Preventive Healthcare
Septic Arthritis: Symptoms, Causes, Risk Factors & Treatment Options
1256 Views
0
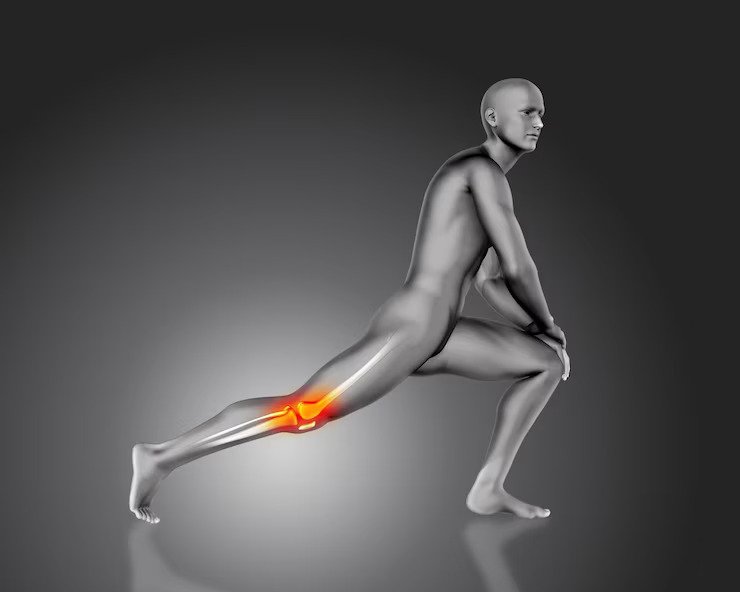
Septic arthritis is a rare and severe infection that affects a person's joints. It can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi that enter the body and spread to the joints through the bloodstream. This causes pain and inflammation in the affected joints and reduces their mobility and normal functioning.
Septic arthritis usually affects the larger joints such as the hip and the knee, but the infection can also spread to your other joints. It is more common in children and in elderly people who have weak immunity.
But do not worry. Septic arthritis can be treated if it is diagnosed early. So read on further to know all about the symptoms, causes, and possible treatment options for septic arthritis.
Symptoms of Septic Arthritis
The symptoms of this disorder vary according to your age, the severity of the infection, and the medications that you take. Common septic arthritis symptoms include
- Swelling and redness around any of your joints.
- The affected joint feels warm and has a limited range of motion.
- Severe joint pain that worsens when you try to move.
- Fever and chills.
- Decreased appetite.
- A rapid heart rate.
- General weakness and fatigue while performing routine tasks.
Causes and Risk Factors of Septic Arthritis
Septic arthritis is caused due to an infection in the body. Common septic arthritis causes include infection due to bacteria, viruses, fungi, or other pathogens. The microorganisms that usually cause septic arthritis are Staphylococcus aureus, MRSA, and group A and B streptococci.
Some people are more likely to get this infection. Septic arthritis is more common in young children and elderly people. The risk factors that can make you more susceptible to this infection include:
- Having joint problems due to arthritis or osteoporosis, or having a history of joint surgery. These issues can weaken the joints and increase the risk of contracting septic arthritis.
- Having open wounds and a compromised skin barrier due to skin diseases can cause pathogens to easily enter the body and cause infection.
- Consumption of alcohol, tobacco, and illegal drugs is another risk factor. Intravenous drug use can introduce harmful bacteria and other pathogens into your bloodstream.
- Having diabetes, cancer, or HIV can result in a weak immune system and increase the chances of infection and developing septic arthritis.
Treatment Options For Septic Arthritis
Septic arthritis needs to be treated aggressively to prevent any risk of permanent damage to the joints and restore their normal functioning. Your doctor can prescribe one or multiple treatment options based on the severity of the infection and how well you respond to them. The treatment options include
Prescription Drugs
This is usually the first line of treatment in case of bacterial or fungal infection. Your doctor will prescribe a course of antibiotics to kill the pathogens in the affected joints.
There are two ways to administer antibiotics. Your doctor can give intravenous antibiotics that directly enter the bloodstream and treat the infection quickly. A course of oral antibiotics can also be prescribed for a duration of six to eight weeks.
Synovial Fluid Drainage
Synovial fluid is the liquid present between the joints. During septic arthritis, it gets infected and often needs to be drained out. To do this, your doctor will make small incisions around the affected joint and drain the infected fluid using a suction tube.
Surgical Treatment
If the above methods are unable to completely treat the infection, then open surgery is performed. This helps drain any remaining infected fluid. The doctor can also replace the damaged sections of the joint or even the entire joint once the infection is treated.
Post-surgery care includes the use of anti-inflammatory drugs, splinting the joint, and consistent physical therapy to regain adequate strength and mobility of the joints.
Diagnosis of Septic Arthritis
There are multiple ways to diagnose septic arthritis. The doctor will first physically examine your joints to check their mobility and look for any signs of swelling and redness. If an infection is suspected, diagnostic tests are carried out to reach a conclusion. Common tests include:
Synovial Fluid Aspiration
In this, your doctor withdraws synovial fluid (the liquid present around your joints) with a fine needle. The fluid is then sent to the laboratory and checked for bacteria or other pathogens. The presence of pathogens in the synovial fluid confirms the diagnosis of septic arthritis.
Blood Test
This is another diagnostic method of septic arthritis. A blood test can determine if your immune system is responding to an infection and figure out any other anomalies. A high white blood cell (WBC) count usually indicates the presence of an infection.
X-Ray, MRI, and Ultrasound
A combination of these procedures can help the doctor make an accurate assessment of the spread of the infection. Once septic arthritis is confirmed, your doctor will figure out a treatment plan that works best for you.
Conclusion
Septic arthritis is a serious but treatable condition if diagnosed early and treated properly. Untreated septic arthritis can cause permanent damage to the joints and a host of other problems. As a result, it is important to be aware of the risk factors and symptoms of this condition.
What you need to do is be vigilant and take a few precautions. Maintain a healthy lifestyle and practice good hygiene. This can reduce the risk of pathogens entering your body and causing infections. Have a consistent exercise and mobility routine to maintain the strength of your joints.
Contact a medical professional if you notice any pain and swelling in your joints. Your doctor will help diagnose the cause and figure out the best treatment plan for you.













1701259759.webp)









 WhatsApp
WhatsApp