Preventive Healthcare
Understanding Coronary Artery Disease: Symptoms, Causes, Treatment, and Diagnosis
1401 Views
0
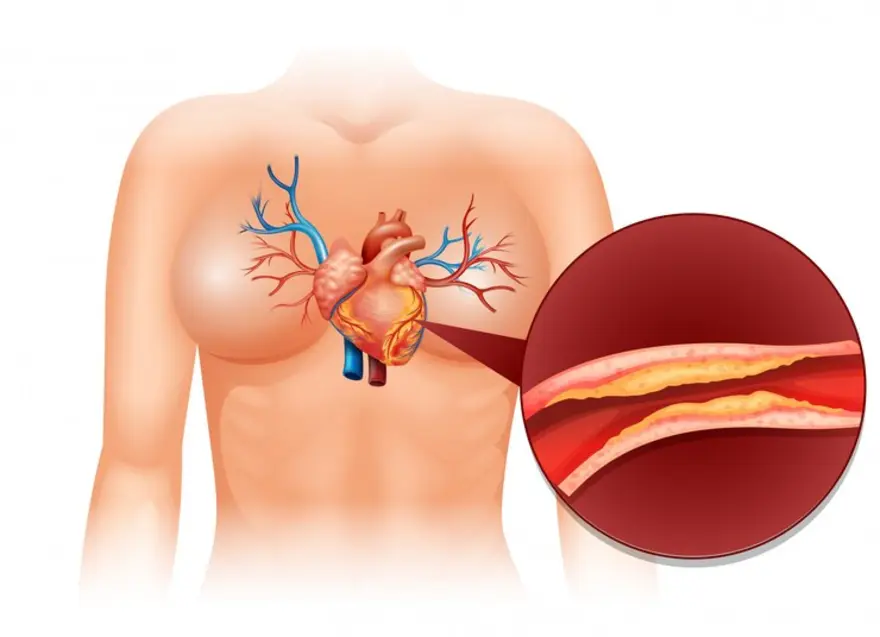
Coronary artery disease remains a leading cause of death worldwide, affecting millions each year. In this comprehensive guide, we discuss the important details of coronary artery disease, exploring its origins, risk factors, treatment, and preventive strategies. Continue reading to learn more.
What is coronary artery disease?
Coronary artery disease is a condition in which the coronary arteries, which supply oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle, become narrowed or blocked due to the buildup of plaque( fatty deposits ). This restricts blood flow to the heart, leading to chest pain and heart attacks.
What are the types of coronary artery disease?
Coronary artery disease types are broadly classified as chronic (gradual) and acute (sudden). Normally, it is classified as:
- Atherosclerosis: It is caused by the build-up of plaque in your arteries.
- Coronary Artery Spasm: This occurs when your coronary arteries constrict suddenly, reducing blood flow.
- Coronary Microvascular Disease: Affects the smaller arteries of your heart, impairing blood flow despite clear larger arteries.
- Coronary Embolism: Caused by a blood clot that travels through your bloodstream and blocks a coronary artery.
How common is coronary artery disease?
Approximately 200 million people are believed to be affected by coronary artery disease. It ranks as the third most common cause of death globally and is linked to 17.8 million deaths each year.
What are the symptoms of coronary artery disease?
Common Coronary artery disease symptoms may include:
- Chest Pain (Angina)
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Sweating, nausea, vomiting and dizziness during a heart attack
- You may also experience irregular heartbeats and even fainting spells.
Note that coronary artery disease symptoms may vary from person to person and can range from mild to severe.
What causes coronary artery disease?
Atherosclerosis is one of the primary coronary artery disease causes. It is a gradual process that begins with damage to the inner lining of your arteries, often caused by factors like high blood pressure, smoking, etc.
When the inner lining is damaged, substances like cholesterol, fat, and calcium start to accumulate at the site of injury. Over time, these substances form a plaque, which hardens and narrows the artery, reducing blood flow to your heart.
As the plaque grows, it can eventually rupture, triggering a blood clot to form. If the clot blocks the artery completely, it can lead to a heart attack or stroke. Moreover, high LDL cholesterol ("bad" cholesterol) levels contribute to plaque build-up in your arteries, one of the other key to coronary artery disease causes.
What are the risk factors for coronary artery disease?
Here's a breakdown of the common risk factors associated with coronary artery disease:
- High blood pressure
- Tobacco smoke
- Uncontrolled diabetes
- Being overweight or physically inactive
- Diets high in saturated fats, trans fats, cholesterol, and sodium
- A family history of coronary artery disease
- Chronic stress
What are the complications of coronary artery disease?
Potential complications of coronary artery disease may include:
- Heart Attack
- Angina
- Heart Failure
- Arrhythmias (Irregular heartbeats)
- Sudden Cardiac Arrest
- Stroke
How is coronary artery disease diagnosed?
Coronary artery disease diagnosis typically involves a thorough physical examination, imaging tests and blood tests to evaluate the heart's function and blood flow and detect any blockages in the arteries.
What tests are done to diagnose coronary artery disease?
Given below are common coronary artery disease diagnosis tests:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG): This non-invasive test records your heart's electrical activity to detect abnormal heart rhythms or signs of a previous heart attack.
- Stress Test: This test monitors your heart rate, blood pressure, and ECG changes during physical activity to reveal signs of reduced blood flow to the heart.
- Coronary Angiography: It provides detailed images of blockages or narrowed areas in your arteries.
- Cardiac CT Scan: This imaging test uses X-rays to detect calcium deposits in your coronary arteries, indicating plaque build-up.
- Blood Tests: These tests measure cholesterol levels, cardiac enzymes, and markers of inflammation, providing important clues about heart health and potential coronary artery disease risk.
How is coronary artery disease treated?
Coronary artery disease treatment depends on the severity of the condition. The most common coronary artery disease treatment methods include:
- Medications: Your doctor may prescribe medications such as statins, beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, or antiplatelet drugs to manage coronary artery disease risk factors, such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, or diabetes.
- Angioplasty and Stenting: In this method, a catheter with a balloon at its tip is inserted into your blocked artery. The balloon is inflated to compress the plaque, and a stent (a small mesh tube) is placed to keep the artery open.
- Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery (CABG): This procedure, recommended in severe cases, involves rerouting blood flow around blocked arteries using blood vessels from other parts of the body.
- Cardiac Rehabilitation: After treatment, participating in a cardiac rehabilitation program can help you recover faster and improve heart health through exercise, education, and support.
What are the complications/side effects of the treatment?
Side effects of coronary artery disease treatment may include:
- Muscle pain
- Cough
- Bleeding, blood clots, or artery damage.
- Infection
- Stroke (in rare cases)
Can coronary artery disease be prevented?
Yes, coronary artery disease prevention can be achieved through lifestyle changes and proactive management of risk factors. You can reduce your risk by adopting a healthy diet, staying physically active, avoiding tobacco and smoking, managing stress, and regularly monitoring your blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
What is the outlook for coronary artery disease?
The likelihood of surviving coronary artery disease hinges on several factors, such as the condition's severity and the effectiveness of its treatment. Yet, with early detection of coronary artery disease symptoms and appropriate medical care, most individuals with the condition can lead a fulfilling and long life.
Conclusion
In conclusion, coronary artery disease poses significant health risks but can be managed and even prevented with lifestyle changes and medical interventions. By understanding it, you can take control of your heart's health and lead a healthy life. Did you know that a simple blood test can detect coronary artery disease early and prevent complications in the majority of cases? Book a blood test with Metropolis Labs for top-notch diagnostic services, fast and accurate reports and at-home testing facilities with no hidden charges!