Latest Blogs
Strategies to Manage Multiple Sclerosis Management
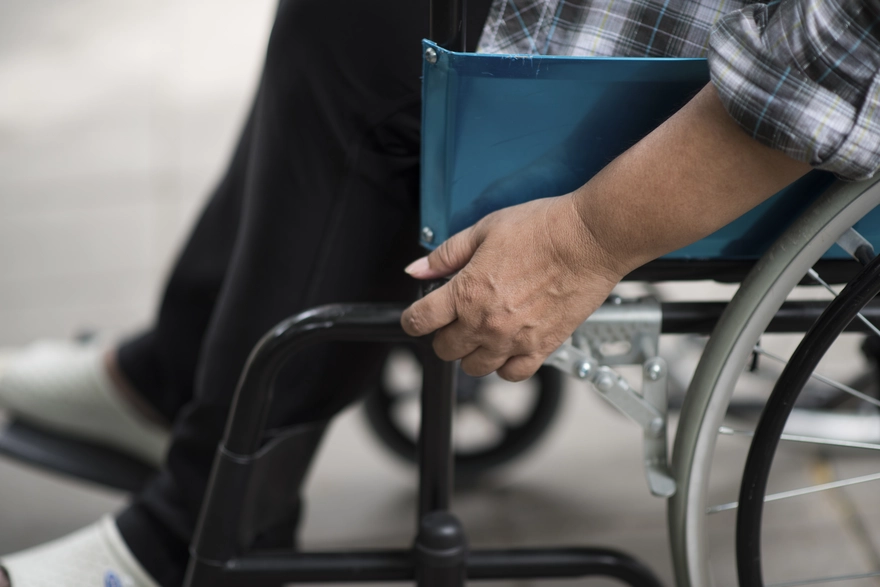
Introduction Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic autoimmune disorder that affects the central nervous system, leading to a wide range of symptoms that can impact daily life. While there is no cure for MS, effective multiple sclerosis management involves a combination of medical treatments, lifestyle modifications, and self-care practices. By implementing these strategies, individuals with MS can reduce the severity and frequency of symptoms, improve their overall well-being, and maintain a better quality of life. In this article, we will explore practical multiple sclerosis management tips and MS self care strategies to help you navigate the challenges of living with this condition. Understanding multiple sclerosis Before delving into multiple sclerosis management strategies, it's essential to understand the basics of the condition. MS occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the protective covering (myelin) of nerve fibres in the brain and spinal cord. This damage disrupts the transmission of nerve signals, leading to various multiple sclerosis symptoms, such as: Numbness or weakness in the limbs Vision problems, such as blurred or double vision Fatigue and difficulty with coordination and balance Bladder and bowel dysfunction Cognitive issues, including memory and concentration difficulties There are four main types of MS: Relapsing-remitting MS (RRMS): This type of MS is characterised by periods of relapses, or flare-ups, followed by periods of remission where symptoms improve or disappear. Secondary-progressive MS (SPMS): SPMS begins as RRMS but eventually transitions into a phase where the disease progresses steadily, with or without relapses. Primary-progressive MS (PPMS): PPMS is marked by a gradual worsening of symptoms from the onset, without distinct relapses or remissions. Progressive-relapsing MS (PRMS): This rare form of MS involves a steady progression of the disease, with occasional flare-ups or relapses. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing the progression of MS and improving patient outcomes. If you experience any concerning symptoms, consult a doctor for proper evaluation and guidance. Top strategies for managing MS Effective multiple sclerosis management requires a multifaceted approach that includes both medical interventions and lifestyle modifications. Here are the key strategies to help you manage your MS: Making accommodations Making necessary accommodations in your daily life can greatly enhance your comfort and functionality. Consider the following: Home modifications: Install grab bars, ramps, or stairlifts to improve accessibility and safety. Rearrange furniture to create wider pathways for easier navigation. Assistive devices: Utilise mobility aids like canes, walkers, or wheelchairs to maintain independence. Invest in adaptive equipment for daily tasks, such as button hooks or long-handled reachers. Workplace adjustments: Discuss your needs with your employer and explore accommodations like flexible work hours, ergonomic workstations, or remote work options to manage fatigue and other symptoms. Balancing your body temperature Heat sensitivity is a common concern for people with MS. Elevated body temperature can temporarily worsen symptoms, a phenomenon known as Uhthoff's sign. To manage heat sensitivity: Cooling techniques: Wear cooling vests or neck wraps, use portable fans, or take cool showers to regulate body temperature. Hydration: Stay well-hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day. Avoid sugary or caffeinated beverages that can contribute to dehydration. Environmental control: Ensure your living and working spaces are well-ventilated and air-conditioned. Avoid prolonged exposure to hot and humid environments. Engaging in light movement Regular physical activity is crucial for managing multiple sclerosis. Engaging in light movement can help improve strength, flexibility, and overall well-being. Consider the following: Gentle exercises: Participate in low-impact activities like walking, swimming, yoga, or Tai Chi. These exercises can help maintain muscle strength, improve balance, and reduce fatigue. Stretching: Incorporate regular stretching routines to maintain flexibility and prevent muscle stiffness. Gentle stretches can also help alleviate spasticity (abnormal muscle tightness) and improve range of motion. Pacing: Listen to your body and pace yourself. Break down activities into smaller, manageable tasks and take frequent rest breaks to avoid overexertion. Conserving energy Fatigue is one of the most common multiple sclerosis symptoms. Here are some of the effective energy conservation strategies that can help you manage fatigue: Prioritisation: Focus on essential tasks and delegate or eliminate non-essential activities. Break down larger tasks into smaller, manageable steps. Rest breaks: Schedule regular rest periods throughout the day. Take short naps or simply relax in a comfortable position to recharge your energy levels. Ergonomic adjustments: Use labour-saving devices and ergonomic tools to minimise physical strain. For example, opt for lightweight utensils, easy-grip handles, or electric can openers. Anticipating potential risks Proactively addressing potential risks is an essential aspect of multiple sclerosis management. Consider the following: Fall prevention: Assess your living space for fall hazards and make necessary modifications. Use non-slip mats, remove tripping hazards, and ensure adequate lighting. Infection control: Practice good hygiene habits, such as frequent handwashing, to reduce the risk of infections. Stay up to date with recommended vaccinations, including the annual flu shot. Medication management: Keep track of your medications and follow the prescribed dosage and schedule. Use pill organisers or set reminders to ensure timely intake. Moving as often as possible In addition to structured exercise, incorporating movement throughout the day is crucial for managing multiple sclerosis symptoms. Consider the following: Frequent position changes: Avoid prolonged sitting or standing. Regularly change positions to promote circulation and prevent stiffness. Stretching breaks: Take short stretching breaks every hour to maintain flexibility and reduce muscle tension. Perform gentle neck rolls, shoulder shrugs, or leg stretches. Household activities: Engage in light household activities like folding laundry, watering plants, or preparing meals to keep your body moving and maintain a sense of accomplishment. Opting for a nutrient-dense diet A well-balanced, nutrient-dense diet is essential for overall health and MS self-care. Consider the following dietary tips: Omega-3 fatty acids: Omega-3 fatty acids, primarily found in fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines, as well as in plant sources like flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts, have powerful anti-inflammatory properties. They may help reduce the inflammation that contributes to MS flare-ups and support overall brain and nerve health. Vitamin D: Vitamin D plays a crucial role in the immune system, and many studies suggest that low levels of vitamin D are linked to an increased risk of developing MS and more severe progression of the disease. Sunlight is the primary source, but fortified foods (like dairy and cereals) and supplements can help maintain adequate levels. Antioxidants: Antioxidants are important in protecting the body from oxidative stress, which can damage nerve cells. Foods rich in antioxidants include berries (like blueberries and strawberries), leafy greens (such as spinach and kale), and colourful vegetables (like bell peppers and carrots). These foods help reduce inflammation and may protect the brain from damage associated with MS. Fibre: A high-fibre diet supports healthy digestion and gut function, which is increasingly recognised as important in managing MS symptoms. Whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes are excellent sources of fibre. Healthy fats: Healthy fats, particularly those from sources like olive oil, avocados, nuts, and seeds, are essential for reducing inflammation and supporting brain health. These fats are rich in monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fatty acids, which can help improve cognitive function and support the nervous system in individuals with MS. By focusing on these nutrient-dense foods, individuals with MS can enhance their immune system, reduce inflammation, and support their overall health. Training your brain Cognitive challenges, such as memory issues or difficulty concentrating, are common in MS. Here are some brain-training activities that can help maintain cognitive function: Mental exercises: Participate in mentally stimulating activities like puzzles, crosswords, or brain-training apps. These exercises can help improve memory, attention, and problem-solving skills. Learning new skills: Engage in learning new skills or hobbies, such as a foreign language or musical instrument. Challenging your brain with novel activities can promote cognitive resilience. Social interaction: Maintain social connections and engage in meaningful conversations. Social interaction stimulates the brain and provides emotional support. Utilising assistive technology Assistive technology can greatly enhance independence and quality of life for individuals with MS. Consider the following: Mobility devices: Explore mobility aids like scooters, power wheelchairs, or exoskeletons to improve mobility and conserve energy. Home automation: Utilise smart home devices to control lighting, temperature, or appliances with voice commands or mobile apps, making daily tasks more manageable. Adaptive software: Use voice recognition software, screen readers, or speech-to-text programs to assist with computer tasks and communication. Prioritising rest and mental well-being Managing the emotional and psychological aspects of MS is just as important as addressing physical symptoms. To prioritise your mental well-being, consider the following: Establish a consistent sleep routine and aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night. Practice stress-reduction techniques, such as deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, or guided imagery. Engage in activities that bring you joy and promote a sense of calm, like listening to music, spending time in nature, or pursuing a creative hobby. Seek support from loved ones, friends, or support groups to share your experiences and feel connected. Consider working with a mental health professional, such as a therapist or counsellor, to develop coping strategies and address any emotional challenges you may face. The takeaway Multiple sclerosis management is a lifelong journey that requires a comprehensive approach, including medical treatments, lifestyle modifications, and self-care practices. By implementing the strategies outlined in this article, you can take an active role in managing your symptoms, improving your overall well-being, and maintaining the best possible quality of life. Remember, everyone's experience with MS is unique, so it's essential to work closely with your healthcare team to develop a personalised management plan that meets your specific needs and goals. At Metropolis Healthcare, we understand the importance of accurate diagnostic testing in the management of MS. Our state-of-the-art laboratories offer a wide range of tests to help monitor disease activity and treatment effectiveness. With our convenient home sample collection service, you can have your blood samples taken in the comfort of your own home by our skilled phlebotomists. FAQ How do you manage a patient with multiple sclerosis? Managing a patient with MS involves a multidisciplinary approach that includes medication, rehabilitation, lifestyle modifications, and emotional support. The goal is to reduce relapses, manage symptoms, and improve overall quality of life. What are self-management strategies for MS? Self-management strategies for MS include energy conservation techniques, regular exercise, stress management, healthy eating habits, and utilising assistive devices. These strategies help individuals with MS maintain independence and effectively cope with the challenges of living with a chronic condition.
The 14 Most Common Types of Cancer
Introduction Cancer remains one of the leading causes of death worldwide, with over 20 million new cases diagnosed annually. While there are over 100 different types of cancer, some are far more common than others. Understanding the most prevalent types of cancer is crucial for raising awareness, promoting early detection, and ultimately improving outcomes. In this article, we'll provide an overview of the 14 most common types of cancer, their risk factors, symptoms, and the importance of timely diagnosis and treatment. Understanding cancer basics Before diving into the list of types of cancer, it's important to grasp the fundamentals of how cancer develops. Cancer occurs when abnormal cells grow uncontrollably, invading surrounding tissues and potentially spreading to other parts of the body through the bloodstream or lymphatic system. While each cancer type has its unique characteristics, they all stem from this basic process of unregulated cell growth. Many cancers result from a complex interplay of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Early detection through regular screenings and awareness of warning signs plays a vital role in successful treatment. Non-melanoma skin cancer Non-melanoma skin cancers, including basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, are the most common type of cancer overall. However, they are often excluded from lists of types of cancer due to their high incidence and low mortality rates. Risk factors include: Excessive UV exposure from the sun or tanning beds Fair skin that burns easily History of sunburns Older age These cancers are highly treatable when caught early. Treatment options may include excision, cryotherapy, or topical medications. Breast cancer Breast cancer is the most common type of cancer in women worldwide. Risk factors include: Being female Older age Family history of breast cancer Certain inherited genes (BRCA1/BRCA2) Obesity and lack of physical activity Symptoms may include: A lump or thickening in the breast Changes in breast size, shape, or skin texture Nipple discharge or inversion Regular mammograms and self-exams are crucial for early detection. Treatment options vary based on the stage and type of breast cancer. Lung cancer Lung cancer is a leading cause of cancer deaths globally. Smoking is the primary risk factor, responsible for about 80% of lung cancer cases. Other risk factors include exposure to secondhand smoke, radon, asbestos, and air pollution. Symptoms often don't appear until the disease is advanced, but may include: Persistent cough Chest pain Shortness of breath Coughing up blood Treatment for lung cancer depends on the specific type (non-small cell or small cell), stage, and the patient's overall health. Options may include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy. Quitting smoking is crucial to reduce risk and improve treatment outcomes. Prostate cancer Prostate cancer is the second most frequent cancer diagnosis in men worldwide. Risk factors include: Older age (over 50) Family history African ancestry Obesity Early prostate cancer usually has no symptoms. More advanced cancers may cause issues like trouble urinating, decreased force in the urine stream, blood in the semen, bone pain, and erectile dysfunction. The prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test and digital rectal exam (DRE) can help detect prostate cancer early. Treatment options include active surveillance, surgery, radiation, hormone therapy, and chemotherapy. Colorectal cancer Colorectal cancer, which includes colon and rectal cancers, is the third most common type of cancer. Risk factors include: Older age (over 50) Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) Family history of colorectal cancer Obesity and sedentary lifestyle Diets high in red and processed meats Symptoms may include rectal bleeding, blood in the stool, abdominal pain, and changes in bowel habits. Screening tests like colonoscopies can detect precancerous polyps early. Treatment usually involves surgery and may include chemotherapy, radiation, or targeted therapy. Melanoma Melanoma, the most serious form of skin cancer, develops in the melanocytes that produce skin pigment. Risk factors include: Excessive UV exposure Having many moles or unusual moles Fair skin, freckling, and light hair Family history of melanoma The ABCDE rule can help you identify potential melanomas: asymmetry, border irregularity, colour variation, diameter over 6 mm, and evolving size or shape. Prevention centres on limiting UV exposure and regularly checking the skin for changes. Early-stage melanomas are highly treatable with surgery, while advanced cases may require immunotherapy, targeted therapy, or chemotherapy. Bladder cancer Bladder cancer typically begins in the cells lining the bladder. Risk factors include: Smoking Exposure to certain chemicals Chronic bladder irritation and infections Prior cancer treatment (radiation to the pelvis) Symptoms include blood in the urine, frequent urination, and pain during urination. Diagnosis involves cystoscopy and biopsy. Treatment options include surgery, intravesical therapy, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy, depending on the stage and grade of the cancer. Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma is a common cancer that starts in the lymphatic system. Risk factors include: Older age (over 60) Certain infections (e.g., HIV, EBV) Autoimmune disorders Exposure to chemicals like benzene Symptoms can include enlarged lymph nodes, fever, night sweats, weight loss, and fatigue. The diagnosis typically requires a lymph node biopsy. Treatment depends on the specific NHL subtype and stage, but often includes chemotherapy, radiation, immunotherapy, or targeted therapy. Kidney cancer Kidney cancer, also called renal cell carcinoma, tends to affect older adults. Risk factors include: Smoking Obesity High blood pressure Family history of kidney cancer Certain inherited syndromes Symptoms may include blood in the urine, a lump in the abdomen, back pain, fatigue, and unexplained weight loss. Treatment usually involves surgery to remove part or all of the affected kidney. Targeted therapy, immunotherapy, and radiation may also be used. Leukaemia Leukaemia is a type of cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow. There are several types, each with different treatment approaches. Risk factors can include previous chemotherapy, Down syndrome, and exposure to certain chemicals. Symptoms may include: Fatigue and weakness Frequent infections Easy bruising or bleeding Enlarged lymph nodes or spleen The diagnosis involves blood tests and a bone marrow biopsy. Treatment typically includes chemotherapy, targeted therapy, radiation, or stem cell transplantation. Pancreatic cancer Pancreatic cancer is difficult to detect early, making it one of the most lethal types of cancer. Risk factors include smoking, chronic pancreatitis, diabetes, obesity and family history. Symptoms, when present, can be vague: Abdominal or back pain Jaundice Loss of appetite Unexplained weight loss Treatment options are determined by stage but may include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation, and targeted therapy. Thyroid cancer Thyroid cancer occurs in the butterfly-shaped gland at the base of the neck. Risk factors include radiation exposure and certain inherited genetic syndromes. Symptoms may include: A lump or swelling in the neck Hoarseness or difficulty swallowing Neck or throat pain Most thyroid cancers are highly treatable, especially when caught early. Treatment typically involves surgery, often followed by radioactive iodine therapy or hormone suppression. Liver cancer Liver cancer includes hepatocellular carcinoma and bile duct cancer. Risk factors include chronic hepatitis B or C, cirrhosis, and excessive alcohol consumption. Symptoms often don't appear until later stages, but may include: Abdominal pain or swelling Unexplained weight loss Jaundice Nausea and vomiting Treatment options depend on the stage and may include surgery, liver transplant, ablation, radiation, chemotherapy, and targeted therapy. Endometrial cancer Endometrial cancer starts in the lining of the uterus and is the most common gynaecologic cancer. Risk factors include obesity, diabetes, hormone therapy, and a family history of Lynch syndrome. Symptoms may include: Abnormal vaginal bleeding or discharge Pelvic pain Unintended weight loss Treatment usually involves surgery (hysterectomy), and may include radiation, chemotherapy, and hormone therapy. 5-year survival rates overview The 5-year survival rates for various cancers vary significantly depending on factors like: Stage at diagnosis Cancer type and subtype Patient age and overall health Treatment response Non-melanoma skin cancer and thyroid cancer have very high survival rates, often near 100% due to early detection. Conversely, pancreatic cancer has one of the lowest survival rates at approximately 11.5%, primarily due to late diagnosis. Cancers like breast, prostate, and melanoma have relatively high survival rates, especially when detected early. However, cancers such as lung and liver cancer tend to have poorer survival rates, reflecting challenges in early detection and effective treatment. Takeaway: Importance of awareness and early detection Awareness of cancer risk factors, signs, and symptoms is crucial for prevention and early detection. Lifestyle choices like avoiding tobacco, maintaining a healthy weight, protecting your skin from the sun, and getting recommended cancer screening tests can lower your risk for many common types of cancer. If you notice any unusual changes in your body, don't ignore them. Talk to your doctor right away, as early diagnosis leads to more effective treatment. FAQ What is 90% of cancer caused by? Environmental and lifestyle factors, rather than inherited genetics, are estimated to cause around 90% of all cancers. This includes factors like smoking, diet, obesity, and exposure to certain chemicals or viruses. Why cancers are common? Cancers are common due to the combined effects of increasing life expectancy, lifestyle factors (smoking, physical inactivity, etc.), and exposure to environmental carcinogens. What are the 5 most common cancers? The five most common types of cancer worldwide are breast, lung, colorectal, prostate, colorectal, and melanoma (skin). However, prevalence varies by country and demographic group. What are the top 5 most treatable cancers? The most treatable cancers when caught early are breast, prostate, thyroid, testicular, and melanoma. However, treatability depends on many individual factors. At Metropolis Healthcare, we understand the importance of early cancer detection. As a leading chain of diagnostic labs across India, we offer accurate pathology testing and health check-up services to help you prioritise your health. Our team of qualified technicians can collect blood samples right in the comfort of your home. You'll receive your reports conveniently via email and on our user-friendly TruHealth app. With personalised care and reliable results, Metropolis empowers you to take control of your well-being. Book your health check-up today.
Chronic Stress And Hypertension—How Is It Connected?
Introduction In today's fast-paced world, stress has become an unavoidable part of daily life. However, when stress becomes chronic, it can have serious implications for our health, particularly in the form of hypertension or high blood pressure. Understanding the connection between chronic stress and hypertension is crucial for effectively managing blood pressure and promoting overall well-being. This article will explore the impact of stress on the body, the physiological mechanisms linking stress and hypertension, and practical strategies for stress management for hypertension control. What is hypertension? Hypertension is a condition characterised by consistently elevated blood pressure in the arteries. It's often called the "silent killer" because it usually has no symptoms until it causes serious complications like heart disease, stroke, and kidney failure. There are two main types of hypertension: Primary (essential) hypertension: This type develops gradually over time with no identifiable cause. Secondary hypertension: This type is caused by an underlying health condition, such as kidney disease or hormonal disorders. Risk factors for hypertension include age, family history, obesity, sedentary lifestyle, high-sodium diet, excessive alcohol consumption, and chronic stress. The physiology of stress When you encounter a stressful situation, your body activates the fight-or-flight response, releasing hormones like adrenaline and cortisol. These hormones prepare your body for action by: Increasing your heart rate and blood pressure Redirecting blood flow to your muscles Releasing glucose for energy Suppressing non-essential functions like digestion The long-term impact of stress on the body can have an influence on your cardiovascular system, even though this reaction is helpful in emergency situations. How does stress contribute to hypertension? The impact of stress on the body and its role in hypertension involves both physiological mechanisms and behavioural responses. Chronic stress can lead to sustained elevations in blood pressure through direct bodily effects and by influencing lifestyle habits. Here's how: Chronic activation of stress response When you experience chronic stress, your body's stress response is repeatedly or continuously activated. This impact of stress on the body leads to: Persistent sympathetic nervous system activation, keeping your heart rate and blood pressure elevated. Increased production of stress hormones like cortisol, which can damage blood vessels and contribute to hypertension. Failure of blood pressure to return to normal levels after stressful events, leading to sustained elevations. Over time, this constant impact of stress on the body can affect the cardiovascular system and cause the blood vessel walls to thicken and lose elasticity, increasing your risk of hypertension. Behavioral responses to stress The impact of stress on the body often prompts unhealthy behaviours that can further exacerbate hypertension risk: Overeating or consuming high-sodium comfort foods Neglecting physical activity Smoking or excessive alcohol consumption as coping mechanisms Poor sleep habits These behaviours can directly contribute to high blood pressure or indirectly influence it by leading to weight gain and other risk factors. Direct physiological effects The impact of stress on the body can have direct physiological consequences that contribute to hypertension. The sustained release of stress hormones like cortisol can cause: Increased sodium retention, leading to fluid buildup and elevated blood pressure Insulin resistance, which is associated with hypertension and other metabolic disorders Inflammation and oxidative stress, damaging blood vessels and promoting hypertension These direct physiological effects highlight the complex interplay between stress and hypertension and the importance of addressing chronic stress for effective blood pressure management. Managing stress to control hypertension Effectively managing stress is a key component of hypertension prevention and control. Some strategies for stress management for hypertension include: Practicing relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga Engaging in regular physical exercise, which helps reduce stress and lower blood pressure Maintaining a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins Limiting alcohol consumption and avoiding smoking Prioritising sufficient sleep and establishing a consistent sleep routine Seeking professional support, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy or counseling, to develop coping strategies Conclusion The link between chronic stress and hypertension is well-established, highlighting the significant impact of stress on the body. By understanding the physiological and behavioural ways stress influences blood pressure, you can take proactive steps to manage both stress and hypertension. Combining effective stress management techniques with a heart-healthy lifestyle and regular check-ups can help keep your blood pressure under control. If you are concerned about your blood pressure or the impact of stress on the body, consider reaching out to Metropolis Healthcare for comprehensive diagnostic services and health check-ups. With a commitment to accurate testing and personalised care, Metropolis Healthcare can help you prioritise your well-being and make informed decisions about your health. FAQs Can stress cause high blood pressure? Yes, the chronic impact of stress on the body can lead to high blood pressure over time. When you're stressed, your body releases hormones that temporarily elevate your blood pressure. With repeated or prolonged stress, these temporary increases can cause long-term hypertension. Why is chronic stress harmful to blood pressure? Chronic stress keeps your body in a constant state of fight-or-flight, with stress hormones continuously elevating your heart rate and blood pressure. Over time, this persistent strain on your cardiovascular system can damage blood vessels and lead to hypertension. What are some common symptoms of stress-related hypertension? Stress-related hypertension may not cause noticeable symptoms initially. However, some people may experience headaches, dizziness, chest pain, palpitations, or shortness of breath. It's essential to monitor your blood pressure regularly, as hypertension is often asymptomatic until complications arise. Can high blood pressure caused by stress be reversed? Yes, high blood pressure caused by the impact of stress on the body can often be reversed through a combination of stress management techniques, lifestyle changes, and medication if necessary. Lowering your stress levels, adopting a heart-healthy diet, exercising regularly, and working with your doctor can help bring your blood pressure back to a healthy range.
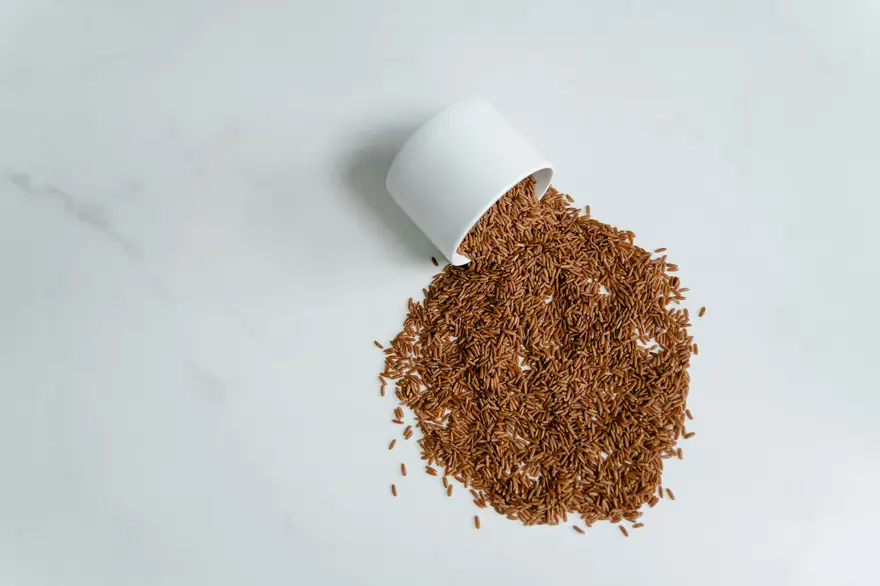
Is Brown Rice Good for Diabetes? How It Can Help Manage Blood Sugar Levels
Introduction For individuals living with diabetes, making informed dietary choices is crucial for managing blood sugar levels and overall health. One common question that arises is, "Is brown rice good for diabetes?" As a nutrient-rich whole grain, brown rice has gained attention for its potential benefits in diabetes management. In this article, we'll explore the properties of brown rice, its impact on blood sugar, and how it can be incorporated into a diabetes-friendly diet. Benefits of brown rice for diabetes Brown rice offers several advantages for individuals with diabetes: High fibre content: Brown rice is an excellent source of dietary fibre, which can help: Slow down digestion and reduce post-meal blood sugar spikes Promote feelings of fullness and support weight management Improve overall digestive health Nutrient-rich: Compared to refined grains, brown rice retains its bran and germ layers, which are packed with essential nutrients. It contains: Magnesium, which may improve insulin sensitivity and lower the risk of diabetes complications B vitamins, which support energy metabolism and nerve function Antioxidants, which help protect cells from damage caused by oxidative stress Lower glycaemic index: The glycaemic index measures how quickly a food raises blood sugar levels. Brown rice has a lower glycaemic index compared to white rice, meaning it causes a slower and more gradual rise in blood glucose. How does brown rice affect blood sugar? When considering "is brown rice good for diabetes patients," it's essential to understand its impact on blood sugar. Here's how brown rice compares to other grains: Brown rice releases glucose into the bloodstream at a slower rate than refined grains like white rice, thanks to its intact bran layer and higher fibre content. Studies have shown that substituting white rice with brown rice can lead to improved blood sugar control and reduced risk of type 2 diabetes. However, portion control remains crucial, as brown rice still contains carbohydrates that can affect blood sugar levels when consumed in excess. Can brown rice help prevent type 2 diabetes? Research suggests that consuming whole grains, including brown rice, may help reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Here's the relation between brown rice and diabetes: The fibre and nutrients in brown rice can improve insulin sensitivity and support healthy blood sugar regulation. Substituting refined grains with whole grains like brown rice may help maintain a healthy body weight, which is a key factor in diabetes prevention. A study found that replacing 50 grams of white rice with brown rice daily was associated with a 16% lower risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Portion sizes and safe consumption To safely incorporate brown rice into a diabetes-friendly diet, consider the following guidelines: Portion control: Aim for about 1/2 cup (100 grams) of cooked brown rice per serving to keep carbohydrate intake in check. Balanced meals: Pair brown rice with non-starchy vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats to create well-rounded, nutrient-dense meals. Monitoring: Regularly check your blood sugar levels and work with your healthcare team to assess how brown rice affects your individual glucose response. Diabetes-friendly brown rice recipes Here are some delicious ways to enjoy brown rice as part of a diabetes-friendly diet: Stir-fries: Combine brown rice with colourful vegetables, lean proteins, and low-sodium seasonings for a nutritious and satisfying meal. Grain bowls: Layer brown rice with roasted vegetables, grilled chicken or tofu, and a drizzle of olive oil for a nourishing and flavourful dish. Salads: Toss cooked and cooled brown rice with fresh greens, diced cucumbers, cherry tomatoes, and a light vinaigrette for a refreshing and fibre-rich salad. Healthy alternatives to brown rice While brown rice is good for diabetes, it's not the only option. If you're looking to mix things up, consider these nutritious alternatives: Quinoa Oats Barley Cauliflower rice Whole-grain pasta Conclusion So, is brown rice good for diabetes? The answer is yes; brown rice can be a valuable addition to a diabetes-friendly diet when consumed in moderation. Its high fibre content, nutrient density, and lower glycaemic index make it a healthier alternative to refined grains. By incorporating brown rice into balanced meals and monitoring portion sizes, individuals with diabetes can enjoy its benefits while effectively managing their blood sugar levels. Remember, every person's dietary needs are unique, so it's essential to work closely with your healthcare team to develop a personalised meal plan. If you have concerns about your blood sugar management or wish to explore diagnostic testing options, consider reaching out to Metropolis Healthcare. With a network of advanced diagnostic labs across India and a team of skilled phlebotomists for at-home sample collection, Metropolis Healthcare is committed to providing accurate results and personalised care to support your health journey. FAQs How much brown rice is safe to eat? For individuals with diabetes, a serving size of about 1/2 cup (100 grams) of cooked brown rice per meal is generally recommended to manage carbohydrate intake effectively. However, it's essential to consider your individual nutritional needs and consult with a doctor for personalised guidance. Is brown rice higher in sugar? No, brown rice is not inherently higher in sugar compared to other rice varieties. In fact, brown rice contains more fibre and nutrients than refined white rice, which can help slow down the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream. Can diabetics eat brown rice daily? While brown rice can be a part of a diabetes-friendly diet, it's important to consume it in moderation and monitor portion sizes. Eating brown rice daily is possible, but it should be balanced with other nutrient-dense foods and aligned with your individual carbohydrates goals. Is brown rice better than chapati for diabetics? Brown rice and whole wheat chapati both offer nutritional benefits for individuals with diabetes. However, brown rice tends to have a lower glycaemic index and higher fibre content compared to refined flour chapatis. Ultimately, the choice between the two depends on personal preferences and overall dietary balance. Which rice is best for diabetics? When it comes to rice options for individuals with diabetes, brown rice is generally preferred over white rice due to its higher fibre content, lower glycaemic index, and nutrient density. Other whole-grain rice varieties, such as wild rice or red rice, can also be suitable choices when consumed in moderation.
Smelly Urine: Causes, Symptoms, and How to Treat It
Introduction Have you noticed an unusual odour in your urine recently? Smelly urine can be a cause for concern, leaving you wondering about the underlying reasons and whether you should see a doctor. While some causes of smelly urine are harmless, others may indicate an underlying health issue that requires medical attention. In this article, we'll explore the common causes of smelly urine, associated symptoms, and when it's time to consult a doctor. What is smelly urine? Smelly urine refers to urine that has a strong, unusual, or unpleasant odour, which can vary depending on the underlying cause. The smell may be described as ammonia-like, sweet, musty, or even fishy. While urine normally has a slight odour, any significant change in smell warrants closer attention. Symptoms of smelly urine Alongside the characteristic odour, smelly urine symptoms may include: Cloudy or discoloured urine Frequent or urgent urination Pain or burning sensation during urination Abdominal discomfort or pain Fever or chills (in case of infection) Common causes of smelly urine Several factors can contribute to smelly urine, ranging from harmless dietary choices to more serious health concerns. Here are some of the most common smelly urine causes: Concentrated urine When you don't drink enough fluids, your urine becomes more concentrated, leading to a stronger ammonia smell. This is usually harmless and can be easily remedied by increasing your water intake. Foods that cause smelly urine Certain foods, such as asparagus, garlic, and onions, contain compounds that can alter the smell of your urine. Coffee and alcohol can also contribute to smelly urine. These odours are typically temporary and not a cause for concern. Medications and supplements Some medications, such as antibiotics and vitamin B6 supplements, can change the odour of your urine. If you notice a sudden change in urine smell after starting a new medication, consult your doctor. Medical conditions linked to smelly urine Smelly urine can be linked to conditions like gout, which produces an ammonia-like odour due to high uric acid levels. Phenylketonuria (PKU) causes a musty smell, while cystitis and prostatitis result in foul odours from bladder or prostate inflammation. Certain medications and dehydration can also alter urine’s scent. Urinary tract infections Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are a common cause of smelly urine, often accompanied by a burning sensation during urination, frequent urges to urinate, and cloudy urine. UTIs occur when bacteria enter the urinary tract and multiply, causing inflammation and infection. Bacterial vaginosis In women, bacterial vaginosis can cause a fishy odour in the urine and vaginal discharge. This condition occurs when there's an overgrowth of harmful bacteria in the vagina, disrupting its natural balance. Diabetes and its effects Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to sweet-smelling urine due to the presence of glucose. When blood sugar levels are high, the body tries to eliminate the excess glucose through urine, resulting in a distinct odour. Liver or kidney problems Liver and kidney disorders can cause changes in urine odour due to the accumulation of toxins that the body is unable to filter effectively. If you notice a persistent change in urine smell accompanied by other symptoms like fatigue, abdominal pain, or swelling, consult your doctor. Trimethylaminuria (fish odour syndrome) Trimethylaminuria is a rare genetic condition that causes a strong fishy odour in urine, sweat, and breath. This disorder affects the body's ability to break down certain compounds, leading to the accumulation of trimethylamine, which has a characteristic fishy smell. Can lifestyle changes like diet or pregnancy cause smelly urine? Certain lifestyle factors can indeed influence the smell of your urine: Eating large amounts of pungent foods like garlic, onions, or asparagus Drinking coffee, alcohol, or sugary beverages in excess Pregnancy, due to hormonal changes and increased likelihood of UTIs Dehydration, which leads to concentrated urine with a stronger odour How to reduce or prevent smelly urine? If you're concerned about smelly urine, there are several steps you can take to minimise the odour and promote urinary tract health: Drink plenty of water Staying hydrated helps flush out bacteria and dilute your urine, reducing the concentration of odour-causing compounds. Aim for at least 8 glasses of water per day. Avoid odour-inducing foods If you notice that certain foods consistently cause smelly urine, consider reducing your intake or avoiding them altogether. Practice good hygiene habits Wiping from front to back after using the restroom and changing out of wet or sweaty clothes promptly can help prevent bacterial growth and reduce the risk of infections that cause smelly urine. Regular bathroom visits Don't hold your urine for long periods. Emptying your bladder regularly helps prevent the buildup of bacteria that can lead to UTIs and smelly urine. Diagnosing the underlying cause If you experience persistent, smelly urine accompanied by other symptoms, your doctor may recommend the following tests: Urine analysis to check for bacteria, blood, or other abnormalities Blood tests to assess kidney and liver function Pelvic exam for women to check for signs of vaginal infections When to see a doctor? While occasional smelly urine is usually not a cause for concern, it's important to seek medical advice if you experience: Persistent foul-smelling urine despite lifestyle changes Pain, burning, or discomfort during urination Cloudy, bloody, or discoloured urine Fever, chills, or abdominal pain accompanying smelly urine Treatment options for smelly urine Smelly urine treatment depends on the underlying cause. Options may include: Antibiotics for bacterial infections like UTIs Antifungal medications for yeast infections Dietary changes and blood sugar management for diabetes Medications to treat liver or kidney problems Counselling and choline supplements for trimethylaminuria Home remedies For mild cases of smelly urine caused by dehydration or dietary factors, simple home remedies can be effective: Increasing water intake Avoiding trigger foods and beverages Practicing good hygiene Medical treatments For more serious conditions, medical interventions may be necessary: Intravenous antibiotics for severe kidney infections Insulin therapy and lifestyle changes for uncontrolled diabetes Surgery to remove blockages or correct anatomical abnormalities in the urinary tract Conclusion Smelly urine can be a sign of various underlying causes, from harmless dietary factors to more serious health concerns. By understanding the potential causes of smelly urine, associated symptoms, and when to seek medical advice, you can take proactive steps towards maintaining your urinary tract health. If you experience persistent, smelly urine symptoms, don't hesitate to consult a doctor for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. At Metropolis Healthcare, we understand the importance of early detection and diagnosis in managing your health. Our state-of-the-art diagnostic facilities and expert team of pathologists are committed to providing reliable, timely results to help you make informed decisions about your well-being. With our convenient at-home sample collection service, you can prioritise your health without compromising on comfort or quality. Take charge of your health today by booking a test or health check-up. Frequently asked questions (FAQs) Why does my urine smell fruity? Fruity-smelling urine can be a sign of uncontrolled diabetes. When blood sugar levels are high, the body tries to eliminate excess glucose through urine, resulting in a sweet, fruity odour. If you consistently notice this smell, consult your doctor for a diabetes screening. Why does my pee burn? A burning sensation during urination is often a sign of a urinary tract infection (UTI) or sexually transmitted infection (STI). Other symptoms may include frequent urges to urinate, cloudy or bloody urine, and pelvic pain. If you experience burning during urination, seek medical advice for proper diagnosis and treatment. Why does my urine smell even when I am hydrated? If your urine has a strong odour despite staying well-hydrated, it may be due to other factors such as your diet, medications, or an underlying medical condition. Certain foods, vitamin supplements, and antibiotics can cause smelly urine. If the odour persists or is accompanied by other symptoms, consult your doctor to rule out any potential health issues.
Groin Pain: Common Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Groin pain is a common complaint that can affect people of all ages, genders, and activity levels. Whether you're an athlete, a desk worker, or a senior citizen, experiencing discomfort in the groin area can be concerning and disruptive to your daily life. Groin pain causes can be varied, ranging from muscle strains and hernias to hip joint problems and urological conditions. Identifying the underlying reason is crucial for proper treatment. This article will provide a comprehensive overview of groin pain symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options, empowering you with the knowledge to manage this condition effectively. What is groin pain? Groin pain is discomfort or soreness in the area where the abdomen meets the upper thigh. This region contains muscles, ligaments, nerves, and organs, making it prone to pain from injury or medical conditions. Groin pain can occur on one or both sides, may develop suddenly or gradually, and vary in intensity from a dull ache to a sharp, stabbing sensation. The characteristics of the pain, such as its location, duration, and severity, often provide clues about the underlying cause. Common groin pain causes include muscle strains, hernias, kidney stones, or nerve issues. Identifying the exact cause is essential for proper groin pain treatment, and consulting a healthcare provider is recommended if the pain persists, worsens, or is accompanied by other concerning symptoms. How common is it? Groin pain is a common complaint, particularly among athletes and individuals engaged in physical activities that involve rapid changes in direction or repetitive movements. However, groin pain can also affect less active individuals due to various non-athletic causes. What causes groin pain? Groin pain causes can vary widely and may include muscle strains, hernias, hip issues, nerve problems, and urinary or reproductive conditions. Gastrointestinal issues, such as appendicitis or kidney stones, can also trigger groin pain. Identifying the exact cause is essential for effective groin pain treatment. Consulting a healthcare provider can help determine the underlying issue and guide appropriate care. Whether the pain is sudden or persistent, understanding its source is key to managing symptoms and promoting recovery. Causes of primary groin pain Athletic or movement-related injuries Muscle strains are a frequent cause of groin pain, particularly in athletes who engage in sports that involve quick directional changes, kicking, and twisting movements. The adductor muscles of the inner thigh are especially prone to strains. Hernias Weaknesses in the abdominal wall can allow internal tissues to protrude, causing a painful groin bulge. Inguinal hernias are the most common conditions for groin pain in males. Hip conditions Problems in the hip joint, such as arthritis, labral tears, and femoroacetabular impingement, can cause groin pain. Nervous system conditions Compression or irritation of the nerves that supply the groin area, such as the ilioinguinal nerve, can lead to groin pain and sensory changes. Urological conditions Kidney stones, infections, and other disorders of the urinary tract may cause pain that radiates to the groin. Gynaecological conditions In women, conditions like ovarian cysts, endometriosis, and pelvic inflammatory disease can be sources of groin discomfort. Gastrointestinal conditions Although less common, some digestive problems like hernias and intestinal inflammation may refer pain to the groin. Causes of secondary groin pain Secondary groin pain can arise from systemic conditions that affect multiple body parts. These conditions may indirectly cause discomfort in the groin area due to referred pain or inflammation. Examples include infections, autoimmune disorders, or certain cancers. What does groin pain feel like? The sensation of groin pain can vary depending on the underlying cause. It may present as a dull ache, a sharp or stabbing pain, or a burning sensation. The pain can be constant or intermittent, and its intensity may fluctuate. Groin pain symptoms often worsen with physical activity, such as walking, running, or climbing stairs, and improve with rest. In some cases, the groin pain may radiate to the inner thigh, lower abdomen, or scrotum. Additionally, individuals may experience stiffness, weakness, or a pulling sensation in the affected area. Diagnosing the source of groin pain Diagnosing the source of groin pain involves a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional. The diagnostic process typically includes a thorough medical history review and physical examination. The doctor may inquire about the onset, duration, and characteristics of the pain, as well as any associated symptoms or aggravating factors. During the physical exam, the healthcare provider will assess the groin area for tenderness, swelling, or visible abnormalities. They may also perform specific tests or manoeuvres to evaluate the range of motion, strength, and stability of the hip joint and surrounding muscles. Imaging tests, such as X-rays, ultrasound, or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), may be ordered to visualise the internal structures and rule out certain conditions. For example, an X-ray can help identify fractures or arthritis, while an MRI can provide detailed images of soft tissues, including muscles, tendons, and ligaments. In some cases, additional diagnostic procedures may be necessary for groin pain. For instance, if a hernia is suspected, the doctor may recommend an ultrasound or a specialised test called a herniography. If a nerve entrapment is suspected, nerve conduction studies or electromyography may be performed to assess nerve function and muscle activity. How do we relieve groin pain? Groin pain treatment approach depends on the specific cause identified. However, some general measures that can help alleviate discomfort include: Rest: Avoiding activities that aggravate the pain and allowing the affected area to heal Ice: Applying cold packs to the groin for 15-20 minutes several times a day to reduce pain and inflammation Heat: Using heat therapy to relax tense muscles and promote circulation Over-the-counter pain relievers: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen can help manage pain and inflammation Physical therapy: Stretching and strengthening exercises can improve flexibility, stability, and support of the groin muscles and surrounding structures. When should we be concerned about groin pain? While most cases of groin pain resolve with conservative measures, some signs warrant prompt medical attention. See a doctor immediately if the pain is severe, comes on suddenly, or is accompanied by fever, chills, nausea, or vomiting. Can groin pain be prevented? Preventing groin pain involves maintaining the strength and flexibility of the muscles and structures in the region. This can be achieved through regular exercise, proper warm-ups before physical activity, and avoiding excessive strain or overuse. Maintaining a healthy body weight and addressing any underlying medical conditions also helps reduce the risk of developing groin pain. When to see a doctor Minor groin pain can often be managed with self-care measures. However, it's important to consult a doctor if the pain persists beyond a few days, gets progressively worse, or interferes with your daily activities. Seek prompt medical care if the groin pain is severe or you notice symptoms like swelling, fever, or difficulty bearing weight on the affected leg. Conclusion Groin pain is a common but potentially debilitating condition that can stem from various musculoskeletal, neural, and organ-related causes. If you're experiencing persistent groin pain, it's crucial to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate groin pain diagnosis and personalised treatment plan. Metropolis Healthcare, with its network of advanced diagnostic labs and skilled technicians across India, can be your trusted partner in this journey. Our state-of-the-art pathology services and convenient at-home sample collection can help identify the root cause of your groin pain, empowering you to take control of your health.
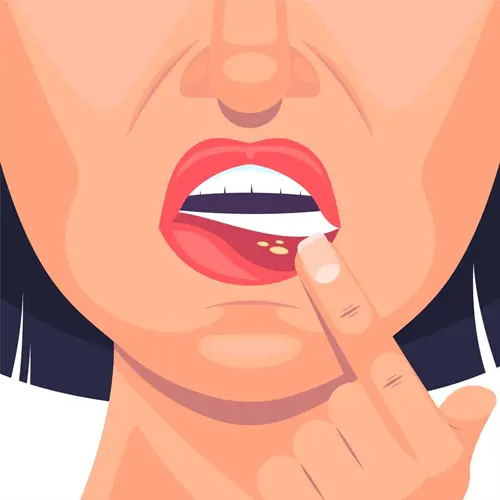
White Spots on Lips: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Noticing white spots on lips can be worrying, leaving you wondering about the underlying cause and whether treatment is needed. While some causes, like Fordyce spots, are harmless, others, like oral thrush, require medical attention. This guide will help you understand the various reasons white bumps on lips may appear, the associated symptoms, and white spots on lips treatment options. Armed with this knowledge, you can take proactive steps to care for your lip health. What are white spots on lips? White spots on lips refer to small, pale bumps or patches that appear on the lips or surrounding skin. They can occur due to several reasons, ranging from benign conditions like Fordyce spots and milia to more serious issues like oral thrush or even oral cancer. The appearance of these white spots on lips can vary, with some being more raised or textured than others. Depending on the underlying cause, they may be accompanied by other symptoms like itching, pain, or dryness. Regularly inspecting your lips and noting any changes is important for early detection and appropriate management. 5 Common Causes of White Spots on Lips Fordyce Spots Main cause of Fordyce spots Fordyce spots are one of the most common white spots on lips causes. These tiny, painless bumps are actually enlarged oil glands called sebaceous glands. They are considered a normal anatomical variation and are not contagious or harmful. Fordyce spots tend to be more noticeable in people with oily skin and typically appear during puberty or adulthood. While the exact cause is unknown, factors like hormonal changes, genetics, and sun damage may play a role. These white bumps on lips are often confused with other conditions like milia or herpes, but a dermatologist can provide an accurate diagnosis. Medical Treatment Since Fordyce spots are benign, medical treatment is generally not necessary unless they cause significant cosmetic concern. In such cases, options like laser therapy, electrodessication, or surgical excision may be considered to reduce the appearance of these white spots on lips. However, it's crucial to weigh the potential risks and costs against the aesthetic benefits. Consulting a dermatologist can help determine if treatment is appropriate for your situation. Home Remedies As Fordyce spots are a natural occurrence and not a sign of poor health, specific home remedies are not required. Maintaining good oral hygiene practices like brushing twice daily, flossing, and using an antiseptic mouthwash can help prevent other lip concerns and keep your smile healthy. If the appearance of these white spots on lips causes distress, using a lip balm or moisturiser can help minimise their prominence. Remember, Fordyce spots are extremely common and are not a cause for embarrassment or alarm. Milia Main cause of Milia Milia are tiny, keratin-filled cysts that appear as white bumps on lips or surrounding skin. They form when dead skin cells become trapped beneath the surface, rather than shedding normally. Milia are common in newborns but can occur in people of all ages. Risk factors include sun damage, skin resurfacing procedures, use of heavy skincare products, and certain medical conditions like rosacea or dermatitis. These pearly white spots on lips are often confused with whiteheads, but milia lack an opening and cannot be effectively extracted at home. Medical Treatment In most cases, milia clear up on their own within a few weeks or months without treatment. However, if these white spots on lips casues cosmetic concern or persist, a dermatologist may recommend extraction, cryotherapy, or laser treatment. Professional removal techniques are more effective and safer than attempting to extract milia at home, which can lead to scarring or infection. If you suspect your lip bumps are milia, consult a skincare professional for personalised guidance and white spots on lips treatment options. Home Remedies While medical extraction is the most effective way to clear milia, some white spots on lips remedy at home may help prevent their formation or encourage natural healing. Gentle exfoliation with a lip scrub or soft toothbrush can help remove dead skin cells and unclog pores. Applying a retinoid cream or face peel containing alpha-hydroxy acids may also promote cell turnover. Canker Sores (Aphthous Ulcers) Main cause of Canker Sores Canker sores, medically known as aphthous ulcers, are small, shallow lesions that develop on the soft tissues of the mouth or lips. Unlike cold sores, canker sores are not contagious and are not caused by the herpes simplex virus. The exact cause is unknown, but triggers may include: Minor injury to the mouth from dental work, hard brushing, or biting Toothpastes and mouthwashes containing sodium lauryl sulfate Food sensitivities, particularly to acidic or spicy foods Vitamin deficiencies, especially B-12, zinc, folic acid, or iron Hormonal shifts during menstrual cycles Emotional stress or lack of sleep Bacterial infections like H. pylori Autoimmune disorders or gastrointestinal diseases While not a direct cause of white spots on lips, canker sores can be mistaken for them in the early stages when they appear as small, round, white or yellowish lesions before developing into painful ulcers. Medical Treatment Most canker sores heal within one to two weeks. Over-the-counter pain relievers, gels, or pastes can ease discomfort and promote healing. For severe or persistent sores, a doctor may recommend corticosteroids, antibacterial mouthwash, or oral medication. Frequent or slow-healing sores may require medical evaluation for underlying issues. Home Remedies To soothe canker sores and promote healing, try home remedies like warm saltwater rinses, baking soda paste, or dabbing milk of magnesia. Honey and aloe vera can also reduce irritation. Avoid spicy or acidic foods. Though often mistaken for white bumps on lips, canker sores aren’t contagious and heal naturally. Oral Thrush (Candidiasis) Main Cause of Oral Thrush Oral thrush is a fungal infection triggered by an overgrowth of Candida species, particularly Candida albicans. While this yeast normally resides in the mouth harmlessly, certain factors can upset the natural balance, allowing Candida to thrive. Common risk factors include weakened immune systems from conditions like HIV/AIDS, diabetes, or cancer. Medications such as corticosteroids or broad-spectrum antibiotics may also disrupt oral flora. Wearing dentures, especially if poorly fitted or unclean, can increase susceptibility. Smoking, dry mouth, and poor oral hygiene are additional contributors, particularly in infants and older adults. Medical Treatment Treating oral thrush promptly is crucial to prevent its spread. Antifungal medications like nystatin or fluconazole are commonly prescribed in the form of lozenges, tablets, or liquid suspensions. These treatments target Candida overgrowth and help restore oral flora balance. Individuals with weakened immune systems or recurrent infections may require extended treatment. Addressing underlying conditions and risk factors is vital for preventing future episodes. Home Remedies Home remedies can complement medical treatment. Rinsing with warm saltwater soothes irritation, while a soft toothbrush minimises discomfort. Cleaning dentures and consuming probiotics, like yoghurt, can support healthy bacteria. Reducing sugar and yeast-rich foods may further curb Candida growth. Practicing good oral hygiene is key to preventing these white bumps on lips. Oral Cancer Main Cause of Oral Cancer Oral cancer is a serious condition that can present as persistent white spots on lips or inside the mouth. While not as common as other causes of lip discolouration, oral cancer can be life-threatening if untreated. Key risk factors include tobacco use (smoking or chewing), heavy alcohol consumption (especially when combined with smoking), and prolonged sun exposure to the lips, particularly in fair-skinned individuals. Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection, especially strains 16 and 18, also increases risk. A weakened immune system due to conditions like HIV/AIDS or certain medications can further heighten vulnerability. Poor oral hygiene and chronic irritation may contribute as well. Medical Treatments Early detection is vital for successful treatment. Regular dental check-ups and self-examinations can help identify concerning white spots on lips or other warning signs. If oral cancer is suspected, a biopsy is typically performed to confirm the diagnosis. Treatment options vary based on the cancer’s stage and location but may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, or immunotherapy. A multidisciplinary care team will create a personalised treatment plan, and follow-up care is crucial to prevent recurrence. Home Remedies While no home remedies can cure oral cancer, healthy habits can help reduce risk and support recovery. Quit smoking, limit alcohol intake, and protect your lips with SPF lip balm. Vitamin Deficiency Main Cause of Vitamin Deficiency While vitamin deficiencies, particularly of B vitamins, can lead to changes in the oral mucosa, their direct association with white spots on lips is less common. However, severe deficiencies in vitamins B2 (riboflavin), B3 (niacin), and B12 (cobalamin) can cause oral symptoms such as inflammation, ulceration, and discolouration. Medical Treatment Treatment for vitamin deficiencies involves replenishing the body's stores of the deficient vitamin(s) under medical supervision. This may include: Oral supplements: Taking vitamin pills or liquids to correct the deficiency Intramuscular injections: In cases of severe vitamin B12 deficiency, injections may be necessary to bypass any absorption issues. Dietary changes: Incorporating vitamin-rich foods into the diet to maintain adequate levels Home Remedies Preventing vitamin deficiencies through a balanced, nutrient-rich diet is the best approach for this type of white spots on lip remedy. Some tips include: Consuming a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats Choosing fortified foods, such as breakfast cereals and plant-based milks Considering a multivitamin supplement, especially for those with restricted diets or absorption issues Consulting a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen Allergic Reactions Main Cause of Allergic Reactions Allergic reactions to certain foods, cosmetics, or oral care products can cause irritation and inflammation of the lips, potentially leading to the appearance of white spots on lips. Common allergens include: Food additives, such as preservatives or artificial colours Fragrances and flavouring agents in lip balms or toothpaste Metals, such as nickel in dental fillings or jewelry Latex in dental dams or gloves Medical Treatment Treatment for allergic reactions on the lips focuses on identifying and avoiding the allergen, as well as managing symptoms. Some medical white spots on lips treatment options include: Antihistamines: Oral or topical antihistamines can help reduce itching, swelling, and inflammation. Corticosteroids: Topical corticosteroid creams or ointments can help alleviate more severe allergic reactions. Allergy testing: Skin prick tests or patch tests can help identify the specific allergen(s) responsible for the reaction. Home Remedies Preventing and managing allergic reactions on the lips can be done through some simple home remedies: Identifying and avoiding known allergens Reading ingredient labels carefully on cosmetics, oral care products, and food items Applying a cold compress to the lips to help reduce swelling and discomfort Using a mild, fragrance-free lip balm to keep the lips moisturised and protected Leukoplakia Main cause of Leukoplakia Leukoplakia is a condition characterised by thick, white patches on the lips, gums, tongue, or inside of the cheeks. While not always harmful, leukoplakia can be a precursor to oral cancer. The primary cause of leukoplakia is chronic irritation of the mucous membranes in the mouth. Risk factors include: Tobacco use (smoking or chewing) Alcohol consumption Ill-fitting dentures Chronic sun exposure to the lips In some cases, leukoplakia may be associated with an underlying health condition, such as HIV/AIDS or Epstein-Barr virus infection. Medical Treatment Treatment for leukoplakia depends on the severity and underlying cause of the condition. Your doctor may recommend: Biopsy to rule out cancer or precancerous changes Removal of the patch (if cancerous or precancerous) Addressing any underlying health conditions Lifestyle changes (e.g., quitting smoking, limiting alcohol) Regular follow-up appointments are essential to monitor for any changes or recurrence of the white patches. Home Remedies While there are no specific home remedies for treating leukoplakia, you can take steps to reduce your risk of developing this condition: Quit smoking and using tobacco products Limit alcohol consumption Maintain good oral hygiene Ensure proper fit of dentures or other dental appliances When to see a doctor? While many causes of white spots on lips are harmless, it's essential to seek medical attention if you experience: Painful or bleeding spots Persistent spots that do not heal within 2-3 weeks Difficulty eating or swallowing Unexplained weight loss Lumps or thickening of the lip tissue Your doctor can perform a thorough evaluation and recommend the appropriate white spots on lips treatment based on the underlying cause. Conclusion White spots on lips can have various causes, ranging from harmless Fordyce spots to more serious conditions like oral cancer. By understanding the potential causes and their symptoms, you can take proactive steps to maintain healthy lips and overall oral health. At Metropolis Healthcare, we understand the importance of early detection and personalised care. Our team of expert pathologists and technicians provide accurate diagnostic services, including blood tests and health check-ups, to help you stay informed about your health. With our convenient at-home sample collection and user-friendly online reports, prioritizing your well-being has never been easier.













 WhatsApp
WhatsApp