Preventive Healthcare
Managing Pneumothorax (collapsed lung): Symptoms, Types, Causes and Treatment
2621 Views
0
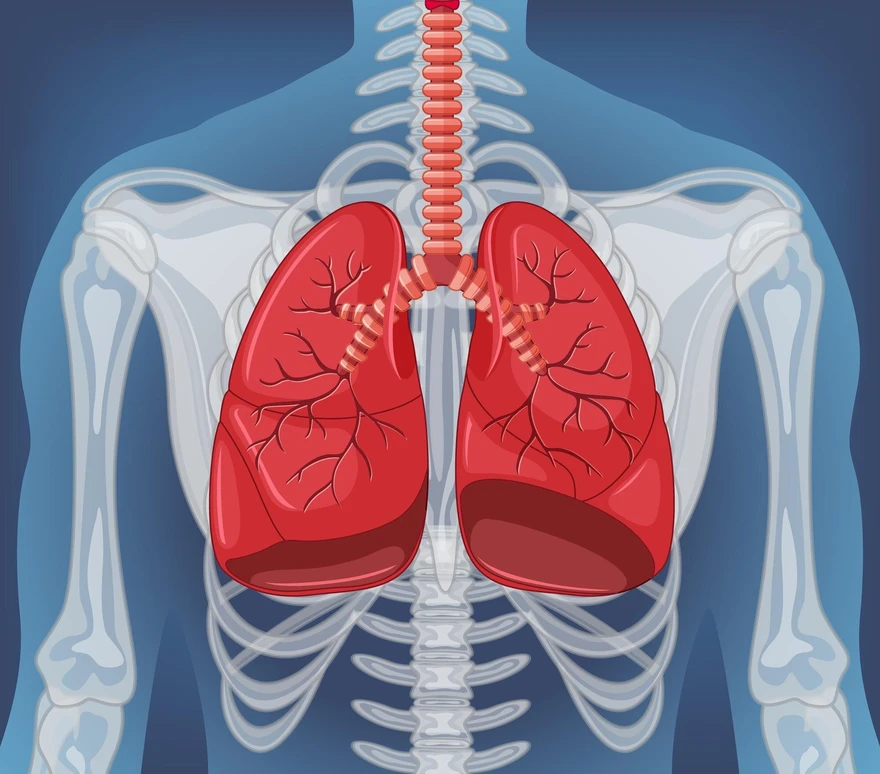
Introduction
Like vital air purifiers, our lungs inhale oxygen and remove carbon dioxide. But, when they can not expand to expel air outside your body, that medical condition is called pneumothorax or collapsed lungs. Join us in this blog to explore its types, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.
What is a Pneumothorax?
Pneumothorax, commonly called collapsed lungs, occurs when air leaks into the space between your lungs (pleural space) and the chest wall. This air in the pleural space (fluid-filled space that covers the lungs) exerts pressure against your lungs, causing them to partially or completely collapse.
What are the Different Types of Pneumothorax?
There are two main types of pneumothorax: spontaneous and traumatic.
Spontaneous pneumothorax:
Primary spontaneous pneumothorax: This pneumothorax type happens when your lungs collapse for no apparent reason. It could be due to tiny air pockets in your lungs breaking apart. This is more likely to occur in people who smoke or if someone has a family history of pneumothorax.
Secondary spontaneous pneumothorax: This pneumothorax type can be caused by lung diseases such as pneumonia, asthma, lung cancer, etc. These conditions can lead to blockage in your lungs, creating bulging areas that may burst, causing a collapsed lung.
Traumatic pneumothorax:
Traumatic pneumothorax is caused due to injuries or medical procedures. These pneumothorax types include:
- Injury-related pneumothorax: This type of collapsed lung results from chest injuries like fractures or wounds that puncture your lung.
- Iatrogenic pneumothorax: When a medical procedure, such as a lung biopsy, accidentally punctures your lung, this can lead to a collapsed lung.
Other Types of Pneumothorax:
- Tension pneumothorax: This is not a classification of the pneumothorax type but denotes the severity of the condition. It is more of a medical emergency. This severe form can occur when air gets in but cannot escape, causing pressure inside your chest, which can lead to a collapsed lung. You can experience this if you have a penetrating injury, a blow to the chest, and some medical procedures.
- Catamenial Pneumothorax: This is a rare condition connected to endometriosis. In endometriosis, tissue growing outside the uterus can form a cyst. If this cyst bleeds into the pleural space, it can lead to a collapsed lung.
How Serious is a Pneumothorax?
A pneumothorax can range from mild to life-threatening, depending on the severity of a collapsed lung. In severe cases, especially tension pneumothorax, it can impact your breathing and heart and be considered a medical emergency requiring immediate attention.
What are the Symptoms of a Pneumothorax?
Signs and symptoms of pneumothorax include:
- A sudden attack of chest pain is the very first and the main pneumothorax symptom.
- Shortness of breath
- Fast breathing
- Chest tightness
- Cough
- Fatigue
- Rapid heart rate
- Anxiety
- Bluish skin, lips, or nails
Make sure you consult your doctor immediately if you experience any of these pneumothorax symptoms.
What Causes a Pneumothorax?
There are three leading pneumothorax causes. These include:
Medical Conditions
Here are a few medical conditions that can lead to collapsed lungs:
- Tuberculosis
- Asthma
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
- Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
- Emphysema
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)
- Pneumonia
- Collagen Vascular Disease
- Lung Cancer
- Cystic Fibrosis
Injuries
A list of injuries that can lead to collapsed lungs are:
- Car crash
- Gunshot wounds
- Stab wounds
- A blunt and penetrating injury to the lungs.
- During medical procedures that involve the insertion of a needle into the chest. For instance, lung biopsy, central venous line placements, and nerve blocks.
Lifestyle Factors
There are a few lifestyle factors to beware of, as they can lead to collapsed lungs:
- Smoking
- Drug usage
- Engaging in activities such as diving, flying, or being at high altitudes where air pressure changes.
What are the Risk Factors for Pneumothorax?
The risk factors of pneumothorax are as follows:
- Men are generally more prone to collapsed lungs than women.
- The collapsed lungs caused by ruptured air blisters are more common in individuals aged 20 to 40, especially if they are very tall and underweight.
- Other risk factors include having a family history of collapsed lungs, pregnancy, and endometriosis.
- Ongoing assisted respiratory care and inflammation in the airways can also contribute to this medical condition.
- Working in risky environments like construction sites, industrial settings, or jobs at heights (e.g., roofing, tree trimming, etc.) increases the chance of pneumothorax.
What are the Complications of a Pneumothorax?
Complications of a pneumothorax may include:
- Air Leakage: Persistent air leakage may require additional medical interventions.
- Infection: Open wounds or medical procedures can increase infection risk in the pleural space.
- Tension Pneumothorax: Severe cases can lead to a medical emergency with chest pressure build-up.
- Respiratory Distress: Significant collapse may cause breathing difficulties.
- Cardiac Complications: Rare instances may impact heart function.
- Recurring Episodes: Those with collapsed lungs may be at risk of repeat occurrences.
How is Pneumothorax Diagnosed?
Your doctor decides the method of pneumothorax diagnosis based on your condition. Your collapsed lung is diagnosed through imaging tests like chest X-rays or CT scans, allowing healthcare providers to visualise your collapsed lung and determine the extent of the condition.
How is Pneumothorax Treated?
Pneumothorax treatment varies based on its severity. It may include observation for minor cases, insertion of a chest tube to remove trapped air, or surgery for more severe collapses. The approach depends on the extent of the collapsed lung and individual health factors.
Can Pneumothorax be Prevented?
Yes, collapsed lungs can be prevented in the following ways:
- Quit smoking to reduce the risk.
- Stay alert for pneumothorax symptoms and seek prompt medical attention.
- To prevent collapsed lungs, avoid chest injuries, especially during sports where impacts or collisions can pose a risk to the chest area. So, one should always play cautiously.
- Practice safety measures in high-risk workplaces, such as wearing protective gear and following established protocols, to reduce the risk of collapsed lungs.
What Can I Expect if I Have a Pneumothorax?
If you have collapsed lungs, you may have to be in the hospital for a couple of days or longer under the supervision of your doctor for a complete and effective pneumothorax treatment.
How Long Does It Take a Collapsed Lung to Heal?
Your collapsed lungs can typically heal within a few days to two weeks.
Can You Fully Recover from a Pneumothorax?
Yes, full recovery from a punctured lung is possible. However, you do have a chance of recurrence. Therefore, you must follow the recommended pneumothorax treatment plan and follow-ups to ensure complete recovery.
Is Pneumothorax Life-Threatening?
In severe cases, pneumothorax can be life-threatening, especially if it leads to tension pneumothorax, a condition requiring immediate medical attention due to increased pressure within the chest.
How Do I Take Care of Myself?
You need to follow your doctor's advice, rest, avoid smoking, refrain from air travel during the recovery period, and avoid lifting heavy objects and strenuous exercise that might strain your lungs during this time.
When to See a Doctor?
You should see a doctor right away if you have sudden chest pain or trouble breathing, as these could be signs of pneumothorax. Early medical help is essential for effective pneumothorax treatment.
Conclusion
A collapsed lung is treatable, and if you notice pneumothorax symptoms, consult your doctor promptly for immediate care. Follow the preventive measures to avoid recurrence of this condition. Elevate your health with precision diagnostics from Metropolis Labs. Choose Metropolis for accurate and timely results for a proactive approach to your well-being. Explore more blogs on our website and take charge of your health for a healthier tomorrow.






















 WhatsApp
WhatsApp