Preventive Healthcare
Tonsil Cancer: Symptoms, Causes, and Risk Factors
46 Views
0
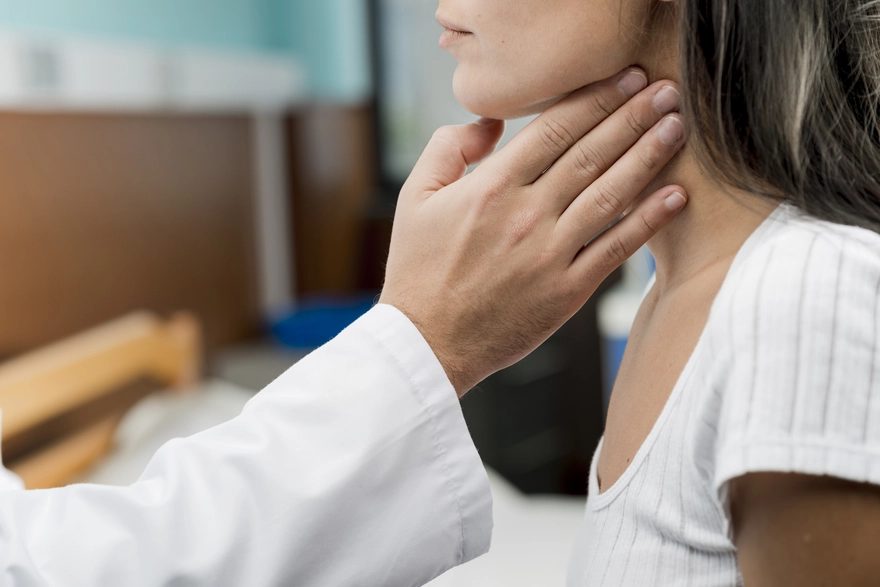
What is Tonsil Cancer?
Tonsil cancer is a type of throat cancer that develops in the tonsils, two oval-shaped pads of tissue at the back of the throat. As part of the body's lymphatic system, the tonsils help fight off infections by trapping germs that enter through the mouth or nose. Unfortunately, these infection-fighting tissues can sometimes develop cancerous tumors.
Tonsil cancer falls under the category of oropharyngeal cancers, which affect the part of the throat just behind the mouth. While relatively rare, it's important to be aware of the potential signs and risk factors for this condition. Early detection and prompt tonsil cancer treatment can significantly improve outcomes and quality of life for those affected.
In this article, we'll delve into the specifics of tonsil cancer, including its symptoms, causes, risk factors, diagnosis, and treatment options. Our goal is to empower you with the knowledge to take charge of your health and seek appropriate medical care if needed.
What are Tonsils and Their Role in the Body?
Before diving into the details of tonsil cancer, let's first understand what tonsils are and their function in the body. Tonsils are small, round masses of lymphoid tissue located at the back of the throat. There are three types of tonsils:
- Palatine tonsils: The most visible tonsils, located on either side of the back of the throat
- Pharyngeal tonsils (adenoids): Located at the very back of the nose, above the roof of the mouth
- Lingual tonsils: Located at the base of the tongue
Together, these tonsils form a ring of lymphoid tissue called Waldeyer's ring, which serves as a defense mechanism against pathogens that enter through the mouth or nose. The tonsils contain immune cells that can detect and fight off harmful bacteria and viruses.
However, sometimes the tonsils themselves can become infected, leading to conditions like tonsillitis or strep throat. In rare cases, cancerous changes can occur in the tonsil tissue, resulting in tonsil cancer.
Types of Tonsil Cancer
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Over 90% of tonsil cancers are squamous cell carcinomas, which develop in the flat squamous cells lining the tonsils. This type is often linked to HPV infection.
- Lymphomas: These cancers originate from immune system cells and can affect the tonsils, leading to symptoms like swollen tonsils.
- Minor Salivary Gland Cancers: These rare cancers arise from the small salivary glands embedded within the tonsil tissue.
- Sarcomas: Extremely rare, these cancers develop in the connective tissues of the tonsils.
If you experience persistent tonsil issues, including tonsil cancer symptoms like difficulty swallowing, persistent sore throat, or unexplained weight loss, consult a doctor. Diagnosis typically involves a biopsy and microscopic examination of tumor cells to determine the cancer type. Early detection and treatment improve outcomes, making medical evaluation crucial for anyone with concerning tonsil abnormalities.
Symptoms of Tonsil Cancer
In its early stages, tonsil cancer symptoms may not be noticeable. As the tumor grows, however, it can lead to a variety of signs and symptoms, including:
- Persistent Sore Throat: A sore throat that lingers for weeks without improvement
- Difficulty Swallowing (Dysphagia): Trouble swallowing food, liquids, or even saliva
- Feeling of Something Stuck in the Throat: A constant sensation of blockage in the back of the throat
- Swelling or Lump in the Neck: Enlarged lymph nodes or an unexplained lump
- Ear Pain (Especially on One Side): Pain in one ear that isn’t caused by an infection
- Swollen Tonsils: One tonsil appearing larger than the other, sometimes with redness or sores
- Mouth Pain or Bleeding: Unexplained pain, sores, or bleeding in the mouth or throat
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Losing weight without changes in diet or exercise
- Voice Changes: Hoarseness or a different-sounding voice for no clear reason.
These symptoms can have other causes, but if they last more than 2-3 weeks, consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis. Early detection improves treatment outcomes.
Causes and Risk Factors
While the exact tonsil cancer cause is not always clear, several factors can increase a person's risk of developing this condition:
- HPV infection: Infection with certain strains of human papillomavirus, especially HPV 16 and 18, significantly raises the risk of tonsil cancer.
- Tobacco use: Smoking cigarettes or using other tobacco products increases the risk of many head and neck cancers, including tonsil cancer.
- Alcohol consumption: Heavy alcohol use, especially when combined with tobacco, can irritate the lining of the throat and increase cancer risk.
- Age: Tonsil cancer is most commonly diagnosed in people over age 50, although it can occur at any age.
- Gender: Men are more likely than women to develop tonsil cancer.
Some other potential risk factors include:
- A diet low in fruits and vegetables
- Poor oral hygiene
- A weakened immune system
While having one or more risk factors doesn't mean you will definitely develop tonsil cancer, it's important to be aware of them and take steps to reduce your risk where possible.
Diagnosis of Tonsil Cancer
If your doctor suspects you may have tonsil cancer, they will likely recommend one or more of the following tests:
- Physical exam: Your doctor will examine your throat, neck, and mouth for any visible signs of cancer, such as swollen tonsils or lumps.
- Endoscopy: A thin, flexible tube with a light and camera (endoscope) is inserted through your nose or mouth to get a closer look at your throat and tonsils.
- Biopsy: If any abnormal areas are found, a small tissue sample will be removed and examined under a microscope for cancer cells. This is the only way to definitively diagnose tonsil cancer.
- Imaging tests: CT, MRI, or PET scans may be used to determine the extent of the cancer and whether it has spread to nearby lymph nodes or other parts of the body.
- HPV testing: Since HPV is a major risk factor for tonsil cancer, your doctor may test tumor samples for the presence of the virus.
Staging is an important part of the diagnostic process. The stage of tonsil cancer (I through IV) describes the size of the primary tumor and how far the cancer has spread. Early stage tonsil cancer is limited to the tonsils and hasn't spread to nearby tissues or lymph nodes. More advanced stages indicate larger tumors and wider cancer spread.
Treatment Options for Tonsil Cancer
Tonsil cancer treatment depends on several factors, including the size, location, and stage of the cancer, as well as your age, health, and personal preferences. The main treatment options include:
- Surgery: The primary tumor and some surrounding healthy tissue are removed to ensure all cancer cells are eliminated. Minimally invasive surgical techniques may be used to reduce side effects and recovery time.
- Radiation therapy: High-energy beams are used to kill cancer cells. This may be the main treatment for early stage cancers, or used after surgery to destroy any remaining cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: Anti-cancer drugs are given intravenously or in pill form to kill cancer cells throughout the body. Chemo is often combined with radiation therapy to enhance its effectiveness.
- Targeted therapy: Drugs that specifically target cancer cells with certain genetic mutations may be used, often in combination with chemo or radiation.
- Immunotherapy: Medications that help the body's own immune system recognise and attack cancer cells are sometimes used for advanced tonsil cancers.
Living with Tonsil Cancer: Support and Recovery
A tonsil cancer diagnosis can be overwhelming, but support is available to help you navigate treatment and recovery. Lean on loved ones and consider joining a cancer support group to connect with others who understand your journey. Work with a nutritionist to maintain a healthy diet, especially if eating becomes difficult due to treatment side effects. Good oral hygiene and regular dental visits are essential to prevent complications like tooth decay and gum disease. Stay active with regular exercise to reduce fatigue, boost mood, and aid recovery. Most importantly, attend all follow-up appointments to monitor for recurrence and manage long-term effects.
Conclusion and Key Takeaways
Tonsil cancer is a rare but serious condition. Key symptoms include a persistent sore throat, difficulty swallowing, a neck lump, and swollen tonsils. Risk factors include HPV, tobacco, alcohol use, and aging. Early detection improves prognosis, so seek medical help for lasting symptoms. Treatment options and support are available.
If you have concerns about your risk for tonsil cancer or are experiencing potential symptoms, don't hesitate to speak with your healthcare provider. At Metropolis Healthcare, we offer advanced diagnostic testing to detect tonsil cancer at its earliest, most treatable stages. Our team of experts is here to provide the comprehensive care and support you need every step of the way.






















 WhatsApp
WhatsApp