Preventive Healthcare
Serological Test: Overview, Differences, Types And Uses
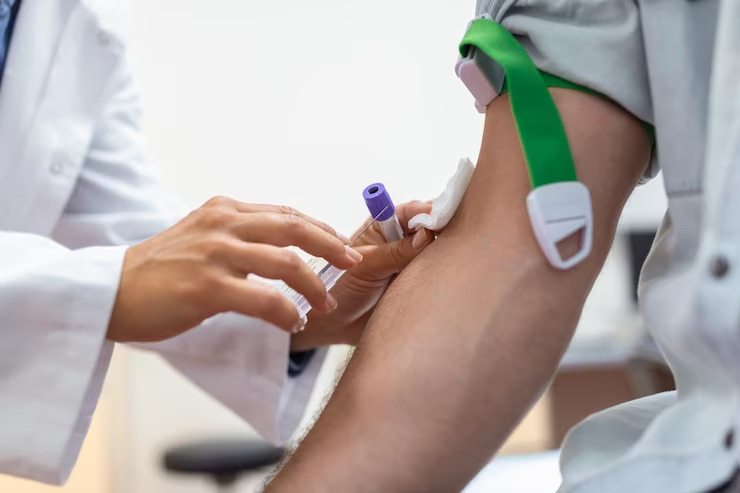
Table of Contents
- What is serology?
- What is a serological test?
- What diseases does a serological test show?
- Primary Vs Secondary Serological Tests
- Different Types of Primary And Secondary Serological Tests
- When is a serological test performed?
- How does a serological test work?
- How do I prepare for this test?
- What should I expect during a serological test?
- What are the risks of a serological test?
- What does a high serological test indicate?
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What is serology?
Serology is the scientific study of blood serum, focusing on the analysis of antibodies and other proteins present in the serum. These antibodies are produced by the immune system in response to foreign substances called antigens, which can be viruses, bacteria, or other pathogens.
The meaning of serological testing lies in its ability to identify the presence of antibodies, which serve as markers of past or current infections, as well as indicators of the body's immune status. By understanding the serology test meaning and its applications, healthcare professionals can diagnose infections, monitor autoimmune disorders, and assess the effectiveness of vaccinations.
What is a serological test?
A serological or serology test, also known as an antibody test or serology blood test, is a laboratory analysis performed on a sample of blood serum to detect the presence of specific antibodies. These tests are crucial in diagnosing various infectious diseases, autoimmune disorders, and other conditions by measuring the immune system's response to specific antigens.
The serology test works by introducing a known antigen to the blood sample and observing whether antibodies in the serum react with the antigen. This reaction can be measured using various techniques, such as enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs), flocculation tests, neutralization tests, and chemiluminescence immunoassays.
What diseases does a serological test show?
Serology tests can detect a wide range of diseases and conditions, including:
- Infectious diseases caused by viruses (e.g., HIV, hepatitis, COVID-19), bacteria (e.g., syphilis, Lyme disease), fungi, and parasites
- Autoimmune disorders, such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and celiac disease, by identifying antibodies that mistakenly attack the body's own tissues
- Blood compatibility issues, including blood typing and screening for transfusion reactions
For example, an HIV serology test can detect antibodies produced in response to the human immunodeficiency virus, helping diagnose HIV infection. Similarly, a hepatitis serology blood test can identify antibodies against hepatitis viruses, indicating current or past infection.
Primary Vs Secondary Serological Tests
|
Aspect |
Primary Serological Tests |
Secondary Serological Tests |
|
Purpose |
Detect the presence of antibodies in a patient's serum |
Confirm the presence of antibodies and determine their type |
|
Use Case |
Diagnostic and screening purposes |
Primarily used for diagnostic purposes |
|
Speed |
Provide rapid diagnosis |
Require more time and resources |
|
Application in Medicine |
Used for initial detection and quick assessments |
Used for confirmation and detailed analysis |
|
Significance |
Important for early detection and mass screening |
Essential for accurate confirmation and specific diagnoses |
Different Types of Primary And Secondary Serological Tests
Serology is the study of serum and other bodily fluids. It is a key part of diagnosing and treating many diseases. There are different types of serological tests, each with its own unique importance. Here is a serology test list compiled for you:
1. Agglutination Test
The first type of serological test is the agglutination test. It is used to identify antigens in a sample. In this test, a reagent containing antibodies is added to a sample of suspected material. If the sample contains the antigen the antibodies will bind to it. They will cause the particles to clump together forming an agglutinate.
2. ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay)
The second type is the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). It is used to measure the presence of specific antibodies or antigens in a sample. This test uses an enzyme-coated plate containing specific antibodies. They bind to the antigen or antibody in the sample. When the antigen or antibody binds to the specific antibody, the enzyme produces a coloured product that can be measured.
3. Hemagglutination Test
The third type of serological test is the hemagglutination test. It is used to measure the presence of antibodies in a serum sample. In this test, a known amount of red blood cells is mixed with the sample. It is then incubated. If the sample contains antibodies, they will bind to the red blood cells. They will cause them to clump together.
4. Precipitin Test
The fourth type is the precipitin test. It is used to identify antigens in a sample. In this test, a reagent containing an antibody is mixed with the sample containing the antigen. If the sample contains the antigen, the antibody will bind to it. It will also form a visible precipitate that can be seen under a microscope.
5. Western Blot Test
The fifth type is the western blot test. Western blot is another type of serological test. It is used to detect the presence of particular proteins in a sample. It is a more involved process than ELISA. It is often used to confirm the diagnosis of certain diseases.
6. Immunofluorescence Assay (IFA)
Immunofluorescence Assay (IFA) is a serological test. It uses fluorescent dyes to detect the presence and amount of particular antibodies in a sample. It is usually used to diagnose autoimmune diseases. It is a very sensitive method of detection.
7. Flow Cytometry
Flow cytometry is a technology used to detect and measure particles in a sample. It is used in serological testing to measure the number of antibodies present in a sample. It can also be used to measure the size and number of cells in a sample.
8. Radioimmunoassay (RIA)
Radioimmunoassay (RIA) is a powerful technique. It is used to measure the concentration of antigens or antibodies in a sample. It is based on the principle of competitive binding, where an antigen present in the sample competes with a labelled antigen for antibody binding sites. The amount of labelled antigen bound to an antibody can then be determined by measuring the radioactivity associated with it.
When is a serological test performed?
A serology test is performed in various situations, such as when a doctor suspects an infection based on symptoms and wants to confirm the diagnosis. It is also used to screen for immune responses after vaccination to determine if an individual has developed immunity. Additionally, they help detect autoimmune diseases by identifying abnormal antibodies and are crucial for blood typing and compatibility testing before blood transfusions or organ transplants. These tests also play a vital role in epidemiological studies to track the spread of diseases within populations and to monitor the effectiveness of public health interventions.
How does a serological test work?
Serology tests work by detecting specific antibodies or antigens in the blood serum. When the immune system encounters foreign antigens, such as proteins from viruses or bacteria, it produces specific antibodies to fight off the invaders. The serology test mixes the patient's serum with known antigens or antibodies and measures the reaction between them.
How do I prepare for this test?
Preparing for a serology test is generally straightforward, with minimal requirements. Fasting or special diets are usually not necessary unless the test is combined with other blood tests that require fasting. Since serology tests involve a blood draw, it is recommended to stay well-hydrated and wear clothing that allows easy access to the veins in your arm.
What should I expect during a serological test?
During a serology test, a healthcare professional will insert a needle into a vein to draw a small amount of blood into a vial or syringe. The blood sample will be sent to a laboratory for analysis. The procedure usually takes only a few minutes and causes minimal discomfort.
What should I expect after?
After a serology blood test, you may experience some minor side effects at the puncture site, such as bruising or discolouration, soreness or tenderness, or a small amount of bleeding. These side effects are usually mild and resolve within a few days.
Your healthcare provider will receive the test results from the laboratory, usually within a few days to a week, depending on the specific serology test performed. They will then discuss the results with you and recommend any necessary follow-up actions or treatments based on the findings.
What are the risks of a serological test?
Serology tests are generally very safe, with minimal risks. Potential complications may include:
- Mild pain, bruising, or swelling at the puncture site
- Rarely, an infection at the site where the needle was inserted
- Occasionally, individuals may feel dizzy or faint during or shortly after the blood draw
These risks are minimal, and serious complications are extremely uncommon. If you experience persistent pain, swelling, or signs of infection at the puncture site, contact your healthcare provider promptly.
How often should serological tests be done?
The frequency of serological tests depends on various factors, such as:
- The specific disease being monitored (e.g., HIV or hepatitis screening guidelines)
- The need to check immune status after vaccination
- Clinical requirements for monitoring autoimmune diseases or assessing blood transfusion compatibility
Routine serological testing is not typically necessary unless indicated by symptoms, exposure risk, or specific treatment protocols. Your healthcare provider will determine the appropriate frequency of testing based on your individual health needs and medical history.
What does a high serological test indicate?
A high antibody level in a serology test can indicate:
- Recent or past infection with the specific pathogen being tested for
- Successful immune response to a vaccine
- The presence of an autoimmune disorder, depending on the specific antibodies detected
Interpreting serology test results requires expertise and should be done by a qualified healthcare professional. They will consider factors such as the specific antibodies detected, their levels, and the clinical context to make an accurate diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment.
Conclusion
A serological test is typically used to diagnose or monitor infections, autoimmune diseases, and other conditions, such as allergies. It can provide information on the cause and severity of a condition. It can also be used to monitor the effectiveness of treatments.
In addition, serological tests are also used to detect previous exposure to a particular infectious agent. This is especially important in the study and management of infectious diseases such as HIV, hepatitis, and tuberculosis. By determining the presence and concentration of antibodies, health professionals can gain important insight into the progression of an illness, as well as the effectiveness of treatments.
In addition to this, serological tests are also frequently used in pregnancy. This is done to screen for certain infectious diseases that can affect the health of both the mother and the baby. In such cases, these tests can detect the presence of antibodies in the mother's blood. This can provide an indication of exposure to certain diseases.
To sum up, serological tests are a vital tool for medical and healthcare investigations. They are used to diagnose and monitor infectious diseases. They can also provide information about previous exposure to specific agents.
FAQs
What is the most common serology test?
One of the most common serology tests is the ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay), which is used to detect antibodies against various infectious agents, such as HIV, hepatitis viruses, and SARS-CoV-2 (the virus that causes COVID-19). ELISA tests are widely used due to their high sensitivity, specificity, and ability to process large numbers of samples simultaneously.
What is a serology blood type test?
A serology blood type test, also known as blood typing or blood grouping, is a serological test that determines an individual's blood group (A, B, AB, or O) and Rh factor (positive or negative). This test is essential for ensuring compatibility in blood transfusions and for identifying potential risks during pregnancy, such as Rh incompatibility between the mother and foetus.
Why is it called serology?
The term "serology" comes from the Latin word "serum", which refers to the clear, yellowish fluid that remains after blood clots. Serology tests focus on analysing the antibodies and other proteins present in the blood serum, hence the name "serology". The study of serum and its components has been crucial in understanding the body's immune response and in diagnosing various diseases.
What is the cost of a serology test?
The serology test price varies depending on factors such as the specific test performed, the laboratory conducting the analysis, and the healthcare provider or institution ordering the test. In India, the cost of a serology test can range from a few hundred to several thousand rupees.