Preventive Healthcare
An in-depth guide to Thyroiditis: Decoding the mystery behind Thyroid Inflammation
1327 Views
0
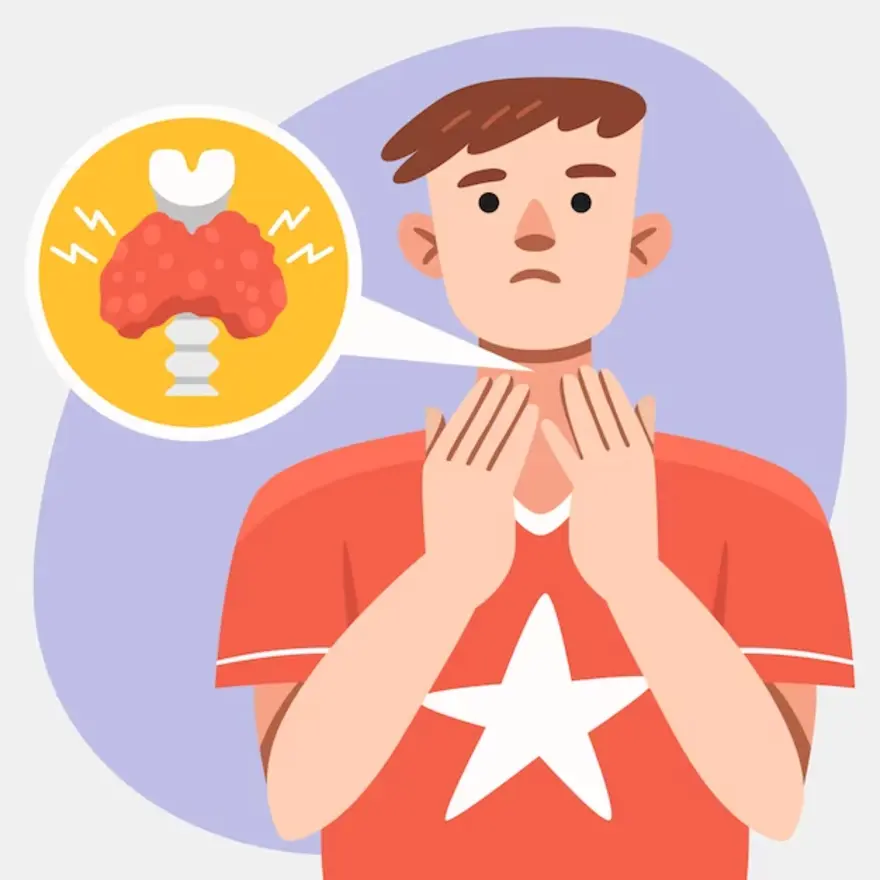

Have you ever wondered about the importance of your thyroid gland? It is a small gland in your body that helps regulate your metabolism and overall health. But sometimes, things can go wrong, and inflammation can disrupt this delicate balance, leading to a thyroid disorders called thyroiditis. But worry not; we are here to help you decode this condition.
In this blog, we will talk about the causes of thyroiditis, what symptoms and treatments of thyroiditis to look out for, and when to consult a doctor. Whether it is an autoimmune thyroiditis like Hashimoto's or one of the other types caused by viruses or pregnancy, we have covered it all for you. So, by the end, you will have all the knowledge you need to fully understand thyroiditis and make smart choices about your thyroid health. So let's get started!
What is Thyroiditis?
Thyroiditis is a condition when your thyroid gland is affected by inflammation. This thyroiditis typically progresses through several phases:
- Initial Inflammation: Thyroiditis often begins with an acute phase marked by thyroid gland inflammation. This may result in the release of thyroid hormones into your bloodstream and an initial surge in thyroid hormone levels.
- Hypothyroid Phase: Following the initial inflammation, some thyroiditis may progress to a hypothyroid phase. This occurs when your thyroid gland is damaged, leading to a decrease in the production of thyroid hormones.
- Hyperthyroid Phase: It is a transient phase due to the release of stored thyroid hormones from the damaged thyroid gland into your bloodstream.
- Resolution or Chronic Phase: Depending on the cause and your response to treatment, thyroiditis may either resolve on its own or enter a chronic phase. In chronic cases, your thyroid gland may remain inflamed, and there could be a long-term impact on thyroid function.
- Recovery Phase: You may experience a gradual return to normal thyroid function after the acute phase. The thyroid gland may recover its regular activity, and symptoms can subside over time.
When inflammation occurs, it can affect the normal functioning of your thyroid, leading to a range of thyroiditis symptoms and complications.
What are the types of thyroiditis?
Each type of thyroiditis has unique characteristics. Here are some prominent types of thyroiditis :
- Hashimoto's Thyroiditis: This is the most common form and is an autoimmune disorder where the immune system mistakenly attacks your thyroid tissue. Over time, this can lead to a gradual decline in your thyroid function, resulting in hypothyroidism.
- Subacute Thyroiditis: This involves inflammation of your thyroid gland. It may cause pain and tenderness in the neck and symptoms of hyperthyroidism initially, followed by a hypothyroid phase.
- Postpartum Thyroiditis: Occurring in the postpartum period, this type of thyroiditis affects some women after giving birth. It involves inflammation and may lead to transient hyperthyroidism followed by hypothyroidism.
- Silent Thyroiditis: Similar to postpartum thyroiditis, silent thyroiditis is painless and often presents with a period of hyperthyroidism followed by hypothyroidism. It may resolve on its own without long-term consequences.
- Infectious Thyroiditis: This is a rare condition usually caused by a bacterial infection. You may experience severe symptoms such as fever, neck pain, and difficulty swallowing.
- Drug-Induced Thyroiditis: Certain medications can induce thyroid gland inflammation, causing thyroiditis.
- Radiation-Induced Thyroiditis: Radiation exposure, such as during radiation therapy for head and neck cancers, can lead to inflammation of your thyroid gland.
Who does Thyroiditis affect?
Thyroiditis can affect individuals of any age, gender, or background. However, certain factors may increase your vulnerability, including a family history of thyroid disorders, autoimmune conditions, recent childbirth (postpartum thyroiditis), viral infections, or exposure to specific medications or radiation.
Women are more prone to thyroiditis than men, and it often manifests during periods of hormonal fluctuations, such as puberty, pregnancy, or menopause. While Hashimoto's Thyroiditis is standard, other types, like Subacute Thyroiditis or Silent Thyroiditis, can also impact a diverse population.
How Common is Thyroiditis?
Thyroiditis is a relatively common condition worldwide, with its prevalence varying among different types. The incidence of thyroid disorders is exceptionally high in India, with about 42 million people affected.
Is thyroiditis life-threatening?
In general, thyroiditis is not considered life-threatening, but its influence on your health can vary depending on the type and severity.
Most forms, such as Hashimoto's thyroiditis or Subacute thyroiditis, are manageable with proper medical intervention. However, complications may arise, especially if your thyroid function is significantly impaired. Untreated or severe cases of thyroiditis can lead to long-term hypothyroidism, affecting your metabolism and overall health.
Acute infectious thyroiditis, though rare, can be more severe and may require prompt medical attention, including antibiotics. Additionally, if thyroiditis results in thyroid storm— a rare, life-threatening condition characterised by extreme hyperthyroidism, it demands emergency treatment.
What are the symptoms of thyroiditis?
The symptoms of thyroiditis can change as the condition progresses or transitions between hyperthyroidism (thyrotoxicosis) and hypothyroidism phases in certain types of thyroiditis. These symptoms of thyroiditis can also vary in intensity and presentation, and you may not experience all of them.
Symptoms of Thyrotoxicosis
- Palpitations or a rapid heartbeat are seen.
- You can experience unexplained weight loss despite normal or increased appetite.
- Feeling jittery, anxious, or irritable.
- Difficulty tolerating heat and excessive sweating.
- You may feel tremors, especially in the hands.
- Despite little activity, you may feel fatigued.
- You may have difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep.
Symptoms of Hypothyroidism
- Persistent tiredness and lack of energy.
- Unexplained weight gain or difficulty losing weight.
- Intolerance to cold temperatures is a common symptom of thyroiditis.
- Feelings of sadness or anxiety.
- Dryness and brittleness of skin and hair.
- You may experience weakness, especially in the muscles.
- Difficulty in bowel movements.
- Forgetfulness and difficulty concentrating.
- Changes in menstrual cycles in women.
What are the causes of thyroiditis?
The causes of thyroiditis depend on the specific type of thyroiditis. Given below are the common causes of thyroiditis:
- The most prevalent cause of thyroiditis is an autoimmune response, where your immune system mistakenly targets your thyroid gland. It is characterised by chronic inflammation and gradual thyroid dysfunction.
- Excessive or insufficient iodine intake can be a cause of thyroiditis. Both excess iodine and its deficiency can disrupt your thyroid function and lead to inflammation.
- Some forms of thyroiditis, like Subacute Thyroiditis, are triggered by viral infections. The inflammation results from your body's response to the infection, affecting the thyroid gland.
- Hormonal changes during and after pregnancy are a common cause of thyroiditis.
- If you have a family history of thyroid disorders, you may have a higher risk of developing certain thyroiditis.
- Bacterial infections can also be a cause of thyroiditis. It typically involves a sudden onset of inflammation caused by the invasion of bacteria.
- Certain medications, such as amiodarone, interferon, and lithium, can induce thyroiditis in sensitive individuals. This is known as drug-induced thyroiditis.
How is thyroiditis diagnosed?
Diagnosing thyroiditis involves a comprehensive evaluation of your thyroid gland, including a combination of clinical assessments, blood tests, and imaging studies. The following are some commonly employed steps in the thyroiditis diagnosis:
- Doctors usually begin by conducting a thorough medical history and physical examination. Symptoms such as fatigue, weight changes, and neck pain are discussed, and the medical history may reveal factors such as recent childbirth, medication use, or radiation exposure.
- Blood tests are crucial for assessing your thyroid function and identifying specific antibodies associated with autoimmune thyroiditis. Thyroid function is typically evaluated by measuring levels of Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH), Free Thyroxine (FT4), and Free Triiodothyronine (FT3). Elevated levels of thyroid antibodies, such as anti-thyroid peroxidase (TPO) antibodies, are indicative of autoimmune thyroiditis.
- Ultrasound imaging can reveal the size, structure, and any abnormalities in your thyroid. This is particularly useful for conditions like Subacute thyroiditis, where inflammation and changes in your thyroid structure may be visible.
- In cases where a nodule or lump is present in the thyroid, fine needle aspiration is used for thyroiditis diagnosis. This involves using a thin needle to extract a small tissue sample for examination under a microscope, helping to rule out malignancy.
- A Radioactive Iodine Uptake Test (RAIU) measures your thyroid's ability to take up iodine. While not commonly used for routine thyroiditis diagnosis, it may be used to assess your thyroid function in certain situations.
- A thyroid scan also involves administering a small amount of radioactive material, which is taken up by your thyroid gland. This scan further provides information about your gland's structure and function, aiding in diagnosing certain thyroid disorders.
How is thyroiditis treated?
Thyroiditis treatment varies based on the type and phase. The treatment of thyroiditis may include medications to address your symptoms, hormone replacement therapy, or even surgery in severe cases.
Thyrotoxicosis Treatment for Thyroiditis
Thyrotoxicosis in thyroiditis treatment is typically managed with medications like beta-blockers to alleviate symptoms of thyroiditis, such as rapid heart rate and anxietyb. In some cases, anti-thyroid drugs may be prescribed to control excessive thyroid hormone production.
Hypothyroidism Treatment for Thyroiditis
Hypothyroidism in thyroiditis treatment is managed with hormone replacement therapy, primarily involving the synthetic thyroid hormone levothyroxine. This medication restores adequate thyroid hormone levels in your body, alleviating thyroiditis symptoms such as fatigue, weight gain, and cold sensitivity.
The dosage is adjusted based on periodic monitoring of thyroid function through blood tests. Therefore, you need to adhere to prescribed medications consistently. In cases of Postpartum Thyroiditis or Silent Thyroiditis, where hypothyroidism might be transient, thyroiditis treatment duration may vary. Lifestyle factors, including a balanced diet and stress management, may complement your medical treatment. If hypothyroidism is mild and symptoms are minimal or absent, you may not require medication.
Other Treatments for Thyroiditis
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) may be prescribed to manage pain and inflammation, especially in cases like Subacute Thyroiditis.
- In certain types of thyroiditis, particularly those with significant inflammation, corticosteroids may be used to reduce your immune system activity and inflammation.
- In cases of persistent hyperthyroidism, particularly in Graves' disease, Radioactive Iodine treatment may be considered to reduce your thyroid activity.
- Adequate rest, hydration, and pain management are essential components of supportive care during acute phases of thyroiditis.
- Surgical removal of part or all of your thyroid gland may be recommended in cases where nodules or goitres cause compression or when you have thyroid cancer.
- In Acute Infectious Thyroiditis caused by bacterial infections, antibiotic therapy is essential to resolve your infection and reduce inflammation.
Can Thyroiditis be Prevented?
Yes, non-genetic thyroiditis can be prevented by addressing the underlying causes and maintaining overall health. Some of the measures include:
- Ensuring a balanced iodine intake, as excessive or insufficient iodine may contribute to thyroiditis.
- Practising good hygiene reduces the risk of viral or bacterial infections that can trigger thyroiditis.
- Smoking has been linked to an increased risk of autoimmune thyroid diseases, including Hashimoto's thyroiditis. Quitting smoking may lower the risk.
- Be aware of potential side effects of medications that could induce thyroiditis.
What is the Prognosis (Outlook) for Thyroiditis?
The prognosis for thyroiditis varies based on factors such as type and timely intervention. Many cases respond well to treatment, allowing individuals to lead healthy lives.
For instance, Hashimoto's Thyroiditis and Postpartum Thyroiditis are often manageable with hormone replacement therapy, and the latter can resolve within 12-18 months. Subacute Thyroiditis may resolve on its own, while Acute Infectious Thyroiditis responds to antibiotics. However, some cases may lead to permanent hypothyroidism. Moreover, the recovery times can vary; Subacute Thyroiditis typically resolves within a few months, while autoimmune conditions like Hashimoto's thyroiditis require lifelong treatment.
When Should I See My Healthcare Provider About Thyroiditis?
You should promptly consult a doctor if you experience thyroiditis symptoms like unexplained fatigue, weight changes, neck pain, rapid heartbeat or cold sensitivity. Moreover, if you have a family history of thyroid disorders or are pregnant and notice changes, schedule a consultation to assess your thyroid health.
Conclusion
Understanding thyroiditis helps you recognise symptoms, seek timely medical attention, and navigate personalised treatment plans. Regular monitoring, lifestyle adjustments, and consultation with doctors ensure you have optimal thyroid health and a positive outlook. If you are looking to accurately evaluate your TSH and thyroxine levels or a full thyroid blood test panel at affordable prices, look no further than Metropolis Labs. With state-of-the-art testing facilities, trained phlebotomists and reliable digital reports, Metropolis Labs is the first choice for top hospitals and doctors in India.






















 WhatsApp
WhatsApp