Preventive Healthcare
Understanding Knee Pain: Causes, Treatment, and Types
1966 Views
0
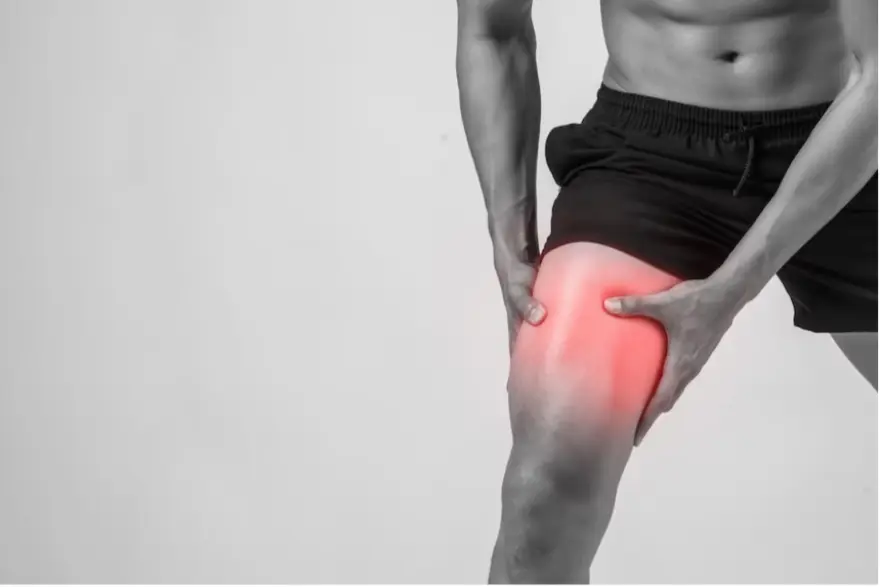
Knee pain is a common problem that affects people of all ages. If you have ever experienced knee pain, you know how it can affect your daily life. Whether it's a dull pain or a sharp twinge, it is important to clearly know all about the knee pain to effectively treat this condition.
In this article, we will discuss the knee pain causes, various types of knee pain, and most importantly how you can find relief. We will also discuss knee pain in ladies.
What is knee pain?
Knee pain is a common problem that can range from mild discomfort to severe agony. It is often caused by the wear and tear of the knee joint, which plays a crucial role in supporting your body weight and facilitating movements. The pain thus caused can spread to the entire knee.
What are the most common causes of knee pain?
Knee pain causes can be many and several factors lead to knee pain. Being overweight can put you at a greater risk for knee issues. Overuse or injuries such as sprains, strains, and tears can also be the causes.
Medical conditions such as arthritis both osteoarthritis (a degenerative joint condition causing cartilage wear and pain) and rheumatoid arthritis (chronic inflammatory disorder affecting joints that causes swelling, redness, and pain in the joints)can also lead to chronic knee pain.
Additionally, underlying medical conditions, like gout (a type of arthritis) happen when there's too much uric acid in your blood. It leads to painful swelling and stiffness in your joints, often affecting the big toe) or infections, which may cause knee discomfort.
What are the types of knee pain?
Knee pain symptoms and causes are different and specific for every individual. Some common types of knee pain include:
- Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome (PFPS): Often referred to as "runner's knee," PFPS results from the misalignment of the kneecap. It is the most common knee pain in ladies. It is known that females experience it around 2.5 times more frequently than males.
- Ligament Injuries: Injuries to ligaments (strong, stretchy bands that connect bones, providing stability to your joints), such as the ACL or MCL, can cause intense knee pain and instability.
- Meniscus Tears: The meniscus, rubbery cartilage, which is a smooth, rubbery tissue that cushions and protects the joints in your body can tear due to sudden twists or aging.
- Bursitis: Inflammation of the bursae, small fluid-filled sacs that cushion the knee joint, leads to pain and swelling.
How is knee pain treated?
Treatment needed for knee pain depends on its causes. Your doctor will recommend knee pain treatment based on the severity of your pain, condition, and the cause. Here are a few things which your doctor may suggest you to follow:
RICE Method for Knee Pain
Rest: Give your knee the rest it needs to heal by avoiding activities that worsen the pain.
Ice: Apply ice to the affected area for 15-20 minutes every 2-3 hours to reduce swelling and numb the pain.
Compression: Use a compression bandage to minimise swelling and provide support to the injured knee.
Elevation: Keep your knee elevated above the level of your heart to reduce swelling.
Medications for Knee Pain
Your doctor may recommend you to take prescribed medications to manage inflammation and underlying conditions.
If you are taking over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen to alleviate mild to moderate knee pain, make sure not to take them for more than 10 days in a row if you have liver and kidney problems.
Knee Braces
A knee brace supports your knee and holds it in place, thus maintaining alignment. Knee braces are usually constructed from rigid plastic or metal, they also feature cushions and straps wrapping around your knee and leg.
Knee braces come in various types, such as sleeves, hinged braces, and wraparound braces. Your doctor will suggest to you the right type of brace you need and how often you should wear it.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is particularly beneficial for recovering from injuries or surgeries. Also, your doctor may suggest physical therapy if you have arthritis. Your physical therapist will guide you on how to perform the exercise that can strengthen the muscles around the knee, improving flexibility and reducing pain.
Knee Surgery
In severe cases, when conservative treatments fail, surgical intervention may be necessary. Procedures range from arthroscopy (a minimally invasive procedure using a tiny camera to examine or treat joint issues) to repair ligaments or remove damaged cartilage to total knee replacement for advanced arthritis.
How can I prevent knee pain?
Preventing knee pain involves adopting healthy habits:
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Engage in regular exercise to strengthen your leg muscles.
- Avoid excessive high-impact activities.
- Ensure proper warm-up and stretching before physical activities to reduce the risk of injuries.
When to call the doctor for knee pain?
While many cases of knee pain can be managed at home, you should consult a doctor if:
- The pain is severe and persistent.
- You have difficulty bearing weight on the knee.
- There is redness, warmth, or swelling around the knee joint.
- The knee appears deformed or feels unstable.
When to go to the hospital for knee pain
Head to the hospital immediately during emergencies, such as sudden and severe injuries, fractures, or dislocations. If you experience signs of infection, such as fever and chills, seek urgent medical attention.
Conclusion:
Understanding knee pain ensures you maintain good joint health. From identifying the causes and types to exploring treatment options and knee pain prevention strategies, you must know how to make informed decisions about your well-being.
Remember that proactive healthcare plays a pivotal role in your well-being. Beyond the insights shared here, visit Metropolis Labs to get yourself tested. With a commitment to cutting-edge diagnostics and personalised services, Metropolis Labs ensures accurate assessments.










1736506020.webp)
1701259759.webp)









 WhatsApp
WhatsApp