Preventive Healthcare
What is Parkinsonism? Types, Symptoms, and Treatment Approaches
169 Views
0
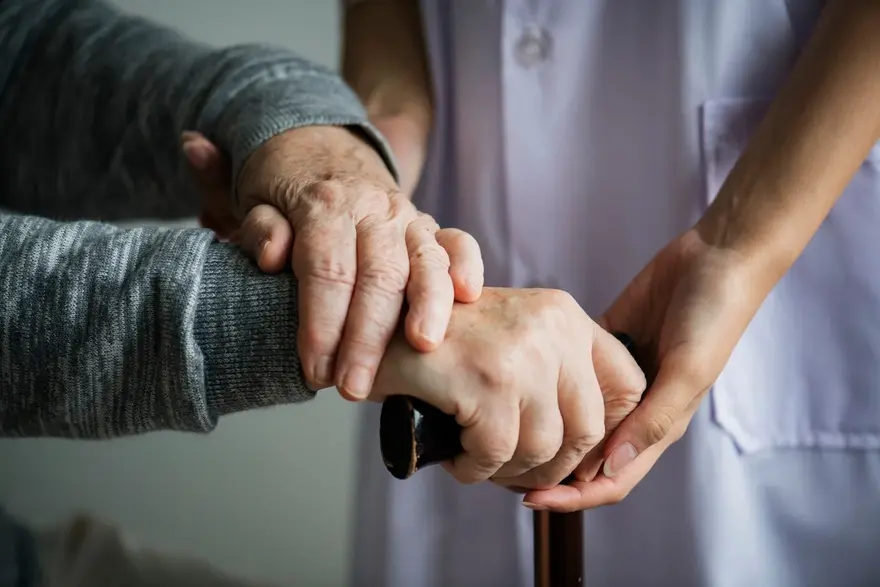

What is Parkinsonism?
Parkinsonism refers to a group of neurological disorders that cause movement symptoms similar to those seen in Parkinson's disease. However, while Parkinson's is a specific disease, parkinsonism is an umbrella term for conditions that lead to Parkinson's-like symptoms.
Parkinsonism can result from various causes, such as side effects of certain medications, brain injuries, strokes, or neurodegenerative disorders other than Parkinson's disease. Identifying the underlying cause is crucial for determining the appropriate treatment approach.
If you or a loved one are experiencing symptoms of Parkinsonism, or Parkinson's disease, it's essential to consult a neurologist for an accurate diagnosis.
Parkinsonism vs. Parkinson's Disease: Key Differences
While Parkinsonism and Parkinson's disease share similar symptoms, there are important differences between the two conditions:
|
Features |
Parkinson's Disease |
Parkinsonism |
|
Primary Cause |
Degeneration of dopamine-producing brain cells |
Various conditions (medications, brain injuries, etc.) |
|
Symptoms |
Progressive tremors, stiffness, slow movements |
Similar symptoms plus others based on underlying cause |
|
Treatment Response |
Responds well to levodopa medication |
Often less responsive to levodopa |
|
Progression |
Gradually worsening over time |
Varies depending on the specific cause |
Unlike Parkinson's disease, which primarily involves the death of dopamine-producing cells in a part of the brain called the substantia nigra, Parkinsonism can have diverse causes. These may include:
- Side effects of certain medications, especially antipsychotics and anti-nausea drugs
- Brain injuries or tumours
- Strokes affecting the brain's movement control centres
- Neurodegenerative disorders like multiple system atrophy or progressive supranuclear palsy
Types of Parkinsonism
Parkinsonism can be classified into several types based on the underlying cause:
- Drug-induced Parkinsonism: Certain medications, particularly antipsychotics used to treat psychiatric disorders and anti-nausea drugs like metoclopramide, can cause parkinsonian symptoms as a side effect. These symptoms usually resolve once the offending medication is discontinued.
- Vascular Parkinsonism: This type results from one or more small strokes that damage the brain's movement control centers. The symptoms may appear more suddenly compared to the gradual onset of Parkinson's disease.
- Post-traumatic Parkinsonism: Head injuries, especially those involving damage to the basal ganglia or midbrain regions, can lead to Parkinson's symptoms. Boxers and football players are at an increased risk due to repeated concussions.
- Toxin-induced Parkinsonism: Exposure to certain toxins, such as carbon monoxide, cyanide, and manganese, can cause damage to the brain's movement control circuits, resulting in Parkinsonism.
- Multiple system atrophy (MSA): This neurodegenerative disorder affects multiple brain areas, leading to parkinsonism along with impaired autonomic functions like blood pressure control and bladder function.
- Progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP): PSP is characterised by Parkinsonism, eye movement abnormalities, and cognitive decline. Falls are a common early symptom in this condition.
Identifying the specific type of Parkinsonism or types of Parkinson's disease is crucial for determining the most appropriate Parkinson's disease treatment approach.
Symptoms of Parkinsonism
The symptoms of Parkinsonism can vary based on the underlying cause, but common signs include:
- Tremors: Involuntary shaking, usually starting in the hands, fingers, or legs. These tremors are most noticeable at rest and may lessen with movement.
- Rigidity: Muscle stiffness that limits flexibility and can cause discomfort. Muscles may feel tight and contracted.
- Bradykinesia: Slowness of movement, making everyday tasks like dressing and eating more challenging.
- Postural Instability: Poor balance and coordination, leading to a stooped posture and increased fall risk.
- Shuffling Gait: Walking with short, shuffling steps and reduced arm swing.
Some early symptoms of Parkinson's disease may also include:
- Reduced facial expressions (facial masking)
- Soft or hoarse voice
- Difficulty swallowing
- Constipation
- Sleep disturbances
- Cognitive changes, such as slowed thinking and attention difficulties
It's important to note that not everyone with parkinsonism will experience all these symptoms, and the severity can vary from person to person. If you notice any of these Parkinson's symptoms in yourself or a loved one, it's essential to consult a neurologist promptly for a thorough evaluation.
Causes and Risk Factors
Parkinsonism is a complex neurological syndrome that affects movement and balance. While Parkinson's disease is the most common cause of Parkinsonism, several other conditions can lead to similar symptoms. Understanding the underlying Parkinson's disease causes and other Parkinsonian disorders is crucial for early detection and effective management.
- Idiopathic Parkinson's disease, which accounts for the majority of Parkinsonism cases, has no known specific cause. However, researchers believe that a combination of genetic and environmental factors may contribute to its development.
- Vascular Parkinsonism results from reduced blood flow to the brain, often due to small strokes or chronic cerebrovascular disease.
- Drug-induced Parkinsonism can occur as a side effect of certain medications, such as antipsychotics and calcium channel blockers.
- Parkinson-plus syndromes, like multiple system atrophy and progressive supranuclear palsy, involve additional neurological symptoms beyond typical Parkinsonian features.
- Age remains the most significant risk factor for Parkinsonism, with incidence increasing dramatically after age 60. Other potential risk factors include family history of Parkinson's disease or related disorders, exposure to environmental toxins like pesticides and heavy metals, or head trauma or brain injury.
Diagnosis of Parkinsonism
Diagnosing Parkinsonism requires a thorough clinical evaluation by a neurologist or movement disorder specialist. There is no single definitive Parkinson's test, so diagnosis relies on identifying characteristic symptoms and ruling out other potential causes.
The diagnostic process typically involves:
- Detailed medical history to assess symptom onset, progression, and risk factors
- Physical and neurological examination to evaluate Parkinsons symptoms like tremor, rigidity, and bradykinesia
- Cognitive and psychiatric assessment to detect non-motor symptoms
- Brain imaging tests (MRI, PET, DaTscan) to visualize brain structure and function
In some cases, a levodopa challenge may be performed to assess responsiveness to dopamine replacement therapy, which can help differentiate idiopathic Parkinson's disease from other Parkinsonian syndromes. However, confirming a specific diagnosis often requires monitoring symptom progression over time.
If you notice any early symptoms of Parkinson's disease, such as tremor, stiffness, or changes in gait, it's essential to consult a healthcare provider for a proper evaluation.
Treatment Options for Parkinsonism
While there is no cure for Parkinsonism, various Parkinson's treatment approaches can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. The primary goals of treatment are to:
- Alleviate motor symptoms like tremor, rigidity, and slow movement
- Address non-motor symptoms such as depression, anxiety, and sleep disturbances
- Maintain independence and functional ability for as long as possible
Medications
Medication is the cornerstone of Parkinson's disease treatment. The most effective drug is Levodopa, often combined with Carbidopa. Other medications include:
- Dopamine Agonists (Ropinirole, Pramipexole)
- MAO-B Inhibitors (Selegiline, Rasagiline)
- COMT Inhibitors (Entacapone, Tolcapone)
- Anticholinergics (Trihexyphenidyl)
Surgical Treatment
For advanced cases, Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) may be recommended. This procedure involves implanting electrodes in the brain to regulate abnormal activity.
Complementary Therapies
- Physical Therapy: Enhances mobility, balance, and flexibility
- Speech Therapy: Helps with communication and swallowing difficulties
- Occupational Therapy: Supports daily activities and home safety
A personalised Parkinson's disease treatment plan will be developed based on symptoms, disease stage, and individual needs.
Living with Parkinsonism: Management and Coping Strategies
In addition to medical treatment, making certain lifestyle adjustments can go a long way in managing Parkinson's symptoms and coping with the challenges of living with a chronic neurological condition. Consider implementing the following tips:
- Stay active with regular exercise tailored to your abilities, such as walking, swimming, or cycling. Physical activity can help improve mobility, balance, and mood.
- Eat a balanced diet rich in fiber, antioxidants, and omega-3 fatty acids. Adequate nutrition supports brain health and overall well-being.
- Practice stress-reduction techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or gentle yoga to relax muscles and calm the mind.
- Prioritise sleep hygiene by establishing a consistent sleep schedule, creating a comfortable sleep environment, and avoiding stimulants late in the day.
- Install handrails, grab bars, and non-slip mats in the bathroom and shower.
- Use utensils with large handles or weighted utensils for easier gripping.
- Consider a walker or wheelchair for safe mobility if needed.
Remember, you don't have to face Parkinsonism alone. Seek support from family, friends, and local Parkinson's organisations.
Conclusion
Parkinsonism encompasses a spectrum of neurological disorders that share common features of tremor, stiffness, and slow movement. While Parkinson's disease is the most prevalent cause, various other conditions can lead to Parkinsonian symptoms.
If you notice any concerning signs or early symptoms of Parkinson's disease, don't hesitate to talk to your doctor. At Metropolis Healthcare, we understand the importance of accurate diagnosis for effective treatment planning. Our state-of-the-art diagnostic labs across India offer comprehensive Parkinson's tests and screenings to aid in the evaluation process. With a team of experienced phlebotomists, we provide convenient at-home sample collection for your comfort and safety.






















 WhatsApp
WhatsApp