Preventive Healthcare
Inflammation: What It Is, Types, Causes, Symptoms And Treatment
9503 Views
0
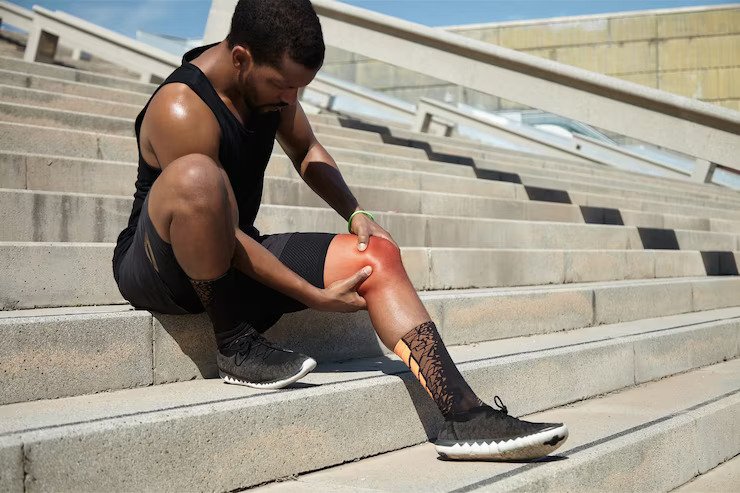

What is Inflammation?
When the body detects an offending agent or an intruder like a virus, bacteria, pathogen, or injury from a foreign body (thorn or toxic chemical), it activates the immune system. The immune system releases inflammatory cells and cytokines (elements that fuel more inflammatory cells) to combat intruders. As the cells begin their protective process, the result can be redness, swelling, pain, or bruising.
Sometimes, the human body perceives its tissues and cells as harmful and begins an inflammatory response. This causes a reaction that further leads to autoimmune diseases. Inflammation, therefore, contributes to several chronic diseases like type 1 and 2 diabetes, obesity, and heart diseases.
Read along to understand more about inflammation, its causes, symptoms, and measures to resolve it.
Types of Inflammation
Inflammation can be broadly categorised into two types: Acute inflammation (short-lived) and chronic inflammation (long-lasting). While acute inflammation will go on for a few hours or a couple of days, chronic inflammation can last for several months and years. Here are the differences and examples to understand both types of inflammation:
i) Acute inflammation: During any sudden body damage, like pricking of thorns or cutting your finger, the inflammatory cells are sent out by the body to heal the area. The cells instantly work towards healing the cut or bruise.
ii) Chronic inflammation: If the body continues to send out inflammatory cells and cytokines even if there is no outside danger, it causes chronic inflammation. For instance, in rheumatoid arthritis, the cytokines and inflammatory cells attack joint tissues. These attacks lead to reoccurring inflammation leading to severe damage, deformity, and joint pain.
Causes of Inflammation
The causes of acute inflammation are the following:
- Exposure to a foreign substance (thorn, dust, or a bee sting)
- A microbial invasion or infection
- An injury causing tissue damage
The causes of chronic inflammation are the following:
- Autoimmune disorders like psoriasis or lupus are where the body mistakenly attacks normal and healthy tissue.
- Exposure to toxins, industrial chemicals, or pollution.
- Untreated injury, infection, or other acute inflammation.
- Certain lifestyle habits and factors contribute to chronic inflammation, like:
- Excessive drinking (alcohol) and smoking habits
- Higher body mass index (BMI) that ranges in obesity
- Over-exercising or not exercising at all
- Stress and tension
It’s important to note that certain factors increase the risk of chronic inflammation. Some of them include the following:
- Obesity
- Older age
- An unhealthy diet that’s loaded with added sugar and fats
- Low sex hormones
- Sleep problems
While inflammation plays a vital role in healing, chronic inflammation can wreak havoc on health! It may lead to the increase of various long-term diseases, including:
- Tuberculosis
- Atherosclerosis
- Some cancers
- Periodontitis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Hay fever
- Asthma
- Chronic peptic ulcer
- Active hepatitis
- Ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease
- Sinusitis
Symptoms of Inflammation
Acute inflammation may cause:
- Heat at the site of the injury
- Flushed skin
- Swelling
- Pain or tenderness.
Chronic inflammation symptoms are more difficult to spot than the symptoms of acute inflammation. Chronic inflammation may cause:
- Chest pain
- Abdominal pain
- Fever (example: tuberculosis)
- Mouth sores (example: HIV infection)
- Joint pain or stiffness (example: rheumatoid arthritis)
- Skin rash (example: psoriasis)
- Fatigue (example: systemic lupus)
Treatment of Inflammation
Inflammation does not typically require any treatment or medicine. For instance, the symptoms of acute inflammation can be treated with ample rest, the application of ice, and good wound care. However, if you have chronic inflammation, your doctor might recommend any of the following treatments depending on your condition:
i) Supplements: Vitamins like A, C, and Vitamin D and supplements like zinc are known for their repair-enhancing properties and reducing inflammation.
ii) Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Some over-the-counter medicines have been proven to lower inflammation. Your doctor may recommend naproxen, ibuprofen, or aspirin.
iii) Steroid injections: Shots like corticosteroids decrease inflammation at a specific muscle or joint. For instance, if you have rheumatoid arthritis that causes back-related problems, your doctor may recommend a steroid shot in your spine. However, you must not take more than three to four steroid injections in the same spot per year.
Conclusion
Inflammation is an imperative part of the body’s healing process. The procedure happens when the inflammatory cells travel to fight any foreign body like bacteria or to heal an injury. If the inflammatory cells are present for a long duration, it may lead to chronic inflammation. To reduce the symptoms of inflammation, you must eat lots of inflammatory foods like nuts, fatty fish, leafy green veggies, olive oil, and fruits.
FAQs
What is Bladder Inflammation?
Bladder inflammation is typically caused by a bladder infection. The common term for bladder inflammation is cystitis which is one of the urinary tract infections (UTI). Bladder inflammation generally affects women more, and mild cases don’t always require treatment.
What Can Help in Relieving Bladder Inflammation?
Bladder inflammation or cystitis pain can be relieved with NSAIDs like naproxen, sodium or ibuprofen. Doctors also recommend tricyclic antidepressants such as imipramine or amitriptyline for bladder relaxation and blocking pain.
Can Hormones Cause Bladder Inflammation?
Oestrogen hormones have a significant role in inflammation. Whenever there is a hormonal imbalance in your body, you may be at higher risk of inflammation, which can also lead to bladder inflammation.
What Foods Can Aggravate Inflammation?
- Highly processed foods
- Fried foods
- Red meat
- Foods and drinks with added sugar
- Saturated and trans fats
- Unhealthy fats
- Refined carbs like pastries, sugar, or white bread
Is Acute Inflammation Painful?
Acute inflammation causes various types of pain with various severities. The pain ranges from throbbing and pulsating, constant and steady, to pinching and stabbing. These pains occur due to the build-up of fluids that leads to swelling of tissues that push against the sensitive nerve endings. Moreover, during any episode of inflammation, several biochemical processes affect the nerve and contribute to the pain.
How Can I Decrease The Risk of Chronic Inflammation?
You may prevent chronic inflammation with healthy lifestyle habits like:
- Quitting or avoiding smoking
- Quitting or limiting alcohol intake
- Maintaining an ideal weight
- Exercising daily or regularly
- Managing stress with meditation or journaling


















 WhatsApp
WhatsApp