Preventive Healthcare
Vitamin B2 Food Sources and Deficiency
1786 Views
0
What is Vitamin B2?
Vitamin B2 or riboflavin, is a substance in high amounts in animal-based and plant-based foods. Vitamin B2 is called riboflavin because of its yellow colour. The word "flavin" comes from the Latin word "flavus,". It means yellow. In contrast to any other vitamin, you can generally tell how much vitamin B2 is in your body by looking at the colour of your pee. It turns bright yellow when you have enough of it.
The body uses vitamin B2 for many different things. It is needed for healthy skin growth, covering the digestive system, brain activity, and making blood cells. Even though it doesn't meet all of an individual's food requirements, it is essential to how the body works and grows. It is also found in vitamins and food aids.
Role of Vitamin B2
Vitamin B2 assists in breaking down carbs, proteins, and fats. It is an essential part of the body's energy source.
Riboflavin helps make ATP (adenosine triphosphate) from carbs. The body produces ATP from food, and ATP makes energy when it needs it. ATP is an essential part of how muscles store energy.
Vitamin B is just as important as vitamin A for:
- Taking care of the gut system's mucous membranes.
- How to keep your liver healthy.
- Niacin, an amino acid, is made from tryptophan.
- Taking care of the eyes, nerves, muscles, and skin.
- Taking in folic acid, iron, and vitamins B1, B3, and B6 and making them work.
- The adrenal glands are in charge of making hormones.
- Keeping people from getting cataracts.
- fetal growth, particularly in places where people don't get enough vitamins.
Some research shows that vitamin B2 can assist with preventing cataracts and migraines. But this needs to be confirmed by more research.
Other studies have shown that doses of vitamins B2, B6, and magnesium seem to lower the amount of abnormal organic acids in the pee of children with autism.
Uses of Vitamin B2
· Cataracts (a disease of the eye).
Individuals who eat more riboflavin in their food are less likely to get cataracts. Also, taking vitamins with riboflavin and niacin seems to help keep cataracts from happening.
- Hyperhomocysteinemia (High amounts of homocysteine in the blood).
Some people can't change the chemical homocysteine into the amino acid methionine. Homocysteine levels are high in the blood of people with this medical condition, particularly those who don't get enough riboflavin.
Some people with this disease seem to have their homocysteine levels drop by up to 40% when they take riboflavin for 12 weeks. Also, some medicines used to treat seizures can raise the amount of homocysteine in the blood. People who take anti-seizure drugs and have high homocysteine levels may be able to lower them by 26% by taking riboflavin, folic acid, and pyridoxine.
- Headaches from migraines.
Taking 400 mg of riboflavin every day seems to cut the number of migraine headaches by a significant amount. But taking riboflavin doesn't seem to lessen the pain or shorten the length of a migraine headache. Additionally, consuming 200 mg of riboflavin every day does not seem to reduce the number of headaches caused by migraines.
Sources of Vitamin B2
It is essential to get the recommended amount of vitamin B2 daily for optimal health. The bulk of the calories you consume each day should come from nutritious food sources if you want your diet to be nutritionally sound and well-balanced.
The following is a list of foods that are very high in vitamin B2 content. They may be found across the diet chart in varied degrees of concentration:
- Meat, like chicken, turkey, beef, and meat.
- Eggs
- Milk and cheese
- Artichokes
- Avocados
- Asparagus
- Cayenne Currants
- Cereals with added vitamins and minerals.
- Kelp
- Lima beans
- Peas
- Nuts
- Molasses
- Mushrooms
- Parsley
- Sage
- Sweet potatoes
- Pumpkins
- Rosehips
- Cruciferous veggies include broccoli, spinach, Brussels sprouts, mustard greens, and watercress.
- Rich bread made with whole grains.
- Extract yeast
Vitamin B2 dissolves in water. It can be lost when food is cooked. When you boil something, you lose about twice the amount of B2 as when you steam or microwave it.
Deficiency of Vitamin B2
This vitamin is essential. It gives the body the energy it needs to do many things. Lack of it can slow down how proteins, fats, and carbs are broken down. This can lead to underlying deficit conditions.
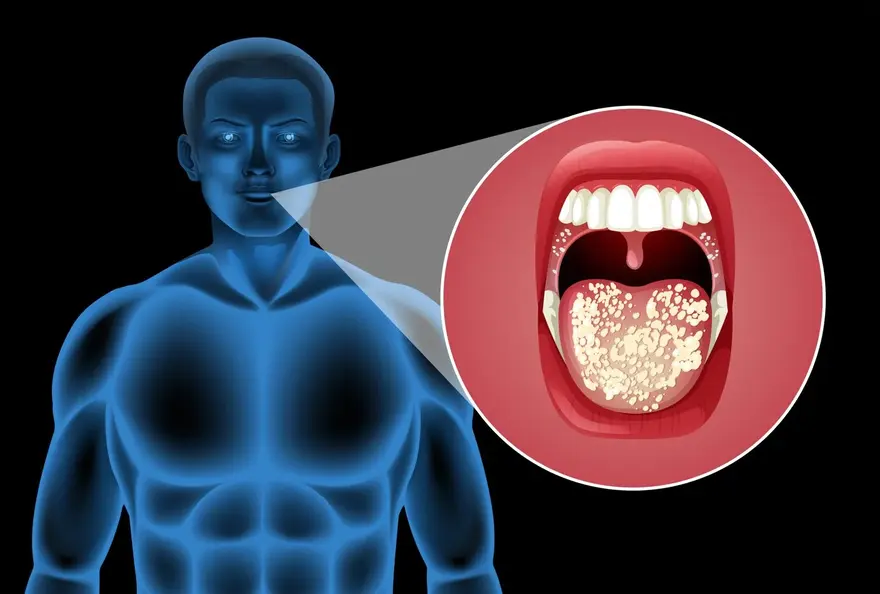
Riboflavin deficiency is also called ariboflavinosis. It causes stomatitis. This includes a painful red tongue and sore throat, red, cracked, and chapped lips (called cheilosis), swelling of the corners of the mouth, swelling of the tongue, mouth ulcers, and cracks at the corners of the mouth.
If you don't get enough of this vital vitamin, you may have bloodshot eyes, high sensitivity to light, a burning feeling in your eyes or itchy, watery eyes, dry or oily hair, dandruff, split nails, dizziness, indigestion, insomnia, etc.
If you don't get enough riboflavin in your food, your adrenal glands won't work right. This can lead to problems like anaemia, cataracts, and chronic fatigue syndrome. It can also cause itchy rashes on both men's and women's genitalia, rashes in the middle of the upper lip, and rashes in the area where the nose meets the chin (called the nasolabial fold).
If a pregnant woman doesn't get enough of this B vitamin, it may result in birth defects, congenital heart problems, abnormal limbs, and other abnormalities in the baby. It can also make people get pellagra or malaria. If you don't treat the signs of riboflavin deficiency for a long time, your brain and nervous system could start to break down.
Conclusion
Vitamin B2 is a nutrient that is water-soluble that is needed to break down fats and carbs into easier forms that give the body energy to do all of its different jobs. As a powerful antioxidant, it is essential for treating various conditions, such as anaemia, migraines, heart, eye, and liver problems. It is also very good for keeping skin and hair healthy. With a wide range of food choices, it is easy to avoid deficit conditions and get the benefits. However, to know more about it visit Metropolis. It is a renowned healthcare centre which is known for giving accurate results.
Final takeaway
Eight water-soluble B vitamins are required for DNA synthesis, enzyme reactions, and other essential bodily processes.
B vitamins are made by organisms other than humans, such as bacteria, plants, and yeast. To survive, we must ingest them through food or dietary supplements.
B vitamins are present in a variety of dietary sources. To acquire sufficient quantities of each, a balanced diet is necessary.






















 WhatsApp
WhatsApp