Preventive Healthcare
Everything You Need To Know About Hypothyroidism
2832 Views
0
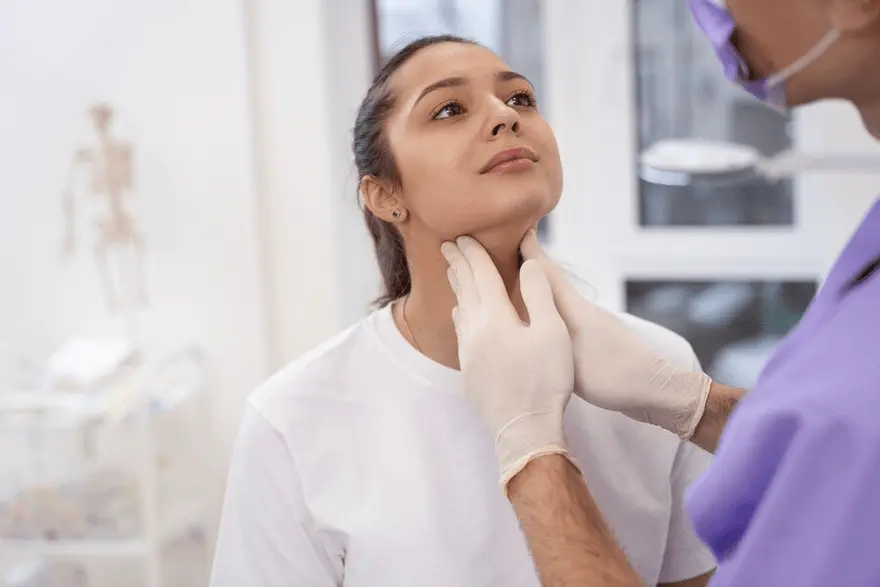
What is hypothyroidism?
Hypothyroidism is a condition in which your bloodstream does not have enough thyroid hormones, due to which your metabolism may slow down. In this condition, your thyroid does not create and release enough thyroid hormone in your body. As this makes your metabolism slow, it can affect your entire body.
Hypothyroidism is also known as underactive thyroid disease, and in cases where your thyroid levels are extremely low, it is called myxedema.
Myxedema is a condition that can cause symptoms like:
- Anemia
- Heart failure
- Coma
- Confusion
- A low body temperature
Generally, hypothyroidism symptoms are highly treatable and are manageable with regular medications, doctor appointments, and some simple lifestyle changes.
How does my thyroid work?
Your thyroid gland is a tiny butterfly-shaped organ in the front of your throat just below your voice box. It looks very similar to a set of wings hugging your windpipe. Your thyroid's main job is controlling your metabolism.
Your metabolism is referred to as the process that turns the food you eat into the energy that your body uses for various functions. The hormones T3 and T4 are secreted by your thyroid gland, which helps to control your metabolism. These hormones are carried throughout the body and control the amount of energy used by the different cells. These hormones also regulate your body temperature and heart rate.
A properly functioning thyroid constantly releases these hormones and instantly replaces them by creating more. This process helps to keep your metabolism working correctly and the rest of your body systems in check. The amount of thyroid hormones present in you is controlled by the pituitary gland that is located in the centre of your skull under your brain. If this gland senses a lack of thyroid hormones, it will adjust the thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) released and send it to your thyroid to know it has to balance the amounts.
Having high levels of thyroid (hyperthyroidism) or low levels of thyroid (hypothyroidism) can impact your entire body.
Who is affected by hypothyroidism?
Hypothyroidism can impact anyone, irrespective of gender, ethnicity, or age. However, it is widespread among women over 60 years of age. Women who have been through menopause are more likely to develop hypothyroidism.
What's the difference between hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism?
Hypothyroidism is when your thyroid gland does not have and secrete enough thyroid hormone. On the other hand, hyperthyroidism is when your thyroid gland excretes too much thyroid hormone. In the case of hyperthyroidism, your metabolism speeds up, while in hypothyroidism, your metabolism slows down.
Hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism are opposites in many ways. Individuals with hypothyroidism have a difficult time handling the cold, and those with hyperthyroidism cannot deal well with heat. These are the opposite sides of thyroid function, and when your thyroid is secreting adequate amounts of T3 and T4, you find yourself in the middle.
Hypothyroidism treatment includes getting your thyroid to function in the middle and secrete the right amounts of hormones.
What causes hypothyroidism?
There can be a primary and secondary cause for hypothyroidism. The primary hypothyroidism cause could be a condition that directly affects your thyroid and causes it to create lower amounts of thyroid hormones than needed.
The secondary cause of hypothyroidism is what causes your pituitary gland to fail, which causes it not to send enough thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) to balance your thyroid levels.
One of the most common primary hypothyroidism causes is an autoimmune condition known as Hashimoto's disease. This condition can also be called Hashimoto's thyroiditis or chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis and is a hereditary condition that is passed down from parents to children. In this condition, your body's immune system attacks and damages the thyroid gland. This does not allow your thyroid to make and secrete enough thyroid hormone.
Other primary causes of hypothyroidism are:
- Inflammation of the thyroid (Thyroiditis)
- Radiation and surgical removal of your thyroid gland are treatment options for hyperthyroidism.
- Iodine deficiency as iodine is a mineral that your body needs to make the thyroid hormones.
- Other hereditary conditions
There are some instances where thyroiditis can be triggered after your pregnancy or after a viral illness.
What causes hypothyroidism in pregnancy?
Women who suffer from hypothyroidism during their pregnancy usually have Hashimoto's disease. As mentioned earlier, this is a condition in which your body's immune system attacks and causes damage to your thyroid gland. Because of this, the thyroid gland does not produce or secrete enough thyroid hormones, affecting the entire body. Hypothyroidism symptoms in females who are pregnant feel very tired, can have a hard time dealing with colder temperatures, and could even experience muscular cramps.
The thyroid hormones are essential during pregnancy as they help with the development of the brain and nervous system of the baby. During pregnancy, it is necessary to maintain your thyroid levels. If your baby does not get enough of these hormones, their brain and nervous system may not develop correctly, causing issues when they are born. If your hypothyroidism during pregnancy is left untreated or the hypothyroidism medication is not taken regularly, it can also lead to complications in the pregnancy, like preterm labour or miscarriages.
Does birth control affect my thyroid?
In some cases, the estrogen and progesterone hormones present in birth control pills can affect the thyroid-binding proteins. If you are taking hypothyroidism treatment then you may need to increase your medication dosage while using birth control pills. You can go back to the regular dosage whenever you stop taking birth control.
Can hypothyroidism cause erectile dysfunction?
In rare cases, you may find a connection between untreated hypothyroidism and erectile dysfunction. If your hypothyroidism is caused due to a problem with your pituitary gland, it can also cause low testosterone levels. Getting the proper treatment can restore your hormone levels.
What are the symptoms of hypothyroidism?
Hypothyroidism symptoms are usually slow to develop and can include:
- The feeling of extreme tiredness or fatigue
- Numbness and a tingling sensation in your hands
- Weight gain
- Constipation
- Soreness throughout your body and muscle weakness
- Feeling depressed
- Higher than normal blood cholesterol levels
- Not being able to tolerate cold temperatures
- Dry and coarse hair or skin
- Frequent and heavy menstrual periods
- Decrease in sexual interest
- Having brain fog or forgetful
- Your voice becomes lower and hoarser
- Physical changes in your appearance, including puffiness in your face and eyes and drooping eyelids.
Will hypothyroidism make me gain weight?
If you have hypothyroidism and it is left untreated, it could cause weight gain. As soon as you start your treatment, your weight should decrease. However, it is also essential for you to start watching your calories and exercise to lose any excess weight. Getting a diet plan that works for you can help you reduce weight.
How is hypothyroidism diagnosed?
It is important to start the hypothyroidism diagnosis timely, without confusing it with other symptoms. If you notice any of the mentioned symptoms of hypothyroidism, it is essential to talk to your healthcare provider about getting treatment.
A common test for hypothyroidism is called the thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) test. You may also have to take other tests to check for conditions like Hashimoto's disease.
Your healthcare provider will also be able to diagnose an enlarged thyroid just by touching the gland.
How is hypothyroidism treated?
Hypothyroidism treatment includes replacing the hormones that your thyroid is not making. This can be done with the help of medication and a hypothyroidism diet. One of the commonly used medications for hypothyroidism is levothyroxine. It is taken orally and can help increase the amount of thyroid hormones produced by your body to even out the levels of hormones.
Hypothyroidism can be easily managed if you take your hypothyroidism medication on time. This helps you normalise your levels of hormones for the rest of your life. Carefully monitoring your hormone levels and regular follow-ups with your healthcare provider can help you lead a relatively normal and healthy lifestyle.
What happens if hypothyroidism is not treated?
Hypothyroidism should not be left untreated The delay in the treatment can worsen the hypothyroidism symptoms.
Hypothyroidism causes the following conditions:
- Trouble breathing
- Developing mental health issues
- Trouble maintaining normal body temperatures
- Heart issues
- Enlargement of your thyroid glands called a goitre
Very low levels of thyroid hormones can also cause myxedema coma, which can happen if you leave hypothyroidism untreated.
Will I have the same dose of medication for hypothyroidism my entire life?
Your hypothyroidism medication doses may change over time as you may need different amounts of medication at other points in your life. Your dose of medicine can be managed based on the symptoms you display, as your thyroid levels can cause excess weight gain or weight loss. Your healthcare provider will keep a close eye on your levels of thyroid hormones and make sure that your medication is working effectively.
Can hypothyroidism be prevented?
There is nothing that you can do to prevent hypothyroidism, and the best way to ensure that it doesn't become a severe condition is to keep an eye out for the symptoms of hypothyroidism and take the required steps to manage this disease. Your hypothyroidism treatment will also be more effective if you start the treatment as soon as possible after the disease is detected in the early stage.
Are there any foods I can eat to help my hypothyroidism?
Several food items contain iodine, so you do not have to worry about changing your routine too much to follow a hypothyroidism diet. Iodine is what helps your thyroid gland produce more hormones, foods rich in iodine help to increase your hormone levels.
The best way of increasing your hormone levels is to get prescription medication from your doctor and consult with them before starting any new diet, especially with severe medical conditions like hypothyroidism.
Foods rich in iodine are:
- Milk and milk products like cheese and yoghurt
- Eggs
- Meat and poultry
- Seafood
- Iodised salt
- Edible seaweed
Talk to your nutritionist or doctor about creating a custom meal plan. As food is the fuel your body uses, make sure you eat good that is good for your body. Ensure you take all your medications as instructed by your healthcare provider and keep you healthy over time. However, consuming excessive amounts of iodine can also have a negative and self-contradictory effect. Soy can be linked with hypothyroidism and lowering thyroid function, which is why it is also essential to control your soy intake when you have hypothyroidism.
Can hypothyroidism go away on its own?
The symptoms of mild hypothyroidism may fade and reduce over time. In some cases, a timely hypothyroidism diagnosis helps you to keep the problem at bay. However, in cases of severe hypothyroidism or myxedema coma, you may need to take medicine to manage your symptoms for the rest of your life and follow a regular schedule.






















 WhatsApp
WhatsApp
