Preventive Healthcare
Behcet's Disease: A Rare Condition Affecting Multiple Body Systems
524 Views
0
What is Behcet's disease?
Behcet's disease, also known as Behcet's syndrome, is a chronic inflammatory condition that leads to inflammation of blood vessels and tissues in multiple parts of the body. The inflammation can affect the mouth, eyes, skin, joints, blood vessels, digestive system, and brain.
Who gets Behcet's disease?
Behcet's disease can affect people of all ages, genders, and ethnicities, but it is more common in certain populations. The condition most often affects young adults in their 20s and 30s, although symptoms can begin earlier or later in life. Behcet's disease is more prevalent in regions along the ancient Silk Road trade route, including Turkey, the Middle East, and parts of Asia. Genetic factors likely play a role, with certain gene variations increasing risk.
What are the symptoms of Behcet's disease?
Behçet's disease is a complex autoimmune disorder characterised by a variety of symptoms that can vary widely among individuals. The Behçet's disease symptoms often fluctuate in intensity, and many can be painful or debilitating. Here are some of the most common signs and symptoms associated with this condition:
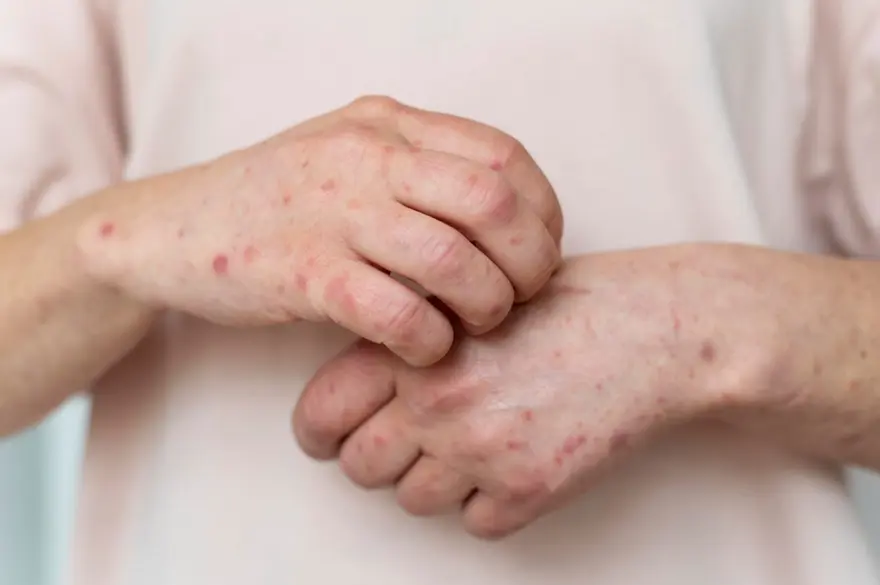
- Mouth Ulcers: One of the most characteristic Behçet's disease symptoms is the presence of painful, recurring mouth ulcers. These sores, resembling canker sores, can make eating, drinking, and speaking difficult. They may take several weeks to heal and can reappear frequently, causing significant discomfort.
- Genital Ulcers: Similar to oral ulcers, genital sores are another hallmark of Behçet's disease. These painful lesions can develop on the scrotum, penis, or vulva, and can be particularly distressing, impacting quality of life and sexual health.
- Eye Inflammation: Uveitis, or inflammation of the eye, is a common complication, affecting over half of those with Behçet's disease. Symptoms may include redness, pain, blurry vision, and sensitivity to light. If not treated promptly, this inflammation can lead to severe complications, including vision loss.
- Skin Problems: Various skin issues can occur, including acne-like bumps, painful nodules known as erythema nodosum, and other sores or lesions. These skin manifestations can vary in appearance and severity.
- Joint Pain and Swelling: Approximately half of those with Behçet's disease symptoms experience joint pain and swelling, often affecting the knees, ankles, elbows, and wrists. This arthritis can cause stiffness and discomfort, impacting daily activities.
- Blood Clots: Behçet's disease causes inflammation within blood vessels, increasing the risk of developing blood clots, such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in the legs or cerebral venous sinus thrombosis in the brain, which can pose serious health risks.
- Digestive Problems: Inflammation along the digestive tract can lead to symptoms such as abdominal pain, diarrhoea, and bleeding. These gastrointestinal issues may mimic those seen in inflammatory bowel diseases.
- Brain and Nervous System Complications: In severe cases, Behçet's disease can affect the brain and nervous system, potentially leading to conditions such as meningitis, seizures, stroke, and impaired balance or movement. These neurological symptoms highlight the seriousness of the disease and the need for effective management.
Behçet's disease is a multifaceted condition that requires ongoing monitoring and treatment by healthcare professionals to manage symptoms effectively and improve patients' quality of life.
What causes Behcet's disease?
The exact Behcet's disease causes are unknown, but it is believed to arise from a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Individuals with specific gene variations, particularly the HLA-B51 gene, are at a heightened risk for developing the condition.
Additionally, abnormal immune system responses likely play a significant role in its onset. Environmental triggers, such as viral or bacterial infections, may provoke these immune reactions, leading to the destructive inflammation characteristic of Behçet's disease in genetically predisposed individuals. This complex interplay between genetics and environmental factors contributes to the variability in symptoms and severity among those affected.
Who is at risk of developing Behcet's disease?
Several factors may increase the risk of developing Behçet's disease.
- Genetics plays a significant role, as individuals with a family history or relatives diagnosed with the condition are more susceptible.
- Ethnicity is another important factor, with higher prevalence among people of Turkish, Middle Eastern, or Asian descent.
- Age is also a key consideration, as symptoms typically emerge between the ages of 20 and 40.
- Additionally, environmental factors, such as infections, may contribute to triggering the disease in those with a genetic predisposition.
Understanding these risk factors can help in early identification and management of the condition.
How is Behcet's disease diagnosed?
Diagnosing Behcet's disease can be challenging, as there is no single definitive test. Instead, doctors must rely on a combination of exams, tests and the patient's clinical history. Some common components of a Behcet's disease diagnosis may include:
- Medical history and physical exam to document symptoms
- Blood tests to check for signs of inflammation and rule out other conditions
- Pathergy test to see if the skin is hypersensitive and overreacts to minor injuries
- Imaging tests like X-rays, CT, or MRI to assess joint, organ, or blood vessel damage
- Skin or tissue biopsy to examine for signs of inflammation under a microscope
Is Behcet's disease hereditary?
While Behcet's disease can run in families, suggesting a genetic component, it does not have a straightforward inheritance pattern. Most cases are sporadic, meaning they occur without a known family history. However, having the HLA-B51 gene variation does increase the risk, and genetic factors likely interact with environmental triggers.
How is Behcet's disease treated?
There is currently no cure for Behcet's disease, so treatment focuses on reducing inflammation, relieving symptoms, and preventing complications. Some common Behcet's disease treatment approaches include:
- Anti-inflammatory medications to quickly reduce inflammation throughout the body
- Immunosuppressant drugs to decrease harmful immune system activity
- Biologic medications to target specific inflammatory processes
- Antibiotics, antivirals or antifungals to treat infections that may trigger flares
- Topical therapies and mouth rinses to manage skin and mouth sores
Treatment plans are highly individualised based on each person's specific symptoms and disease severity. Working closely with a rheumatologist and other specialists is key for optimal Behcet's disease treatment.
What is the outlook for people with Behcet's disease?
The course of Behcet's disease is unpredictable, with periods of remission alternating with flare-ups. While the condition is not considered fatal, serious complications like stroke, blindness, or internal bleeding can occur without proper treatment. However, with early diagnosis and a comprehensive treatment plan, most people with Behcet's disease can effectively control symptoms and maintain a good quality of life.
Is Behcet's disease fatal?
In the vast majority of cases, Behcet's disease is not life-threatening. However, serious complications can arise, such as ruptured blood vessels, stroke, or meningitis. Careful monitoring and treatment adherence are important to reduce risks.
What are ways to successfully cope with Behcet's disease?
Living with a chronic condition like Behcet's disease can be challenging, both physically and emotionally. Some strategies that may help include:
- Learning as much as possible about the condition
- Maintaining open communication with your healthcare team
- Following your prescribed treatment plan consistently
- Keeping a symptom journal to identify potential triggers
- Practising stress management and relaxation techniques
- Connecting with others through local or online support groups
- Making lifestyle changes to support overall health, such as eating an anti-inflammatory diet, getting adequate sleep, and exercising regularly as able
Conclusion
Receiving a Behcet's disease diagnosis can feel overwhelming, but know that you are not alone. With the care of experienced healthcare providers and an individualised treatment plan, it is possible to successfully manage this complex condition.
If you are experiencing symptoms that may point to Behcet's disease, consider reaching out to Metropolis Healthcare for expert diagnostic testing services. Their team of qualified blood collection technicians can conveniently come to your home to collect samples, which are then processed in Metropolis' state-of-the-art labs. Timely access to accurate test results can be an important first step on the path to feeling your best. Remember, knowledge is power - and taking a proactive role in your health is always worthwhile.





















 WhatsApp
WhatsApp