Preventive Healthcare
Adenomyosis: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatments
2463 Views
0
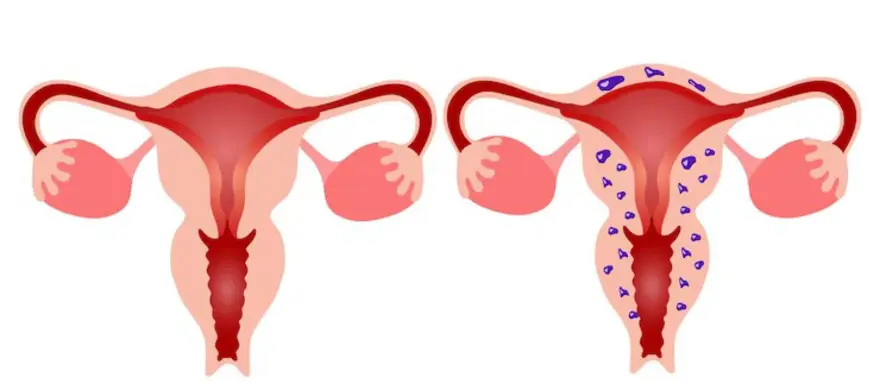
What is Adenomyosis?
Adenomyosis is a medical condition characterised by the presence of endometrial tissue. The tissue normally lines the uterus, however, in this condition, it grows into the muscular wall of the uterus. It is often referred to as the adenomyotic uterus. This can cause the uterus to enlarge, leading to symptoms such as heavy menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain, and discomfort. Adenomyosis can affect women of all ages, particularly those who have had multiple pregnancies or uterine surgeries.
What are the Symptoms of Adenomyosis?
Adenomyosis symptoms include:
- Heavy menstrual bleeding
- Prolonged menstrual periods
- Severe menstrual cramps
- Pelvic pain or pressure
- Discomfort during intercourse
What Causes Adenomyosis?
Adenomyosis is a complex condition with many possible causes. However, there is still no definitive explanation as to why it is caused. Understanding the adenomyosis causes can provide insights into the development and progression of adenomyosis. These causes include:
- Hormonal Imbalance: If there's too much estrogen in the body, it can cause the lining of the womb to grow into the muscle of the uterus. This imbalance could be due to age, certain medications, or other health issues.
- Childbirth and Uterine Trauma: Having many pregnancies or experiencing trauma during childbirth can lead to adenomyosis. The uterus gets stretched and weakened, which might allow the lining cells to move into the muscle wall.
- Inflammation and Immune Response: Long-term inflammation in the uterus can help adenomyosis develop. Inflammation messes up the normal structure of the uterus lining, making it easier for the lining to grow into the muscle. Also, if something is off with the body's immune system, it might contribute to the problem.
- Genetic Predisposition: Sometimes, adenomyosis runs in families, or specific genetic differences related to hormone and immune functions might increase the risk.
- Estrogen Dominance: Having too much estrogen compared to progesterone can cause the lining to grow more and worsen adenomyosis symptoms.
What are the Risk Factors for Adenomyosis?
Several factors may increase the risk of developing adenomyosis. These include:
- Age: Adenomyosis commonly affects women in their 30s and 40s, particularly those who have had children.
- Previous Uterine Surgeries: Women who have undergone procedures such as cesarean sections or fibroid removal may have an increased risk.
- Hormonal Factors: Hormonal imbalances, such as estrogen dominance, can predispose individuals to adenomyosis.
What are the Complications of Adenomyosis?
Adenomyosis causes various complications, including:
- Infertility: Severe adenomyosis may impair fertility by disrupting the uterine environment required for embryo implantation.
- Chronic Pain: Persistent pelvic pain and discomfort associated with adenomyosis can significantly impact the quality of life and daily activities.
- Anaemia: Heavy menstrual bleeding associated with adenomyosis can lead to iron deficiency anaemia, resulting in fatigue and weakness.
How is Adenomyosis Diagnosed?
Adenomyosis diagnosis involves a multifaceted approach to rule out adenomyosis stages. This approach aims at identifying characteristic features such as:
- Medical History Review: Healthcare professionals gather a detailed medical history, including symptoms such as heavy menstrual bleeding, prolonged periods, pelvic pain, and discomfort during intercourse.
- Physical Examination: A pelvic exam is often conducted to assess the size, shape, and tenderness of the uterus. An enlarged or tender uterus may indicate adenomyosis. These findings are not definitive and may require further confirmation through imaging studies.
- Imaging Studies: Imaging modalities such as transvaginal ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) play a crucial role in diagnosing adenomyosis.
- Hysteroscopy: In some cases, a diagnostic procedure called hysteroscopy may be recommended to visualise the inside of the uterus. It helps to confirm the presence of adenomyosis and assess its severity.
How is Adenomyosis Treated?
Adenomyosis treatment aims to alleviate symptoms, reduce pain, and improve overall quality of life. The approach to Adenomyosis treatment may vary depending on factors such as the severity of symptoms, the patient's age, and their desire for future fertility.
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may be prescribed to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation associated with adenomyosis. Hormonal therapies, such as birth control pills, hormonal IUDs, or GnRH agonists, can help regulate menstrual cycles and alleviate adenomyosis symptoms. It does so by suppressing estrogen production.
- Surgical Interventions: In cases where symptoms are severe or medication therapy is ineffective, surgical options may be considered. Procedures such as endometrial ablation, uterine artery embolization, or hysterectomy (removal of the uterus) may be recommended to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Making lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and managing stress can help alleviate adenomyosis symptoms and improve overall well-being.
- Fertility Considerations: For women who desire future fertility, conservative surgical approaches such as adenomyomectomy (surgical removal of adenomyotic lesions while preserving the uterus) may be considered.
How Does Adenomyosis Affect Pregnancy?
Adenomyosis can increase the risk of pregnancy complications such as miscarriage, preterm birth, and placental abnormalities. Additionally, adenomyosis contributes to infertility by impairing embryo implantation or disrupting the normal function of the uterus during pregnancy.
What is the difference between Adenomyosis and Endometriosis?
Adenomyosis occurs when endometrial tissue grows into the muscular wall of the uterus, causing symptoms such as heavy menstrual bleeding and pelvic pain. Endometriosis, on the other hand, involves the presence of endometrial tissue outside the uterus, commonly affecting pelvic organs like the ovaries and fallopian tubes, leading to symptoms such as pelvic pain, infertility, and painful intercourse.
When to See a Doctor?
If you experience symptoms suggestive of adenomyosis, such as heavy menstrual bleeding, prolonged periods, severe menstrual cramps, or pelvic pain, it's essential to consult a healthcare provider.
Conclusion
Adenomyosis, though often overlooked, can significantly impact a woman's quality of life. Early recognition of symptoms and prompt medical attention are crucial for effective management. With proper adenomyosis diagnosis and personalised adenomyosis treatment, individuals can experience relief from symptoms and improve their overall well-being.
Metropolis Healthcare provides a comprehensive range of 4000+ clinical laboratory tests and profiles. Take the first step towards managing your health by scheduling an appointment with our experienced team of professionals for your diagnostic services..























 WhatsApp
WhatsApp