Preventive Healthcare
Alopecia Areata: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment
1079 Views
0
Introduction
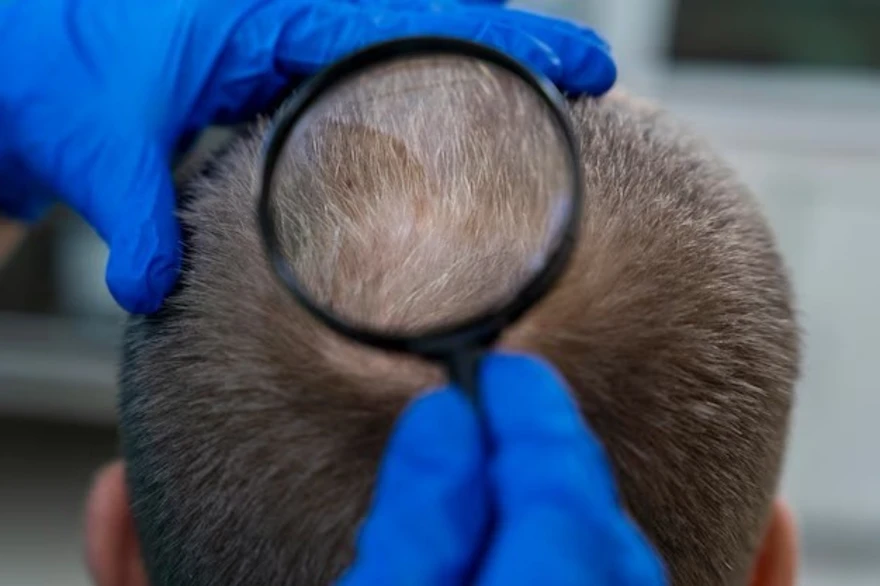
Hair is often viewed as a symbol of self-expression, style, and confidence. Imagine the distress you would feel if you woke up one day to find small patches of hair missing from your scalp! This is the reality for people living with alopecia areata, a condition causing hair loss in patches.
Alopecia areata can affect anyone, regardless of age or gender. It's a common autoimmune disease where the body's immune system mistakenly attacks its hair follicles, resulting in hair loss mainly on the scalp but sometimes elsewhere on the body as well. This article aims to provide an overview of this condition – from its causes and symptoms to diagnosis and treatment methods.
What Is Alopecia Areata?
Often characterised by hair loss in patches, alopecia areata is a type of autoimmune disease. This means that your own immune system starts attacking healthy cells in your body – in this case, the hair follicles. This attack inhibits the growth of new hair strands and leads to unpredictable hair loss in small coin-sized rounds or patches.
Who Gets Alopecia Areata?
Alopecia areata does not discriminate when it comes to age or gender – it can affect men and women equally. The onset often occurs during teenage years or early twenties but it can start at any age. In fact, when children under 10 are diagnosed with alopecia areata, the progression tends to be more extensive.
How Common Is Alopecia Areata?
According to reliable studies, alopecia areata affects approximately 7 million people in the United States alone. This makes it the second-most common form of hair loss, next to male and female pattern baldness. Among those affected, 5% have Alopecia Areata Totalis (loss of all scalp hair) and 1% have Alopecia Areata Universalis (complete hair loss on the scalp and body).
What Happens If You Have Alopecia Areata?
Alopecia areata mainly affects your physical appearance, causing hair loss in patches. In some cases, it can also impact your nails, leading to dents or pits. While it doesn't typically affect your physical health directly, it can significantly impact how you perceive yourself and interact with others. This can lead to psychological stress, anxiety, and in some cases, depression.
What Are the Symptoms of Alopecia Areata?
The most identifiable symptom of alopecia areata is hair loss in patches on the scalp or elsewhere on the body. You might also notice changes to your nails such as dents or pits that give them a sandy or gritty texture.
However, not everyone experiences these typical symptoms. Rarely, patchy areas might itch or change colour. In certain cases, black dots (cadaver hairs) may be visible in hair follicles. Sometimes short hairs that are thicker at the top and narrow towards your scalp (exclamation point hairs) may grow out.
What Causes Alopecia Areata?
While we know that alopecia areata is an autoimmune disorder where the immune system attacks hair follicles, medical experts are yet to understand why this happens. It appears that genetics play a role as those who have a family member with the condition are more likely to get it themselves.
Certain triggers could also stimulate the onset of the disease. These may include:
* Asthma
* Down Syndrome
* Pernicious anaemia
* Seasonal allergies
* Vitiligo
Is Alopecia Areata Contagious?
Contrary to some misconceptions, alopecia areata is not contagious. It cannot be spread through skin-to-skin contact, shared belongings or through the air. It's primarily a result of an autoimmune response and genetic predisposition.
How Is Alopecia Areata Diagnosed?
Diagnosing alopecia areata involves medical consultation and examination. Your doctor will likely:
1. Perform a physical exam: This involves examining the patches of hair loss on your scalp or other parts of your body.
2. Ask about your diet and hair care routine: Unhealthy diet or harsh hair care routines can contribute to hair loss.
3. Conduct a blood test: This can help uncover any medical conditions that are causing hair loss.
4. Pull Test: The doctor gently pulls several dozen hairs to see how many come out. This helps determine the stage of the shedding process.
5. Scalp biopsy: A small sample from your scalp or from a few plucked hairs is examined under a microscope to check if an infection is causing hair loss.
What Tests Will Be Done To Diagnose Alopecia Areata?
Your healthcare provider may perform several tests to diagnose alopecia areata. These tests could include:
- A physical examination of bald spots on your scalp or body.
- Checking your scalp for signs of infections.
- Collecting a sample of your hair for lab analysis.
- Conducting a scalp biopsy to look for skin diseases.
- Performing blood tests to rule out other conditions.
Can Alopecia Areata Go Away?
Unfortunately, there's no permanent cure for alopecia areata. However, with effective alopecia areata treatment, it can be managed successfully. This means hair can regrow over time but may fall out again later.
How Is Alopecia Areata Managed?
Managing alopecia areata involves various treatments that aim to spur hair growth back. Some commonly used methods include:
- Corticosteroids: These anti-inflammatory drugs can either be taken orally or applied topically to the affected areas.
- Topical immunotherapy: This involves applying chemicals to the scalp to produce an allergic reaction which can stimulate hair growth.
- Minoxidil (Rogaine): This over-the-counter medication can help promote hair growth in some people.
It's essential to consult your healthcare provider before starting any alopecia areata medication to ensure it's suitable for you.
Can Hair Grow Back From Alopecia?
Yes, with effective alopecia areata therapy, hair can grow back. The regrowth timeframe can differ from person to person, ranging from four weeks to several months.
How Can I Prevent Alopecia Areata?
Preventing alopecia areata is challenging due to its autoimmune nature. However, managing stress levels, maintaining a balanced diet, and using gentle hair products could potentially reduce the risk of triggering the condition.
What Can I Expect If I Have Alopecia Areata?
If you're diagnosed with alopecia areata, expect occasional flare-ups and periods of remission. Depending on your treatment's effectiveness, you may see new hair growth within a few weeks or months.
How Do I Take Care of Myself?
Living with alopecia areata demands adopting certain self-care measures like using makeup to conceal hair loss, wearing protective coverings, and eating a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals that promote hair growth.
Things To Avoid When You Have Alopecia Areata
When living with alopecia areata, avoid factors that could potentially worsen your condition like excessive stress, hair products containing harsh chemicals, or fad diets that may lead to nutrient deficiencies.
When To See A Doctor?
Seek immediate medical help if you notice sudden hair loss in patches or if your symptoms don't improve despite undergoing alopecia areata treatment.
Conclusion
While living with alopecia areata can be challenging, understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options can empower you to manage the condition effectively. Remember, early diagnosis and treatment can significantly enhance the chances of successful hair regrowth. Therefore, if you or a loved one is dealing with this condition, consider reaching out to Metropolis Healthcare for diagnostic services. With a qualified team of professionals providing accurate pathology testing at your doorstep, managing your health just got simpler.






















 WhatsApp
WhatsApp