Preventive Healthcare
Eczema: What It Is?, Symptoms, Causes, Treatment & Diagnosis
11279 Views
0
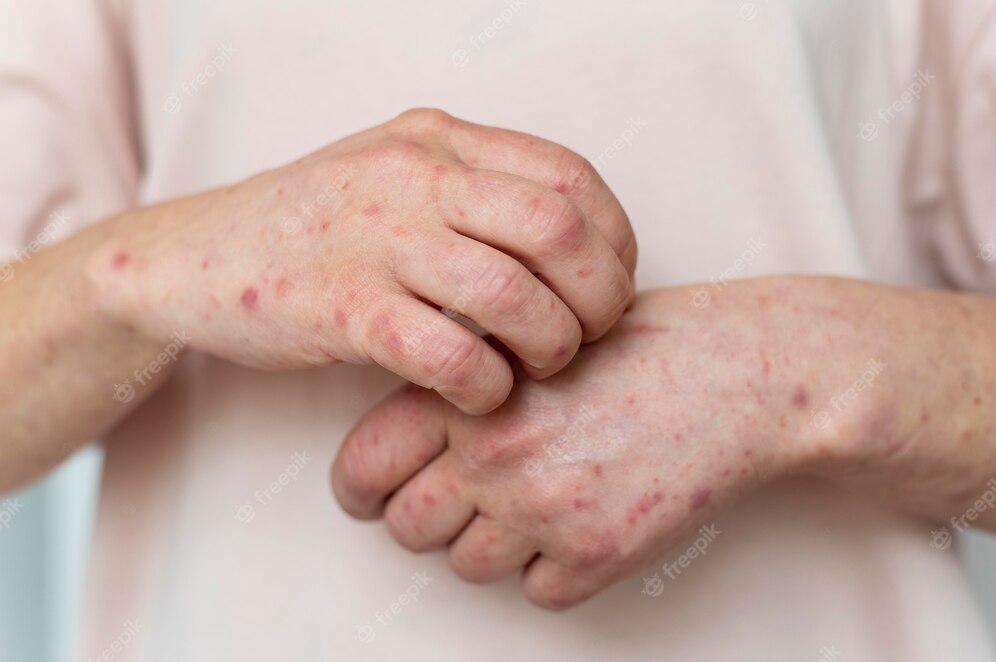
What is Eczema?
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis (AD), is a common skin condition characterised by dry, itchy and inflamed skin. Eczema can appear anywhere on the body and can vary in severity from mild irritation to severe, painful symptoms that can significantly impact a person's quality of life. The exact cause of eczema is not fully understood but it is believed to be a combination of genetic, environmental and immune system factors. Eczema is not contagious and can be managed with proper treatment and lifestyle changes.
Symptoms of Eczema
Symptoms of eczema can vary from person to person but commonly include:
- Dry, red and inflamed skin
- Blisters
- Cracked or scaly skin
- Swelling
- Oozing or crusting
- Itchiness (pruritus)
- Rashes on swollen skin (varies in colour depending on your skin colour)
- Small, raised bumps on brown or black skin
- Thickened skin
- Darkening of the skin around the eyes
- Raw, sensitive skin from scratching
Causes of Eczema
Atopic dermatitis is brought on by a complex interplay of genetic, immunological and environmental factors.
1. Genetics
Eczema tends to run in families, suggesting a genetic component to the condition.
2. Environmental factors
Environmental factors such as individual use of personal care products, soaps, detergents, exposure to climate, pollution, food and other allergens can trigger or exacerbate eczema symptoms.
3. Immune system dysfunction
Eczema is thought to be caused by an overactive immune response to irritants or allergens, leading to inflammation and skin damage.
4. Psychological stress
Your skin's health might be impacted by your emotional well-being, which could lead to an escalation of symptoms. You may experience eczema flare-ups more often if you experience high levels of stress or anxiety.
When Should You See Your Doctor?
You should see a doctor regarding eczema if you or your loved one:
- Have severe itching and discomfort.
- Notice signs of infection (such as oozing, crusting or pus),
- Have eczema in sensitive areas like around the eyes.
- Have symptoms that interfere with sleep and day-to-day activities.
- Have symptoms despite using self-care measures.
Diagnosis of Eczema
Your doctor will diagnose the condition with a combination of physical examinations, a review of medical history and blood tests (IgE tests). In some cases, a skin biopsy may also be performed to help confirm the diagnosis of eczema.
Here is how the diagnosis of eczema is carried out:
1. Physical Examination by a Dermatologist
A doctor may first examine your skin to look for signs of eczema, such as redness, scaling or flaking.
2. Review of Medical History
Your doctor may then ask about your symptoms, family history of eczema and any other medical conditions you have.
3. Blood Tests to Rule out Other Conditions
Next, blood tests may be performed to rule out other conditions that can cause skin irritation, such as allergies or infections. The doctor would suggest the following allergy screening test:
Immunoglobulin E (IgE) tests: IgE tests, also known as allergy blood tests, are diagnostic tests that measure the levels of immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies in the blood. These antibodies are produced by the immune system in response to allergens, which are substances that can cause an allergic reaction. IgE tests can help identify specific allergens that may be triggering allergic reactions, including those that can cause eczema.
The results of IgE tests can help guide the treatment and management of allergies, including the avoidance of specific allergens and the use of medications to reduce symptoms.
Treatment Options For Eczema
After the physical examination and IgE tests are done and the results are out, your doctor will suggest treatment options based on the results.
The most common treatment options for eczema are:
1. Topical Creams and Ointments
Moisturizers, corticosteroids and other topical medications can help soothe skin and reduce inflammation.
2. Oral Medications
In some cases, oral medications such as antihistamines, immune suppressants or antibiotics may be prescribed to treat severe or persistent symptoms.
3. Lifestyle Changes
Avoiding irritants and allergens that trigger eczema. The following tips might lessen the drying effects of bathing:
- Taking lukewarm baths with gentle cleansers
- Applying moisturisers regularly at least twice a day
- Taking a bath or shower daily
- Gently patting the skin with a soft towel after bathing
Studies suggest dietary recommendations that could reduce the symptoms of atopic dermatitis such as:
- Adequate chewing between bites
- Avoiding excessive consumption of sweets, alcohol, coffee, juice, meats and fats
- Avoiding processed foods and additives
Conclusion
Eczema is a common skin condition that can cause a range of symptoms. Diagnosis involves a combination of physical examination, medical history and sometimes blood tests. Treatment options vary depending on the severity of the condition and may include medication and lifestyle changes.
Are you tired of constantly suffering from the uncomfortable and irritating symptoms of eczema? Consider getting an allergy screening test or IgE test from Metropolis Health! Many cases of eczema are caused by allergies and an allergy screening test can help identify the specific allergens triggering your symptoms. With this knowledge, you can take steps to avoid these triggers and find relief from your eczema.
Take control of your health today and schedule an IgE test (done using a highly advanced ImmunoCAP™ machine) with Metropolis Labs!













1701259759.webp)









 WhatsApp
WhatsApp