Preventive Healthcare
Understanding Pulmonary Embolism: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Strategies
1397 Views
0
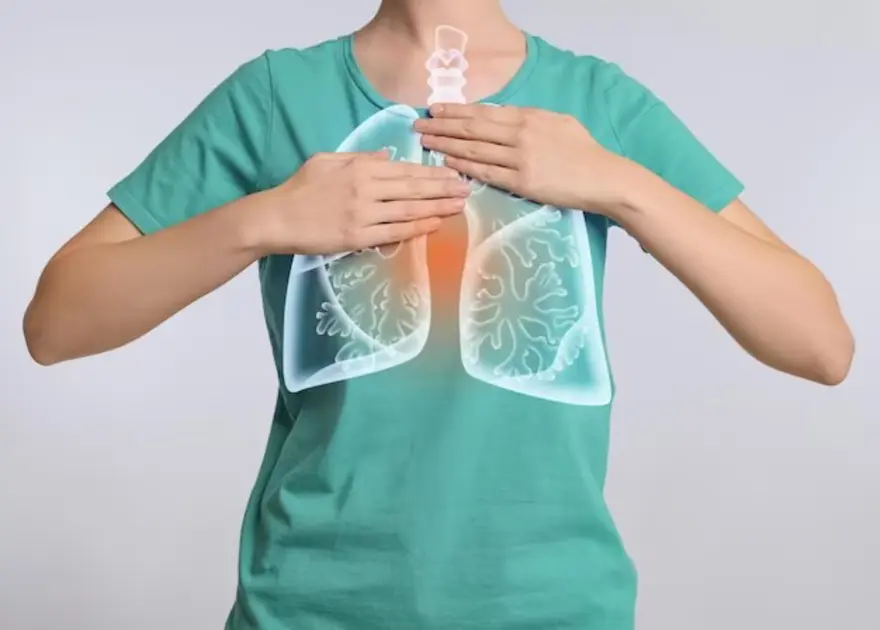
What is Pulmonary Embolism?
A pulmonary embolism is a sudden blockage of one or more pulmonary arteries in the lungs, caused by blood clots that travel from the legs or other parts of the body. This obstruction can be life-threatening, leading to symptoms like chest pain, shortness of breath, and rapid heart rate. It happens when blood can't flow freely through the legs because your body is still for a period during a long flight or drive. It might also happen if you are on bed rest after surgery or illness.
How serious is Pulmonary Embolism?
A pulmonary embolism is a serious medical emergency that can be life-threatening. If left untreated, it may lead to complications such as heart strain or failure. Prompt diagnosis and pulmonary embolism therapy with anticoagulant medications or other interventions are crucial to prevent severe consequences and improve the chances of recovery.
How common is Pulmonary embolism?
Pulmonary embolism are relatively common, with an estimated annual incidence of about two cases per 1000 individuals. The risk increases with factors such as age, surgery, prolonged immobility, and certain medical conditions.
What are the warning signs of a Pulmonary Embolism?
The warning signs of a pulmonary embolism include sudden shortness of breath, chest pain that may become worse with deep breaths, rapid heart rate, cough with bloody or pink sputum, and feeling lightheaded or dizzy.
If experiencing these symptoms, seeking immediate pulmonary embolism therapy or medical attention is crucial for timely diagnosis.
What are the Symptoms of Pulmonary Embolism?
Pulmonary embolism symptoms vary based on the severity of the clot. Sometimes pulmonary embolism may present with subtle signs.
Pulmonary embolism symptoms may include:
- Sudden shortness of breath, often accompanied by chest pain that may worsen with deep breaths
- Rapid heart rate
- Cough with bloody or pink sputum
- Lightheadedness
- Dizziness
- Clammy or discolored skin
- Swelling or tenderness in the affected leg
Prompt medical attention is crucial, timely intervention improves the chances of successful treatment and recovery.
What Causes Pulmonary Embolism?
Pulmonary Embolism causes are:
- Deep Vein Thrombosis: Blood clots often originate in deep veins, commonly in the legs or pelvis.
- Blood Collecting or Pooling: The stagnation of blood, often due to conditions like varicose veins, immobility, or prolonged sitting, increases the risk of clot formation.
- Injury to Veins: Trauma or damage to a blood vessel can initiate the clotting process, leading to the formation of clots that may later travel to the lungs.
- Blood Clotting Disorders: Conditions such as Factor V Leiden mutation, prothrombin gene mutation, or antiphospholipid syndrome can predispose individuals to abnormal clotting, raising the likelihood of pulmonary embolism.
Understanding and addressing these pulmonary Embolism causes are crucial for effective prevention and management.
Who is at Risk for a Pulmonary Embolism?
Here is a list defining who could be at the risk of PE:
- If you have blood clotting in the leg or DVT.
- If you are inactive for a long time due to some illness or via motor or trains or planes, car, buses.
- If you have recently suffered trauma or any sort of injury due to which you have you through surgery it may cause a Pulmonary Embolism.
- If you are taking birth control pills. Any sort of oral contraceptives or going through hormone replacement therapy.
- Had a habit of smoking recently.
- Any medical history of heart failure or stroke.
- You are overweight, a Body Mass Index or BMI greater than 25/obesity (a BMI greater than 30).
- If you are pregnant or have given birth in the previous six weeks.
- Received a central venous catheter through the arm or leg.
How is Pulmonary embolism Diagnosed?
The following tests are done for Pulmonary Embolism diagnosis:
- Blood tests (including the D-dimer test).
- Ultrasound of leg:- This helps identify blood clots in people’s legs, or deep vein thrombosis, which can move to the lungs and become a PE and cause more damage.
- Ventilation/perfusion (V/Q) scan:- If unable to get contrast for a CT scan. This is a nuclear scan that can detect clots in your lung.
- Computed tomography (CT) angiogram.
Other tests your doctor may ask you could be:
- Pulmonary angiogram.
- Chest X-ray.
How is Pulmonary embolism Treated?
Pulmonary Embolism treatment often involves anticoagulant medications, such as heparin and warfarin, to prevent further clot formation. In severe cases, interventions such as thrombolytic therapy or surgical procedures may be necessary to remove or break up clots.
Anticoagulant Medications
Anticoagulant medications such as heparin and warfarin, are primary treatments for pulmonary embolism as prescribed by the healthcare professional. Anticoagulants impede the blood's ability to clot, reducing the risk of further emboli. Regular monitoring of blood clotting parameters is essential, and adjustments to medication dosage made accordingly.
Compression Stockings
Compression stockings are often recommended as a supportive measure for pulmonary embolism. These specialised stockings apply gentle pressure to the legs, promoting blood flow and reducing the risk of clot formation, helping to alleviate pulmonary embolism symptoms and contributing to overall management.
Procedures
If other treatments are not effective and if pulmonary embolism is life-threatening, your healthcare professional may recommend going for a surgery to remove the blood clot from your pulmonary artery.
Thrombolytic Therapy
It involves administering medications to quickly dissolve blood clots in severe cases of pulmonary embolism. While effective, it carries a risk of bleeding and is typically reserved for situations with life-threatening complications, guided by careful evaluation of potential benefits and risks by healthcare professionals.
Side Effects of the Treatment
Common side effects of pulmonary embolism treatments, includes an increased risk of bleeding. Patients should be monitored closely and healthcare providers adjust treatment accordingly.
How can I Prevent Pulmonary embolism?
To prevent pulmonary embolism, ensure to:
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise
- Avoid prolonged immobility, especially during travel
- Stay hydrated
- Limit caffeine and alcohol
- Avoid wearing tight clothes
- Elevate your feet for 30 minutes twice a day
- Reduce your weight, if you are overweight
If at risk, discuss preventive measures with a healthcare professional. Recognising and managing risk factors is crucial for prevention.
What Can I Expect if I have a pulmonary embolism?
You can feel shortness of breath suddenly, which is a very common symptom. Lightheadedness, fainting, feelings of anxiety, and chest pain could be other possibilities that you can expect. It is crucial to diagnose it timely. A timely pulmonary embolism treatment can help a lot.
Will a pulmonary embolism go away?
A pulmonary embolism won't go away on its own. Timely medical intervention is essential for effective treatment and recovery.
Conclusion
In conclusion, pulmonary embolism demands swift recognition and immediate medical attention. With a range of treatments available, early intervention is crucial for successful outcomes. Prioritising preventive measures, staying vigilant about symptoms, and seeking prompt medical care are pivotal in managing this potentially life-threatening condition. Remember, awareness and proactive health measures play a key role in mitigating risks associated with pulmonary embolism.
For comprehensive health assessments and accurate diagnostics, schedule your visit with Metropolis Healthcare. We also provide a test from home facility, where our experts will collect the samples from your doorstep. Book your test today.






















 WhatsApp
WhatsApp