness globally. According to the World Health Organisation, an estimated 250,000 to 500,000 children become blind each year due to vitamin A deficiency, with half of them dying within 12 months of losing their sight. What are the symptoms of vitamin A deficiency? The most common vitamin A deficiency symptoms include: Night blindness (difficulty seeing in low light) Dry eyes (xerophthalmia) Bitot's spots (small white or yellowish patches on the conjunctiva) Corneal xerosis (dryness of the cornea) Impaired immune function Skin problems (dry, rough skin) Delayed growth and development in children If you or your child experience any of these symptoms, it's essential to consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment. What causes vitamin A deficiency? The primary vitamin A deficiency causes include: Inadequate dietary intake of vitamin A-rich foods is common in areas with limited access to nutritious food. Protein-energy malnutrition, which can impair vitamin A absorption and utilisation. Intestinal infections, such as worms, interfere with nutrient absorption. Liver disorders or other conditions that impair vitamin A absorption and storage. Pregnant and breastfeeding women, as well as young children, are particularly at risk due to their higher nutritional needs. Addressing these underlying causes through improved nutrition, fortification programs, and public health initiatives is crucial in preventing vitamin A deficiency. How is vitamin A deficiency diagnosed? Diagnosing vitamin A deficiency involves a combination of: Clinical examination: A doctor may perform an eye exam to check for signs of xerophthalmia and night blindness. Medical history: Assessing dietary intake, health conditions, and risk factors. Laboratory tests: Blood tests, specifically serum retinol tests, measure vitamin A levels. A level below 20 micrograms per decilitre indicates severe deficiency. Electroretinography: In some cases, this test may be used to assess retinal function. Early detection and prompt treatment are essential to prevent long-term complications. If you suspect you or your child may have vitamin A deficiency, don't hesitate to seek medical advice. How is vitamin A deficiency treated? Vitamin A deficiency treatment typically involves supplementation. For mild cases, increasing consumption of vitamin A-rich foods is recommended. Include foods like liver, beef, oily fish, eggs, fortified milk, carrots, mangoes, sweet potatoes, and leafy green vegetables in your diet. For severe cases, high-dose vitamin A supplements are prescribed, often following the World Health Organisation's guidelines for children and pregnant women. In regions with high prevalence, mass distribution of vitamin A capsules is a common practice to reduce child mortality and morbidity. Treatment duration and dosage depend on the severity of the deficiency and individual factors. Your healthcare provider will determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on your specific needs. How can we prevent vitamin A deficiency? Preventing vitamin A deficiency involves a multi-faceted approach: Eat a balanced diet rich in vitamin A and vitamin A sources, such as liver, beef, oily fish, eggs, fortified milk, carrots, mangoes, sweet potatoes, and leafy green vegetables. Implement vitamin A supplementation programs, particularly for children and pregnant women in areas with high prevalence. Promote food fortification programs, such as fortifying cooking oil, sugar, or flour with vitamin A. Address underlying causes, such as malnutrition and intestinal infections, through public health initiatives and improved access to healthcare. Raise awareness about the importance of vitamin A and educate communities on how to prevent deficiency. By adopting these preventive measures, we can significantly reduce the global burden of vitamin A deficiency and its devastating consequences. What can I expect if I have vitamin A deficiency? If you have vitamin A deficiency, prompt treatment can lead to improvements in symptoms. Early stages of deficiency, such as night blindness, often resolve within a few weeks of supplementation. However, severe cases with corneal ulcers may result in permanent vision loss despite treatment, emphasising the importance of early detection and intervention. Conclusion Vitamin A deficiency is a preventable yet prevalent health issue, particularly in developing countries. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and prevention strategies, we can take steps to maintain adequate vitamin A levels and protect our eye health. If you suspect you or a loved one may have vitamin A deficiency, don't hesitate to seek medical advice. Metropolis Healthcare offers reliable diagnostic services, including blood tests for vitamin A levels, with the convenience of at-home sample collection. Their team of qualified technicians and state-of-the-art laboratories ensure accurate results, empowering you to take control of your health. Remember, early detection and treatment are key in preventing the serious complications associated with vitamin A deficiency.
The Hidden Dangers of Vitamin Deficiency in Children: What Every Parent Should Know
Introduction As parents, ensuring our children get all the essential nutrients they need for healthy growth and development is one of our top priorities. However, even with our best efforts, vitamin deficiencies in children are more common than we realise. Inadequate vitamin intake can lead to serious health issues that may have long-term effects. Understanding the importance of vitamins for kids, recognising the signs of vitamin deficiency, and knowing how to prevent it through a balanced diet are crucial for every parent. In this article, we'll delve into the world of paediatric vitamin deficiencies, equipping you with the knowledge to keep your child healthy and thriving. What Are Vitamin Deficiencies in Children? Vitamin deficiencies in children occur when their bodies don't get enough of one or more essential vitamins. Vitamins are vital micronutrients that play key roles in various bodily functions, including growth, immune function, and maintaining healthy tissues. When children don't consume or absorb sufficient amounts of vitamins over time, it can lead to deficiencies that manifest through various symptoms and health issues. Some common causes of vitamin deficiency in kids include: Poor dietary intake Limited sun exposure Malabsorption disorders Certain medications Underlying medical conditions Early detection and treatment of vitamin deficiencies are crucial to prevent long-term health complications such as developmental delays, weakened immunity, and bone disorders. Common Vitamin Deficiencies in Children Let's take a closer look at some of the most common vitamin deficiencies seen in children: Vitamin D Deficiency Vitamin D is essential for strong bones and teeth as it helps the body absorb calcium. Vitamin D deficiency in kids is quite common, especially in those who have limited sun exposure or follow a strict vegan diet. Symptoms may include: Delayed growth Bone pain or tenderness Muscle weakness Increased risk of fractures Severe vitamin D deficiency can lead to rickets, a condition that causes soft, weak bones prone to deformities. Ensuring your child gets enough vitamin D through fortified foods, supplements, and regular sun exposure is key. Vitamin A Deficiency Vitamin A is vital for healthy vision, immune function, and proper growth and development. Vitamin A deficiency in children can cause: Night blindness Dry eyes and skin Frequent infections Delayed growth Including vitamin A-rich foods like eggs, dairy products, orange and yellow fruits and vegetables in your child's balanced diet can help prevent deficiency. Vitamin C Deficiency Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that boosts immunity, promotes wound healing, and aids in iron absorption. While severe vitamin C deficiency leading to scurvy is rare today, mild deficiency isn't uncommon. Signs may include: Fatigue and irritability Dry, rough skin Slow wound healing Bleeding gums Citrus fruits, berries, tomatoes, and leafy greens are excellent sources of vitamin C to incorporate into your child's meals. B-Complex Deficiencies (B6, B12, Folate) B vitamins are essential for energy production, brain development, and proper nervous system function. Deficiency in one or more B vitamins can lead to: Anaemia Fatigue Poor growth Neurological issues Vitamin B12 deficiency is of particular concern for children following a vegan diet, as it's mainly found in animal products. Supplements may be necessary in such cases. Effects of Vitamin Deficiencies on Growth and Development Vitamin deficiencies in children can significantly impact their growth and development. For instance: Vitamin D deficiency affects bone growth and strength, leading to stunting or deformities. Vitamin A deficiency impairs immune function, making children more prone to infections that can hamper growth. B vitamin deficiencies can cause neurological issues and developmental delays. Chronic vitamin deficiencies can have lasting effects on a child's physical and cognitive health, emphasising the importance of vitamins for kids and the need for early intervention. Causes of Vitamin Deficiencies in Children Several factors can contribute to vitamin deficiency in kids: Inadequate dietary intake The most common cause is not consuming enough vitamin-rich foods. Picky eating, restricted diets, or lack of access to fresh produce can all lead to insufficient vitamin intake. Malabsorption disorders Certain medical conditions like coeliac disease, cystic fibrosis, and inflammatory bowel disease can hinder the absorption of vitamins from food, leading to deficiencies despite adequate intake. Medications Some medications can interfere with vitamin absorption or deplete the body's vitamin stores. Long-term use of antacids, for example, can lead to vitamin B12 deficiency. Limited sun exposure Vitamin D is primarily synthesised in the skin upon exposure to sunlight. Children who spend most of their time indoors or live in areas with limited sunlight are at higher risk of vitamin D deficiency. Exclusive breastfeeding without supplementation Breast milk alone may not provide sufficient vitamin D, and exclusively breastfed infants require supplements to prevent deficiency. How to Identify Vitamin Deficiencies in Children? Recognising the signs of vitamin deficiencies in children is the first step towards getting them the care they need. Some general symptoms to watch out for include: Fatigue and weakness Pale skin Delayed growth and development Frequent illnesses Poor wound healing If you suspect your child may have a vitamin deficiency, consult a paediatrician. They may recommend blood tests to check vitamin levels and identify specific deficiencies. A thorough physical examination and review of your child's medical history and diet will also help diagnose the issue. Preventing Vitamin Deficiencies in Children The best way to prevent vitamin deficiency in kids is by ensuring they consume a balanced diet rich in all essential nutrients. Here are some tips: Include a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats in their meals. Choose vitamin-fortified foods like cereals, milk, and juices. Ensure adequate sun exposure, about 10–30 minutes a day, for vitamin D synthesis. Consider vitamin supplements under the guidance of a paediatrician, especially if your child follows a restricted diet or has a medical condition affecting nutrient absorption. FAQs How can I tell if my child is deficient in a vitamin? Look out for symptoms like fatigue, poor growth, frequent illnesses, and skin issues. If you suspect a deficiency, consult your child's doctor for a proper diagnosis through blood tests and physical examination. Are multivitamins safe for children? Multivitamins can be safe for children when used as directed and under the guidance of a healthcare provider. However, they should not be used as a substitute for a balanced diet and healthy lifestyle habits. What vitamins are most important for school-age kids? All vitamins are important for overall health, but some crucial ones for school-age children include vitamin D for bone health, vitamin A for vision and immunity, B vitamins for brain development and energy, and vitamin C for immune function and iron absorption. Conclusion Vitamin deficiencies in children can have serious consequences for their growth, development, and overall health. As parents, being aware of the signs, causes, and prevention strategies is essential to ensuring our children get all the nutrients they need to thrive. By providing a balanced diet, encouraging healthy lifestyle habits, and seeking prompt medical care when necessary, we can set our kids up for a lifetime of good health. If you suspect your child may have a vitamin deficiency, don't hesitate to get their levels checked. Metropolis Healthcare offers convenient at-home sample collection and reliable diagnostic testing to help you stay on top of your child's nutritional health. Remember, with the right knowledge and proactive care, you have the power to nourish your child's potential and help them grow into the healthiest version of themselves.




















 WhatsApp
WhatsApp