Disease
The science behind vitamin B12: Why do you need it?
9229 Views
1
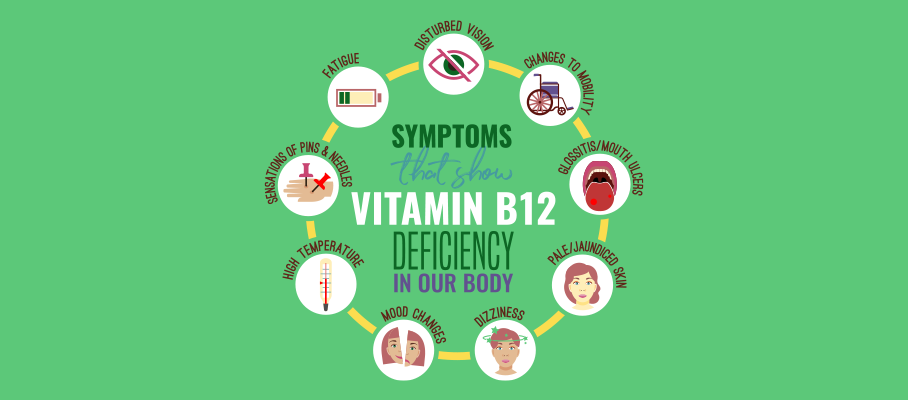
In today’s time, almost everyone is turning towards a plant-based diet. Although it is healthy, it has a few downfalls if you do not take supplements for certain nutrients missing in a plant-based diet. One of these important nutrients is vitamin B12. Falling short of vitamin B12 can have a serious impact on your health
What is vitamin B12?
Vitamin B12 is an essential vitamin for the human body. It is a micronutrient which means your body requires it in small amounts. It is naturally found in animal foods. Vitamin B12 is required for red blood cell formation, optimal functioning of brain and nerve cells, and maintenance of a healthy immune system.
It is also known as cobalamin and is a water-soluble vitamin. This means it can dissolve in water and travel into the bloodstream. Any excess vitamin B12 is excreted in the urine.
Your body can store vitamin B12 for several years in the liver, so a deficiency of this vitamin is usually rare. However, if you are a vegetarian, you might become deficient because plant foods do not contain vitamin B12. To prevent that, you need to take vitamin B12 from supplements.
Where can you get vitamin B12 from?
Vitamin B12 is naturally found in animal foods. Good dietary sources of vitamin B12 include:
- Poultry
- Red meat
- Eggs
- Dairy products like milk, cheese, yogurt
- Fish
- Fortified breakfast cereals
- Fortified nutritional yeast
- Enriched soy milk
How much vitamin B12 do you need?
According to the National Institute of Health, the Recommended Dietary Allowance for men and women aged 14 years and above is 2.4 micrograms (mcg) daily.
For pregnant and lactating women, it is 2.6 mcg and 2.8 mcg daily, respectively.
Want to get your vitamin B12 level checked? Check here
What happens when you do not take an adequate amount of vitamin B12?
This leads to various deficiencies such as:
1. Anemia
When you do not take an adequate amount of vitamin B12, it leads to a type of anemia known as megaloblastic anemia. In this condition, the size of the red blood cells increases. As a result of this, the red blood cells are unable to move from bone marrow to the bloodstream. Consequently, you might face fatigue, weakness, pale skin, and shortness of breath.
2. Tingling sensation in hands and legs
Vitamin B12 plays a vital role in maintaining the covering of nerve cells, called the myelin sheath. It is the fatty material that surrounds and protects your nerves. When you are vitamin B12 deficient, your nerve cells cannot function properly. This eventually might alter the way you move. It can affect your body balance and make you more likely to fall.
3. Brain fog
Your memory can become hazy. You can find it difficult to concentrate.
4. Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a bone disease in which the bones become weak and may break from a fall. Vitamin B12 plays an important role in maintaining good bone health. Low levels might lead to low bone mineral density. This makes the bones delicate and fragile over time, leading to osteoporosis.
Some of the other symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency are confusion, depressive symptoms, and vision loss. Some of the studies had stated that vitamin B12 deficiency could pose a risk of COVID-19 in older patients. However, these studies still remain to be peer-reviewed. Further validation research is required to claim the association of vitamin B12 deficiency and COVID-19.
Who can be at a risk of vitamin B12 deficiency?
- People avoiding animal products
People who follow a strict plant-based diet are at risk of becoming deficient in vitamin B12 since it is found naturally in animal products.
- Elderly people
Gastritis is a condition that affects elderly people the most. In this condition, the body becomes unable to absorb vitamin B12 that is naturally present in food.
- People with certain digestive disorders
Certain digestive disorders like inflammatory bowel disease, Celiac, and Crohn's disease reduces the body's potential to absorb vitamin B12. Thus causing deficiency of vitamin B12.
- People who had undergone gastrointestinal surgery
Weight loss surgeries or surgery to remove part of the stomach often interferes in the proper absorption of vitamin B 12 from the diet.
- Pregnant and lactating women
Vitamin B12 can pass from mother to baby via breast milk. Mothers who exclusively breastfeed their baby and follow a plant-based diet might make their baby deficient of vitamin B12. Without enough vitamin B12, the baby might have growth and developmental delays.
- People with chronic alcoholism
In this condition, the body becomes unable to absorb vitamin B12 efficiently from the diet.
How to overcome vitamin B12 deficiency?
You can take animal-based food and if you are a vegetarian you can take vitamin B12 fortified cereals. You can also take vitamin B12 supplements with doctor’s advice.
Are there any side-effects of vitamin B12?
Vitamin B12 is a water-soluble vitamin. After the body utilises the required amount of vitamin B12, leftover amount will pass through urine. Generally, there are no side-effects seen with excess vitamin B12 intake from food. However, it is always advisable to consult your doctor before starting a high dose of vitamin B12 supplements.
When do you need a vitamin B12 test?
If you think you might be vitamin B12 deficient, it is advisable to consult your doctor and get a blood test done. Vitamin B12 is like a regular blood test and you can get it done from any trustworthy laboratory.
The normal range is 211 - 911 pg/mL irrespective of sex and age.
Bottom line
Vitamin B12 is a water-soluble and essential vitamin. It is responsible for various health benefits like preventing anemia, supporting the nervous system, improving and maintaining healthy bones. You can get the required amount of vitamin B12 from your diet (animal food). However, if you follow a plant-based diet or have a condition that affects absorption, supplements are a simple way to increase your B12 intake.
Take care, stay healthy!


































 WhatsApp
WhatsApp
Kumar Ahuja
18 Nov 20 12:54 pmLike very good information