Preventive Healthcare
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Injury or Tear: Treatment & Recovery Tips
1063 Views
0
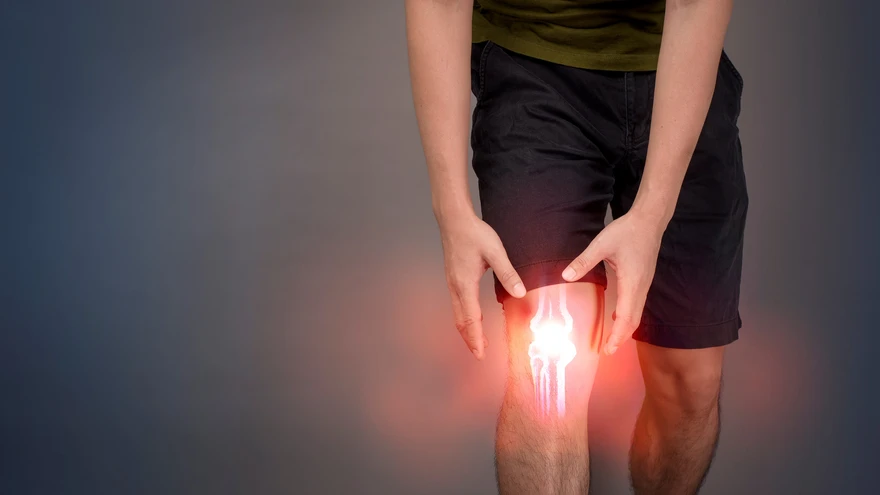
What is an ACL Tear?
The knee is an important hinge joint in our body, held together by four ligaments. These ligaments control joint movement and help keep our bones properly aligned. The two ligaments deep inside the knee are the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and posterior cruciate ligament (PCL).
An ACL tear occurs when the anterior cruciate ligament get injured or torn. The ACL controls how far the tibia (shinbone) can slide forward relative to the femur (thighbone), acting as a protector against excessive forward motion of these bones. However, during certain activities, this guardian can get injured leading to ACL injuries.
What are the Types of ACL Injuries?
ACL injuries are typically classified into three grades:
- Grade 1: Mild damage where the ACL is slightly stretched but still maintains knee stability
- Grade 2: A less common injury where the ACL is stretched and partially torn
- Grade 3: The most severe type, where the ACL is completely torn, resulting in knee instability
In addition to these grades, adolescents may experience what is known as a tibial spine avulsion ACL injury. In this case, the ACL isn't torn but its bony attachment to the tibia gets pulled off leading to instability of the knee if not repaired promptly.
What Does an ACL Tear Feel Like?
People usually know when they have an ACL tear because they often hear a distinct "pop" sound or feel a sudden sensation in their knee during the injury. This is often followed by strong pain, though some might just feel mild discomfort. Many also feel an instability or weakness in the knee, which can make it hard to put weight on the leg.
How Common are ACL Injuries?
ACL injuries are surprisingly common, especially among athletes. The ACL is considered the most frequently injured knee ligament, with an estimated 100,000 to 200,000 people in the United States suffering from ACL tear each year
What are ACL Tear Symptoms?
ACL tear symptoms exhibit certain characteristics like:
- A "pop" in the knee at the time of injury
- Swelling around the knee
- Pain, particularly when attempting to put weight on the knee
- A sensation of instability or "giving way" of the knee
What Causes ACL Tears?
ACL tear causes are primarily linked to activities that involve sudden changes in direction, abrupt stops, or improper landings from jumps. These actions put excessive stress on the anterior cruciate ligament, leading to injury. ACL tear causes also includes direct contact during sports like football or basketball, where collisions may occur.
Additionally, factors such as anatomical differences, hormonal influences in females, and a history of previous knee injuries can increase the risk of ACL tears. Understanding these ACL tear causes is crucial for developing an effective prevention strategies to reduce the likelihood of injury among athletes and active individuals.
What are the ACL Tear Risk Factors?
While anyone can suffer an ACL tear, certain factors can increase an individual's risk:
- Athletic Participation: Athletes, particularly those involved in sports that require sudden stops and changes in direction
- Gender: Women are at a higher risk for ACL tears compared to men
- Wear and Tear: Overuse of the knee joint can weaken it over time, increasing the risk of an ACL tear
What are the Complications of an ACL Tear?
An ACL tear is often accompanied by damage to other parts of the knee as well. These may include tears in other ligaments like the medial collateral ligament (MCL), lateral collateral ligament (LCL), or posterior cruciate ligament (PCL). Other potential injuries include bone fractures, meniscus tears, and muscle strains.
How are ACL Tears Diagnosed?
An ACL tear is diagnosed through a physical examination and imaging tests. A healthcare provider will ask about symptoms, check the knee, and may do specific movements to check the seriousness of the injury. Imaging tests like X-rays, CT scan, or MRI might be necessary for definitive diagnosis.
How are ACL Tears Treated?
ACL tear treatment varies based on the severity of the injury and the patient's activity level
- For minor tears, nonsurgical treatment is often recommended, including physical therapy, activity modification, and using a brace to stabilise the knee. The goal is to strengthen the surrounding muscles around the knee and restore mobility surgery.
- In cases of complete ACL tears, ACL tear treatment usually involves a surgical reconstruction. This procedure replaces the torn ligament with a graft, which can be taken from the patient's own body or a donor. The goal of surgery is to restore knee stability and prevent future injuries.
- Post-surgery, rehabilitation is crucial for recovery, focusing on regaining strength and range of motion. Recovery can take several months, depending on individual circumstances and adherence to rehabilitation protocols.
- Ultimately, the choice between surgical and nonsurgical options depends on factors like age, activity level, and specific injury characteristics.
Can an ACL Tear Heal on its Own?
While minor strains in the ACL might heal over time with rest, cases involving partial or complete tears are unlikely to heal without intervention. For those involved in physical activity or sports or people looking for full functional recovery of their knee joint may require surgical intervention.
ACL Tear Surgery
Surgical treatment for an ACL tear involves reconstructing the torn ligament with a graft made from tendon. This arthroscopic procedure is minimally invasive and you can usually return home the same day. Post-surgery, patients are advised to follow a rehabilitation program which includes physical therapy exercises to help regain strength and mobility in the knee.
How Can I Prevent an ACL Tear?
Preventing an ACL tear involves several proactive strategies. ACL tear treatment can minimise the risk by focusing on strength training to enhance the muscles around the knee, particularly the hamstrings and quadriceps. This support helps stabilise the knee joint during dynamic movements.
Also, practicing balance exercises can help improve stability and reduce the chances of awkward landings or sudden twists that might cause injuries. It's important to warm up and stretch before any activity to prepare your muscles and ligaments, which can help prevent injuries.
Using proper technique in sports, like landing softly from jumps and keeping your knees aligned, is also important for prevention. Wearing the right shoes and using protective gear can help further reduce the risk of injuries.
Finally, consulting with a sports medicine specialist can help identify individual risk factors and tailor a prevention program, ensuring that athletes are well-prepared to avoid ACL injuries. Following these guidelines significantly reduces the likelihood of an ACL tear.
How Long Does It Take to Recover from a Torn ACL?
Recovery time from an ACL injury varies depending on the severity of the tear, the type of treatment received, and individual health factors. Generally, it takes about six to nine months for a complete recovery post-surgery. However, it's important not to rush your recovery. Following post-op care and physiotherapy instructions closely can help prevent re-injury
Can You Walk if Your ACL is Torn?
Some individuals are able to walk with a torn ACL, though this greatly depends on the extent of the injury. However, putting too much pressure on the knee could worsen the condition. If you feel pain or instability in your knee after an injury, consult a healthcare professional immediately.
When to See a Doctor?
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience severe pain in your knee along with swelling or difficulty in weight-bearing. If ACL tear symptoms persist despite rest and self-care measures, it's crucial to get a prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment to avoid complications.
Will an ACL Tear Happen Again?
There is always a possibility of re-injuring a previously torn ACL, especially in athletes. About 10% of people who have had an ACL tear experience a second injury. However, following a well-structured rehabilitation program and taking preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk.
Is an ACL Tear "Career-Ending" for an Athlete?
Thanks to advances in surgical techniques and rehabilitation programs, most athletes can return to their sports after an ACL tear. However, full recovery is crucial before resuming sports activities to prevent re-injury
Conclusion
Understanding an ACL tear, its symptoms, causes, and treatment options is important for managing this common sports injury. Quick diagnosis and prompt treatment are essential to prevent further issues
If you’ve suffered an ACL injury or suspect you might have one, consider reaching out to Metropolis Healthcare for diagnostic services. They provide an accurate pathology testing and at-home sample collection facilitated by qualified technicians, Metropolis Healthcare aims to provide reliable results and personalised care for all patients.
Prioritising your health is a step away with Metropolis Healthcare's patient-centric approach.




















 WhatsApp
WhatsApp