Preventive Healthcare
Still's Disease - Symptoms, Causes And Treatment
3478 Views
0
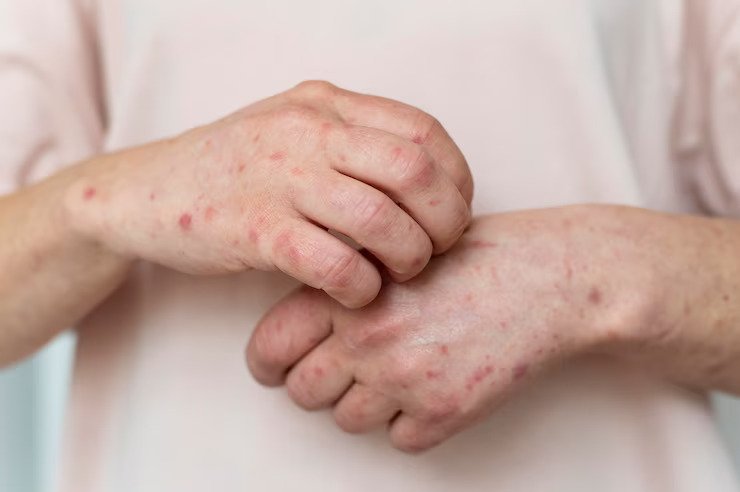
Still’s Disease is an inflammatory disorder. It is officially termed 'Systemic Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis'. It can affect people of all ages, including adults. Characterised by high fever and joint pain, the common identifier of this condition is the "characteristic rash."
Even though Still's Disease can affect people in different ways and last for different lengths of time, a timely diagnosis and an effective treatment plan are essential for reducing the long-term effects of the disease.
Definition of Still’s Disease
Still’s Disease is a chronic, progressive autoimmune condition. It is caused by an abnormal response of the body’s immune system. It is characterised by recurring high fever, joint pain and swelling, and a salmon-coloured rash. Both children and adults can be affected. This can sometimes lead to organ damage.
Although the precise cause of Still’s Disease is yet to be determined, it is generally believed that genetic, hormonal, and environmental components are at its core. Treatment options will vary depending on the symptoms. But anti-inflammatory medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications can help manage the condition.
Symptoms of Still’s Disease
Here are some of the classic indicators of Still’s disease:
1. Fever and Rash: The first signs of Still's disease are usually a fever (sometimes as high as 104–105 degrees Fahrenheit) and a rash that comes with it. The rash is usually pink or purple. It appears on the chest, armpits, hands, and/or feet.
2. Joint Swelling: Swelling and pain in the joints, particularly in the knees, ankles, and larger joints, is another common symptom of Still’s Disease. The person may also experience stiffness and a decreased range of motion.
3. Extreme Fatigue: A person with Still’s disease may feel fatigued, even after sleeping for long stretches. This extreme fatigue often accompanies the other signs and symptoms of the condition.
4. Weight loss and Decreased Appetite: As the inflammation progresses, the person may lose some of their appetites. They may also eliminate some of their favourite foods. Subsequently, they may also notice an unexpected or inexplicable weakening of their body weight.
5. Swelling of Neck Lymph Nodes: Swollen lymph nodes in the neck are another standard indicator of Still’s Disease. If someone has lymph nodes that are unusually big and hard, especially in their neck, they should see a doctor.
Causes of Still’s Disease
Even though no one knows what caused Still's, several things could have led to it.
Here are five main causes of Still's disease.
1. Hormonal Factors: Research suggests that the endocrine system plays a huge role in the development of Still's. It is believed that inflammatory cells tend to increase when the body's hormones are imbalanced. This leads to the symptoms of Still's, like fever and joint pain.
2. Genetic Factors: Heredity also seems to play a role in the development of Still's. If someone in your family has the disease, your chances of having it also increase.
3. Environmental Factors: Prolonged exposure to certain environmental toxins, such as those emitted by industry and agriculture, can damage the lungs, triggering an inflammatory response.
4. Viral Causes: Infection by certain viruses, including parvovirus, rubella, and Epstein-Barr virus, can also lead to the development of Still's.
5. Allergens: It is possible for allergens, such as pollen and pet dander, to trigger an inflammatory response leading to Still's.
Treatment of Still’s Disease
Treating Still’s disease can alleviate symptoms. It can also reduce the risk of flare-ups. The following are five effective still's disease treatments:
1. Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) - These medications reduce inflammatory pain and the signs and symptoms of Still’s Disease.
2. Corticosteroids - These drugs reduce inflammation by reducing the activity of the immune system.
3. Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs) - DMARDs can help slow the progress of Still’s disease and reduce the frequency of flares.
4. Physical Therapy, Exercise, Rest, and a Healthy Diet - These measures will help manage the condition and keep symptoms to a minimum.
Other treatments include antimalarial medications and biological agents to relieve symptoms.
Living with Still’s Disease
Living with Still’s Disease can be difficult and emotional. It often requires long-term treatments. This also has significant physical and psychological impacts. The following provides some best practices and self-care tips for those living with adult Still’s Disease.
• Get Regular Check-Ups: Regular medical check-ups can help those with Still's disease. This will help them to track their progress, address any new developments, and adapt their treatments as necessary.
• Stay Active: Regular exercise can help to reduce inflammation, fatigue, and joint pain. Be sure to consult with your doctor before beginning any new routine.
• Incorporate Healthy Habits: Healthy habits such as proper nutrition, adequate rest, and managing stress can be beneficial for managing Still’s disease.
• Join Support Groups: Connecting with other people with similar experiences can provide emotional support and help those with Still’s disease to feel less alone.
• Seek Treatment Options: Various treatment options are available for Still’s disease. These range from physical therapy to immunosuppressive drugs. Speak to your doctor to discuss your situation.
• Take Care of Your Mental Health: Living with Still’s disease can affect your mental health. Seeking professional help or engaging in mindfulness activities can be important for managing emotions.
Conclusion
Still's Disease is an uncommon form of inflammatory arthritis. It affects adults and, occasionally, children. High fever episodes and generalized joint pain, swelling, and stiffness characterize it. Additional symptoms may include rash, lymph node swelling, lining tissue inflammation, hepatitis, and pleurisy.
While there is no known cause, some evidence suggests that a virus may be the trigger. Treatment may involve steroids and other anti-inflammatory drugs to reduce symptoms. This will also help improve the patient's quality of life. The prognosis for Still's disease is generally good with regular medication and active lifestyle management.
At Metropolis Healthcare, we understand that a diagnosis of Still’s disease can be intimidating. We are committed to helping our patients live well. We do this by providing tailored treatment plans and a supportive, professional care team.
Our physicians will work closely with you to evaluate your condition, develop an effective treatment plan, and monitor your progress. With our help, you can learn, grow, and achieve robust health.





















 WhatsApp
WhatsApp