Preventive Healthcare
Hemangioma: Types, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
76 Views
0
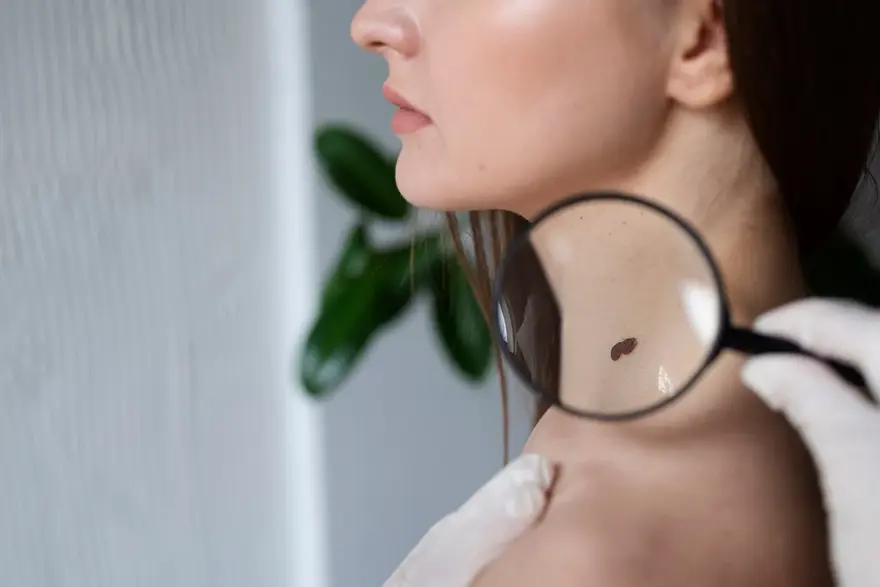

What is a Hemangioma?
A hemangioma is a benign vascular tumour composed of blood vessel cells that commonly appears as a birthmark on the skin or internally. These non-cancerous growths are often referred to as "strawberry marks" and typically become visible in the first few weeks of life. Hemangiomas tend to grow rapidly for about a year before gradually shrinking, with most resolving by the age of 10.
While hemangiomas are usually harmless, some may require treatment if they obstruct vision, breathing, or cause significant cosmetic concerns. It's essential to understand the meaning of hemangioma, its various types, symptoms, causes, and available treatment options to effectively manage this condition.
If you or your child has been diagnosed with a hemangioma, you may have questions about what to expect and when to seek medical advice. This article aims to provide clear, informative guidance on hemangiomas types, empowering you to make informed decisions about your health.
Types of Hemangiomas
Hemangiomas are benign vascular tumors that are classified into different types based on their appearance, location, and growth patterns. Understanding these distinctions is essential for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management. Here's a look at the various hemangioma types:
- Infantile Hemangiomas: The most common type, infantile hemangiomas, typically appear within the first few weeks of life. These lesions often start as small red marks and grow rapidly during the first year before gradually shrinking and fading over time. Most resolve without intervention by the age of 10.
- Congenital Hemangiomas: Unlike infantile hemangiomas, congenital hemangiomas are fully formed at birth. They are further categorised into rapidly involuting congenital hemangiomas (RICH), which shrink quickly within the first year; partially involuting congenital hemangiomas (PICH), which regress more slowly; and non-involuting congenital hemangiomas (NICH), which persist without shrinking.
- Cavernous Hemangiomas: These involve larger, dilated blood vessels and may develop in deeper tissues or internal organs, such as the liver or brain. Depending on their location, they can sometimes cause complications.
- Capillary Hemangiomas: Comprised of small capillary-sized blood vessels, these hemangiomas typically appear as flat, red patches on the skin and are commonly found on the face or scalp.
- Compound Hemangiomas: These combine characteristics of both capillary and cavernous hemangiomas, involving multiple layers of blood vessels with varying sizes.
While most hemangiomas are harmless and resolve naturally, some may require medical attention, particularly if they interfere with vital functions, cause pain, or lead to complications.
Symptoms of Hemangiomas
The symptoms of hemangiomas can vary depending on their location, depth, and size. Some common signs to look out for include:
- A raised, bright red, or purple bump or patch on the skin
- A bluish swelling under the skin's surface
- A strawberry-like appearance with a textured or bumpy surface
- Tenderness or pain in the affected area
- Bleeding or ulceration of the hemangioma
Hemangiomas are most commonly found on the face, scalp, chest, or back, but they can occur anywhere on the body. In some cases, hemangiomas may develop internally, such as in the liver, which can cause abdominal discomfort, nausea, or vomiting.
It's essential to monitor hemangiomas closely, especially during the rapid growth phase in the first year of life. If you notice any sudden changes, increased pain, or bleeding, it's crucial to consult a healthcare provider promptly.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact hemangioma causes remain unclear, but researchers believe a combination of genetic and environmental factors contributes to their development. Several risk factors have been identified that may increase the likelihood of hemangioma formation.
- Gender: Hemangiomas occur more frequently in females than in males, with studies suggesting a three-to-one ratio.
- Premature Birth: Babies born before 37 weeks of gestation have a significantly higher risk, as their vascular system is still developing.
- Low Birth Weight: Infants weighing less than 5.5 pounds (2.5 kg) at birth are more prone to developing hemangiomas.
- Family History: While hemangiomas are not directly inherited, some studies suggest a genetic predisposition that increases susceptibility.
- Caucasian Ethnicity: Hemangiomas are more prevalent in Caucasian infants compared to other ethnic groups.
Although the precise mechanisms behind hemangioma formation are still under investigation, understanding these risk factors helps healthcare providers identify infants who may need closer monitoring for potential hemangioma development.
Diagnosis of Hemangiomas
Diagnosing a hemangioma typically involves a thorough physical examination by a healthcare provider. They will assess the appearance, size, and location of the growth, as well as any associated symptoms.
In many cases, a visual examination is sufficient to diagnose a hemangioma. However, for deeper or internal hemangiomas, imaging tests may be necessary to determine their extent and location. These tests can include:
- Ultrasound: This non-invasive test uses sound waves to create images of the hemangioma and surrounding tissues.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): An MRI uses powerful magnets and radio waves to generate detailed images of the body, helping to visualise the hemangioma and any potential complications.
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: A CT scan combines X-rays from various angles to produce cross-sectional images of the body, which can be useful for evaluating internal hemangiomas.
In some cases, a biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions. This involves removing a small sample of tissue from the hemangioma for microscopic examination.
Treatment Options for Hemangiomas
Most hemangiomas do not require treatment and will resolve on their own over time. However, in some cases, hemangioma treatment may be necessary to prevent complications or address cosmetic concerns.
Some common hemangioma treatment options include:
- Observation: For many hemangiomas, close monitoring is sufficient, especially if they are small and not causing any complications.
- Medications: Beta-blockers, such as propranolol, have been highly effective in shrinking hemangiomas. These medications can be administered orally or topically, depending on the hemangioma's size and location.
- Laser Therapy: Pulsed dye laser treatments can help reduce the redness and size of superficial hemangiomas, particularly those on the skin's surface.
- Corticosteroids: In some cases, corticosteroid medications may be used to slow the growth of hemangiomas or reduce inflammation.
- Surgery: For larger, problematic, or persistent hemangiomas, surgical removal may be necessary. This is typically reserved for cases where the hemangioma is causing significant functional or cosmetic issues.
- Liver Hemangioma Treatment: For hemangiomas in the liver, treatment may involve medications, embolisation (blocking blood flow to the hemangioma), or, in rare cases, surgical resection.
Complications Associated with Hemangiomas
While most hemangiomas are benign and uncomplicated, some may lead to complications, especially if they are large, rapidly growing, or located in sensitive areas. Potential complications include:
- Vision impairment: Hemangiomas near the eye can cause amblyopia (lazy eye) or astigmatism if left untreated.
- Breathing difficulties: Hemangiomas in the airways can obstruct breathing, requiring prompt treatment.
- Bleeding and ulceration: Some hemangiomas may bleed or develop painful ulcers, increasing the risk of infection.
- Scarring: As hemangiomas regress, they may leave behind residual scarring or textural changes in the skin.
Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help identify and manage any potential complications early on.
Living with Hemangiomas: Tips and Support
- Educate yourself: Learning about hemangiomas, their natural course, and available treatments can help you feel more empowered and in control.
- Connect with others: Joining support groups or online communities can provide a sense of connection and allow you to share experiences with others who understand what you're going through.
- Protect the skin: If the hemangioma is on the skin's surface, keep the area clean and moisturised to prevent irritation and infection.
- Address emotional concerns: If the hemangioma is causing emotional distress or self-confidence issues, consider seeking support from a mental health professional.
- Advocate for your child: If your child has a hemangioma, be their advocate by ensuring they receive appropriate medical care and support at school or in social situations.
Prevention and Early Intervention Strategies
While there are no guaranteed ways to prevent hemangiomas from developing, early intervention can help manage their growth and minimize potential complications. Some strategies include:
- Regular check-ups: Scheduling regular visits with a healthcare provider can help monitor the hemangioma's progress and identify any concerns early on.
- Prompt treatment: If the hemangioma is causing complications or impacting vital functions, starting treatment promptly can help prevent further issues.
- Lifestyle modifications: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle during pregnancy, including avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, may help reduce the risk of hemangioma development in infants.
At Metropolis Healthcare, we understand the importance of accurate diagnosis and monitoring for hemangiomas. With a commitment to delivering reliable results and compassionate care, Metropolis Healthcare is here to support you in your health journey.






















 WhatsApp
WhatsApp