Preventive Healthcare
White Blood Cells (WBC): Types, Functions, Counts & Normal Range
30258 Views
0
What are white blood cells?
White blood cells (WBCs) are a type of cells found in blood. They form just 1% of your blood but are entrusted with the function of immunity. So, white blood cells circulate in the blood and help the immune system fight off microbes and infections caused by them.
When the body identifies an intruder or an infection, it releases white blood cells to fight them. This often causes an inflammatory reaction.
White blood cells are produced by stem cells in the bone marrow. In fact, 80 to 90% of white blood cells are stored in the bone marrow.
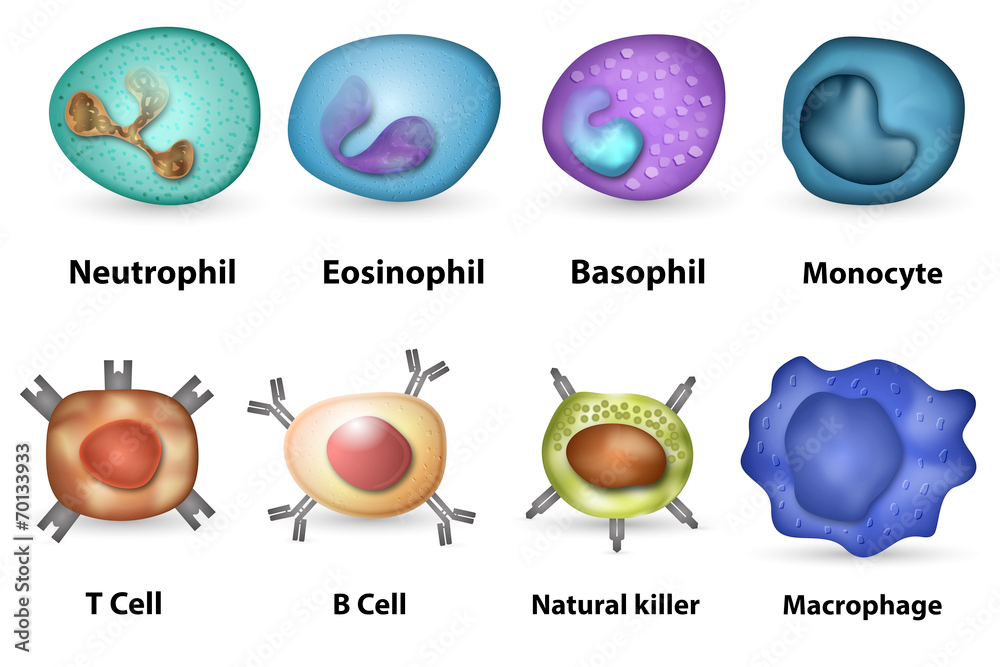
Types and functions of white blood cells
White blood cells can be broadly classified into granulocytes and agranulocytes, depending on the presence or absence of small protein granules in them.
Granulocytes
There are three types of granulocytes, namely:
- Basophils: These form less than 1% of the white blood cells in the body. The basophil number usually increases during an allergic reaction. Basophils produce chemicals like histamine to control the body’s immune response.
- Eosinophils: These white blood cells are primarily responsible for responding to parasitic infections but also play a role in the body’s general immune and inflammatory responses. They have also been found to attack and kill cancer cells.
- Neutrophils: These cells form the majority of white blood cells in the body. They are essentially scavengers that identify an infectious agent like bacteria or fungi and destroy them. Neutrophils form the first line of the body’s defence mechanism.
Agranulocytes
There are two types of agranulocytes. They are:
- Lymphocytes: These white blood cells produce substances called antibodies to fight against microbes and other harmful invaders. Lymphocytes are of three types: B cells: These cells produce antibodies to help the immune system fight infections in the body. They are also called B-lymphocytes.
- T cells: These white blood cells identify and attack infection-causing cells and remove them from the body.
- Natural killer cells: As the name suggests, natural killer cells are a type of white blood cell that attack and kill viral and cancer cells.
- Monocytes: These cells form 2 to 8% of your total white blood cell count. These cells usually have a longer lifespan than other WBCs and are responsible for fighting off chronic infections.
What is the normal count of white blood cells?
The optimum white blood cells count in your body is an indicator that your immune system is functioning normally. The normal range of white blood cells is between 4,000 and 11,000/microlitre. The WBC count may vary depending on your age and gender. The count may be different in children and pregnant women.
What do abnormal WBC counts indicate?
Certain health conditions and diseases can give rise to abnormal white blood cell count. Depending on the disease, the WBC count can be higher or lower than normal.
High white blood cell count
When the body produces excessive amounts of WBCs, it is termed leucocytosis. If you have a high white blood cell count, it may be indicative of one of the following conditions:
- Allergic response (commonly seen in people with asthma and atopic dermatitis)
- Burns
- Trauma
- Heart attack
- Inflammatory conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, IBD, eczema
- Infections caused by bacteria, fungi, parasites or viruses
- Leukaemia
Sometimes, undergoing a surgical procedure can also raise your WBC count temporarily.
Low white blood cell count
When the body produces fewer than normal white blood cells, the condition is called leucopenia. A few conditions that may cause leucopenia include:
- Autoimmune diseases like lupus
- HIV
- Bone marrow disorders
- Lymphoma
- Bone marrow damage due to chemotherapy, radiation therapy or toxin exposure
- Sepsis
- Vitamin B12 deficiency
Wrapping it up
It is important to understand what white blood cells (WBCs) are and their vital role in the immune system. The different types of white blood cells, neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils, have unique features and perform their function to ensure the body is protected from harmful invaders and substances.
A healthy white blood cell count within the normal range is a good indicator of your immune system's strength. However, if you observe any significant deviations from the normal count, you must seek immediate consultation from your doctor for further evaluation.
At Metropolis Labs, we offer accurate and reliable diagnostic testing, made possible by our state-of-the-art facilities and experienced team. Take charge of your well-being by prioritising regular check-ups and screenings at Metropolis Labs. Get your immunity evaluated, and book your test now!























 WhatsApp
WhatsApp
