Preventive Healthcare
Exploring Hemoglobin: Levels, Erythropoiesis, and Factors
4983 Views
0
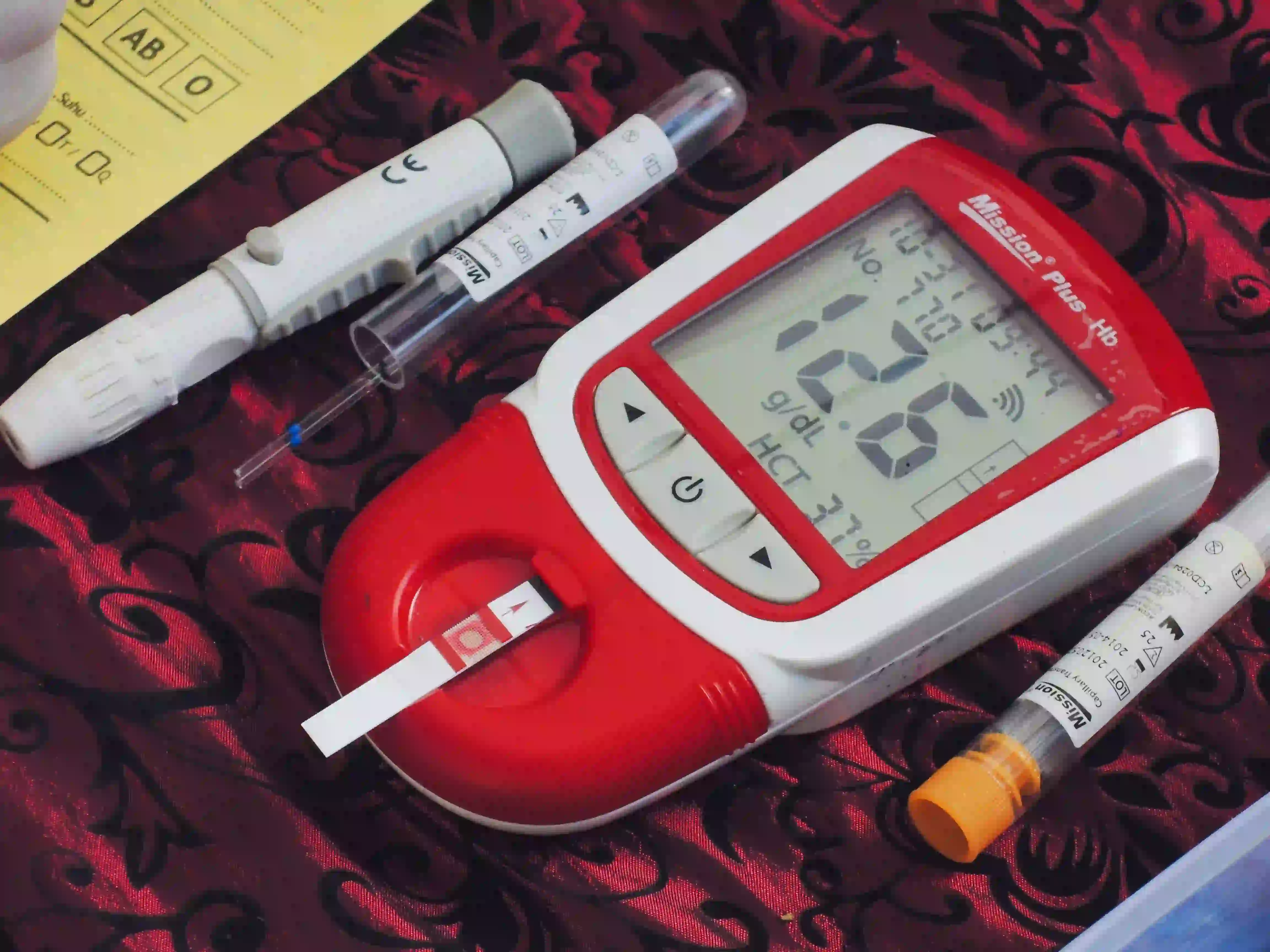
Haemoglobin is a protein molecule found in red blood cells that transports oxygen from the lungs to the body's tissues and returns carbon dioxide to the lungs. Normal haemoglobin levels differ depending on age and gender. It's critical to comprehend the typical range of haemoglobin levels at various life stages to evaluate general health and identify any possible underlying disorders.
What is Haemoglobin?
Haemoglobin is a protein found in your red blood cells. These red blood cells carry oxygen throughout your body, to different organs through the veins. Because of the iron present in the haemoglobin, the blood gets its bright red colour.
Haemoglobin in our body is secreted because of the erythropoiesis hormone to maintain the level of red blood cells in our body.
What is the process of erythropoiesis?
Our body contains a hormone named erythropoietin (EPO) which increases the level of red blood cells in our body. Our kidneys secrete EPO in the body.
The process of erythropoiesis involves the following steps:
- Our tissues are deficient in oxygen because of the low count of red blood cells.
- Our kidneys will then secrete EPO to fulfil the deficiency.
- The EPO will stimulate the bone marrow to produce more red blood cells.
- Once our kidney finds out the increased level of haemoglobin, it reduces the rate of EPO production.
- Our body will maintain the correct balance after getting a suitable amount of red blood cells.
Our kidneys secrete sufficient amounts of EPO to maintain red blood cell production. Our body loses 1% of red blood cells every day. Erythropoiesis replaces the dead red blood cells in our body.
Factors affecting erythropoiesis
There are various factors which can affect our body to regulate red blood cells.
Lungs disease
- Asthma
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
Cancers that impact your bone marrow or blood
- Leukaemia
- Lymphoma
- Myeloproliferative disorders
- Myeloma
Other factors
- Deficiency in nutrition like iron, folate or B12.
- High attitudes.
Haemoglobin Levels at Different Stages of Life
Haemoglobin levels are higher in infancy due to foetal haemoglobin persisting in the bloodstream. However, as the kid develops, these levels naturally drop, reaching a steady range by early childhood. Hormonal changes and rapid growth spurts throughout adolescence might affect haemoglobin levels, causing transient variations.
The haemoglobin range stabilises and remains relatively stable in adults. Haemoglobin levels may drop slightly due to age-related changes and particular health disorders. Understanding the haemoglobin range by age and gender is critical for maintaining good health and detecting potential health problems.
Maintaining a person's general health and well-being depends heavily on haemoglobin. It transfers oxygen from the lungs to all the body's tissues and organs. Depending on age and gender, different haemoglobin levels fall within the normal range. Here is an overview:
- Infancy
Haemoglobin levels in infants throughout the first few months of life are typically greater than those in older children and adults. This is mainly because foetal haemoglobin is still present in their blood. For babies, the average haemoglobin varies from 14 to 24 grams per deciliter (g/dL). It is essential for the infant's growth and development and the oxygen supply required for quick bodily processes.
- Childhood
Children's haemoglobin levels progressively decline and stabilise as they enter early childhood and beyond. For kids between the ages of 1 and 9, the average haemoglobin range is generally between 11 and 14 g/dL. These levels guarantee the developing infant gets enough oxygen for their developing body and brain cells.
- Adolescence
Hormonal shifts and quick growth spurts are frequent during adolescence. These variables may affect haemoglobin levels and cause small changes. During this time, it is common to observe a brief rise or fall in haemoglobin levels. Male adolescents' typical haemoglobin levels vary from 12 to 16 g/dL, and female adolescents' average levels are 11 to 15 g/dL.
- Adulthood
As people grow older, their haemoglobin levels usually stabilize and remain constant. The normal range for men is typically 13 to 17 g/dL, whereas the range for women is 12 to 15 g/dL. The lower end of the spectrum for females is caused by physiological variations between the sexes, including monthly blood loss experienced by women. These levels guarantee the body enough oxygen to maintain daily functions, metabolism and general health.
- Older Adults
Haemoglobin levels may modestly fall in older adults, especially for people over 65. This is frequently brought on by the body's ageing process and the existence of particular medical diseases. The typical normal range for seniors is between 11 and 15 g/dL for females and 12 to 16 g/dL for males. You should remember that these ranges could change based on a person's health and medical issues are crucial.
The Importance of Monitoring Haemoglobin Levels in Each Life Stage
Monitoring haemoglobin levels is essential for regular physical examinations, especially for people exhibiting weariness, breathlessness, or extreme pallor. Low haemoglobin levels indicate anaemia, defined by a shortage of red blood cells or a reduced ability to carry oxygen. On the other hand, elevated haemoglobin levels may indicate dehydration, a few lung conditions, or problems with the bone marrow.
To maintain general health and well-being, you must keep your haemoglobin levels at an adequate level. A well-balanced diet full of iron, folic acid and vitamin B12 can encourage the development of healthy haemoglobin. Individuals should also prioritise getting enough sleep, managing their stress levels and engaging in regular physical activity to promote ideal haemoglobin levels.
Book Haemoglobin Test
Conclusion
The typical range of haemoglobin levels is essential for maintaining overall health, as they range from higher levels in infancy to stable levels in adulthood, with possibly slight declines in later age. People can improve their well-being and length of life by detecting and monitoring these values and taking proactive steps to ensure that tissues and organs are adequately oxygenated. Metropolis Healthcare is a trustworthy pathology service provider that can be considered for your next haemoglobin test. They are known to deliver the most accurate test reports within time with the facility of home sample collection if needed.






















 WhatsApp
WhatsApp
