Preventive Healthcare
What is Neonatal Jaundice: Causes, Treatment, Prevention, Types and Symptoms
3966 Views
0
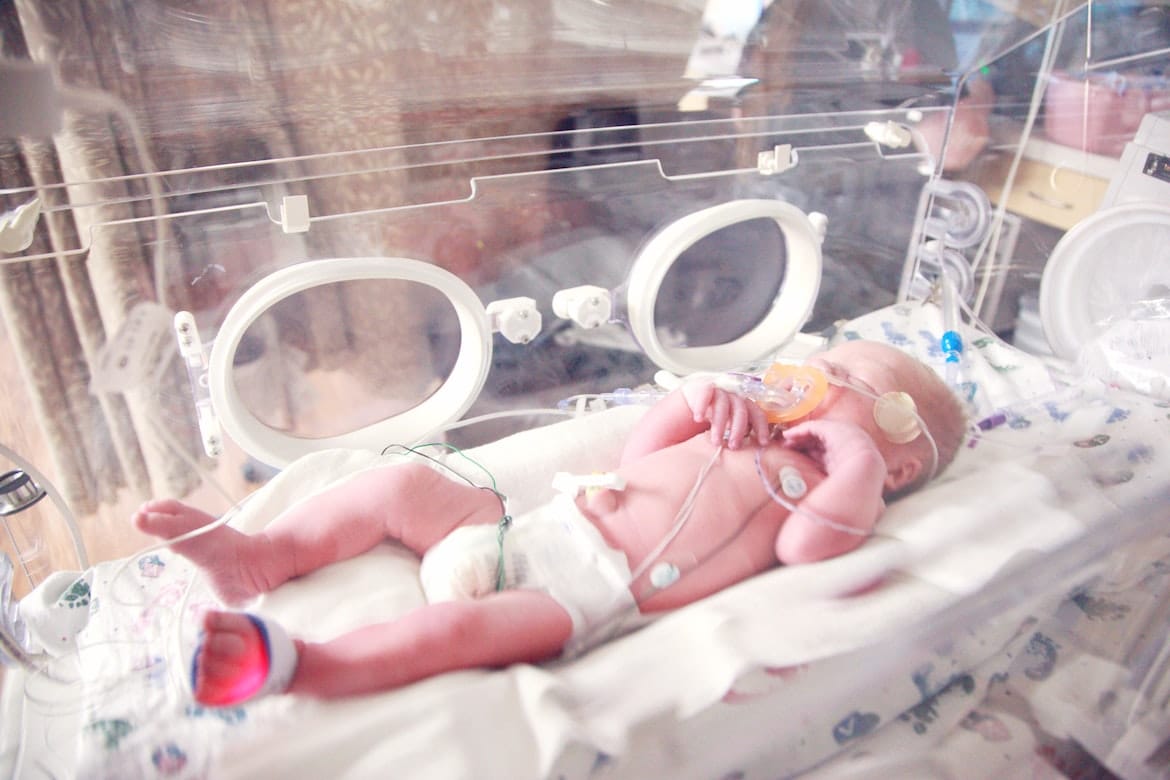
You may think that neonatal jaundice is dangerous. Jaundice among newborn babies is a common medical condition, and you should not worry much. However, there are certain things that you should be aware of.
Almost 50% of term babies and 80% of preterm babies develop neonatal jaundice.
Although it is not serious, you cannot neglect it. Simple neonatal jaundice may indicate underlying conditions like infections, low oxygen levels, serious liver conditions and even brain damage.
What is neonatal jaundice?
Neonatal jaundice is a widespread medical condition among newborn babies. Almost every baby develops jaundice within 2 to 4 days of their birth. Moreover, babies born under 34 weeks are likely to develop neonatal jaundice. It is also called infant jaundice.
Jaundice is a medical condition where you can see a yellowish tone on the skin and eyes of the patient. Hence, if you see your baby's body colour changing, take your baby to a good paediatrician.
Types of neonatal jaundice
Here are three types of neonatal jaundice:
- Physiological jaundice: This is the most common jaundice among newborn babies. Babies develop physiological jaundice within 2 to 3 days after birth. This a common condition when the body cannot remove excess bilirubin. Slowly their liver starts maturing, and they remove excess bilirubin. It resolves within two weeks without any medicine. Physiological jaundice is not severe.
- Breastmilk jaundice: Your baby may develop breastmilk jaundice if they cannot process your milk. That is to say, there may be certain substances in your breast milk that make it hard for your baby's liver to break down the bilirubin. As a result, your baby's body is building up excess bilirubin. You don't have to worry about it as it resolves within one month. This type of jaundice develops among babies who are one week old.
- Breastfeeding jaundice: Breastfeeding jaundice may develop in your one-week-old baby if they don't get enough breast milk. This case is typical among babies who are under exclusive breastfeeding. Formula-fed babies do not have this jaundice. If your body cannot produce sufficient milk or you face problems in nursing, the chances of developing this type of jaundice increase. It may take more than a month to cure.
- Pathological jaundice Other underlying medical conditions may develop pathological jaundice.
Causes of neonatal jaundice
Neonatal jaundice is caused when your baby cannot remove excess bilirubin from their blood. This excess bilirubin is then deposited on the skin layers. You may think, why can't your baby remove the different substances? This is because, during your pregnancy, your body eliminates excess bilirubin from your as well as your baby's body.
But after birth, if your baby is preterm, their liver is not fully developed. As a result, their liver finds it difficult to break the bilirubin. Your baby starts showing a yellowish tone. Usually, it goes within a week. However, there may be other possible causes of jaundice in your baby:
- A rare blood type
- Internal haemorrhage
- Blood infection
- Excessive presence of red blood cells
- Liver conditions like biliary atresia
- Low oxygen level
- Difficult birth and bruising
- Gilbert's syndrome
- Breastmilk
- Difficulty in breastfeeding
- Diabetes during pregnancy
- Congenital hypothyroidism
Risk factors
Certain factors may increase the chance of jaundice in your baby.
- Premature delivery
- Larger-than-normal body
- Down's Syndrome
- Asian descent
Potential complications
Since neonatal jaundice is not that serious, you can rest assured. However, certain medical complications may develop in your baby if you neglect the symptoms:
- Bilirubin Encephalopathy
- Kernicterus
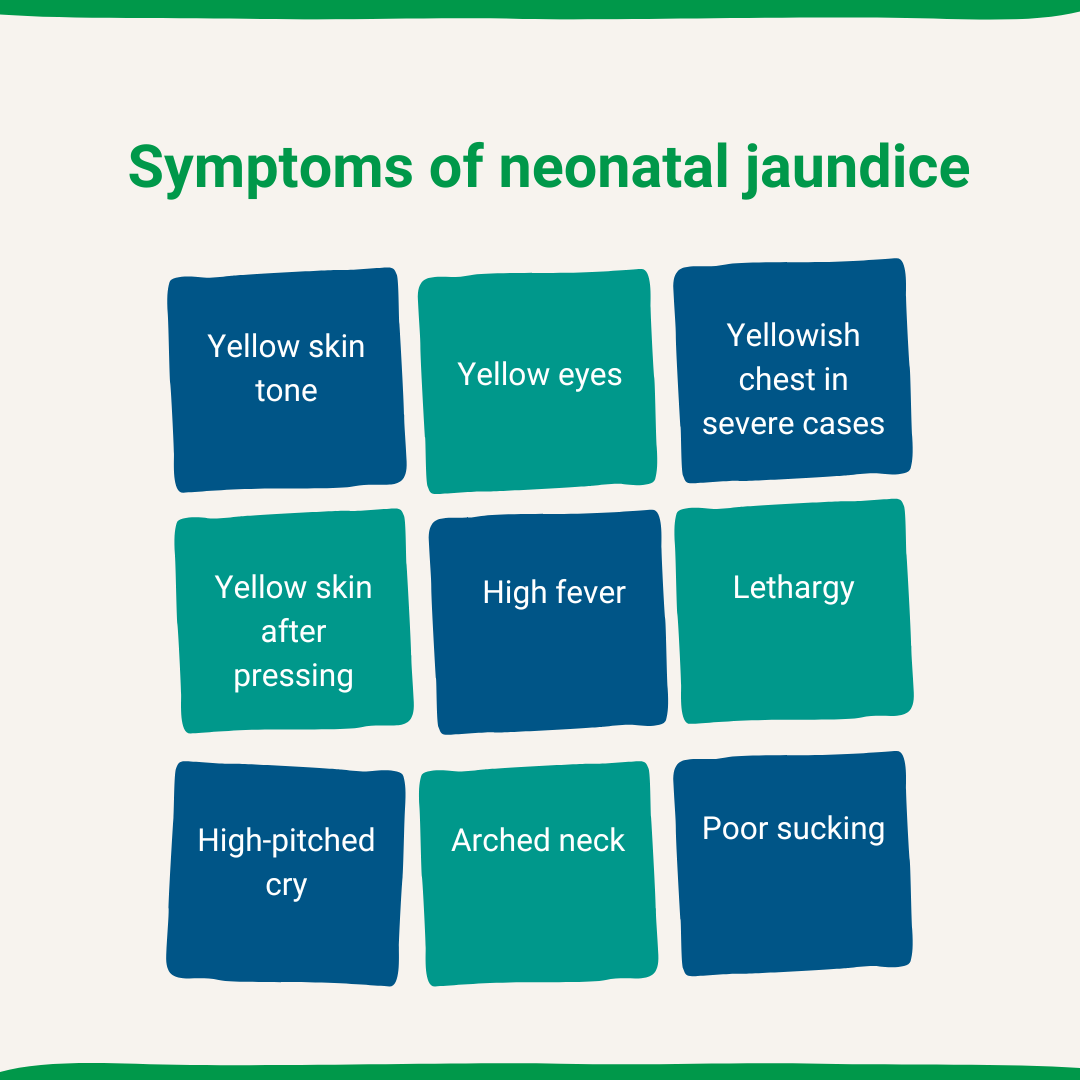
Symptoms of neonatal jaundice
Take your baby to your nearest paediatrician if you spot any of the following symptoms:
- Yellow skin tone
- Yellow eyes
- Yellowish chest in severe cases
- Yellow skin after pressing
- High fever (100 Degrees F)
- Lethargy
- High-pitched cry
- Arched neck
- Poor sucking
Diagnosis and treatment
Your paediatrician will prescribe different tests based on the severity of the jaundice. There are mainly three types of diagnosis methods for jaundice:
- Physical test
- Blood test
- Urine test in severe cases
- Skin test on transcutaneous bilirubin meter
Doctors conduct treatment based on the cause of the jaundice.
- Phototherapy
- Intravenous immunoglobulin
- Exchange transfusion
- Frequent breastfeeding
- Treatment of other underlying causes
What should you do?
Unfortunately, you cannot prevent or even avoid neonatal physiological jaundice. But you can reduce the chances by following this:
- Increase the frequency of breastfeeding. Try to breastfeed your baby 8 to 12 times a day.
- Feed formula if your baby constantly loses weight or can't suck properly.
However, don't try to experiment with your baby. Consult a paediatrician first and act accordingly.
To sum up
There is nothing to worry about your baby's jaundice if you have delivered a healthy baby without any prior complications. If your baby develops jaundice after a day of birth, it's all right. However, you must take immediate action if your baby develops jaundice at home.
Metropolis Healthcare is one of India's leading diagnostic centres. Visit your nearest Metropolis Healthcare Centre for any pathological test. They have a good reputation for satisfying their clients. They assure the maximum safety of your infants.






















 WhatsApp
WhatsApp