Preventive Healthcare
Addison's Disease: Overview, Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis & Treatment
13454 Views
0
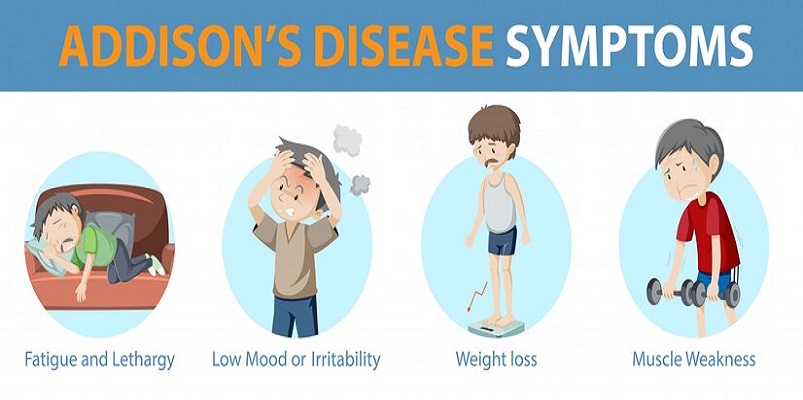
Addison's Disease is a condition that occurs when the adrenal glands do not produce enough of the hormone cortisol. Cortisol helps in regulating metabolism, blood pressure and the immune system. Inadequate production of cortisol has many symptoms, such as fatigue, weight loss, low blood pressure and muscle weakness.
Symptoms of Addison's Disease
Addison's disease is often hard to diagnose because the symptoms are similar to other conditions. If you experience any of these Addison's disease symptoms, it's important to see a doctor for testing:
1. Fatigue
Addison's disease can cause extreme fatigue, even after plenty of rest. This fatigue is often described as "bone-crushing" and can make it difficult to carry out everyday activities.
2. Weight Loss
Weight loss can be a symptom of many different conditions. But sudden and unexplained weight loss may be a sign of Addison's. People with this condition may also have a loss of appetite or difficulty digesting food properly.
3. Low Blood Pressure
One of the hallmark signs of Addison's disease is low blood pressure. This can cause lightheadedness, dizziness or fainting when standing up too quickly.
4. Darkening Skin
Addison's disease can cause the skin to darken, mainly in areas where there is exposure to the sun. This darkening is caused by excess pigment in the skin and appears as a tan or brownish hue.
5. Muscle Weakness
Weakness and pain in the muscles are other symptoms of Addison's disease. This weakness can make it difficult to walk or stand for long durations.
Addison's disease symptoms can be quite subtle at the beginning. It may mimic other conditions such as the flu or stress. Some other major symptoms include:
- Loss of appetite
- Lightheadedness or fainting upon standing (orthostatic hypotension)
- Salt cravings
- Abdominal pain
- Diarrhoea or constipation
Diagnosis For Addison's Disease
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms of Addison's disease, it is important to see your doctor for a diagnosis. Your doctor will note your medical history and ask about your signs and symptoms.
You may also undergo some tests, such as:
Blood Test: A blood test can be used to measure hormone levels. It may also be used to rule out other conditions that can cause similar symptoms. A blood test helps measure the sodium level in your blood, which regulates water retention in cells. It's also possible to test for antibodies associated with Addison’s disease.
Blood Tests can also measure your blood levels of potassium and cortisol. Moreover, it tests for excess or lack of ACTH (which stimulates the adrenal gland) and any antibodies associated with autoimmune Addison's disease.
ACTH Stimulation Test: The ACTH stimulation test is the most commonly used test to diagnose Addison's disease. The test measures the level of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) in the blood. ACTH is a hormone that stimulates the adrenal glands to produce cortisol. Cortisol is a steroid hormone that helps to regulate metabolism, immunity, and stress response.
In people with Addison's disease, the adrenal glands do not produce enough cortisol. As a result, the level of ACTH in the blood is usually high. The ACTH stimulation test involves measuring the level of ACTH in the blood before and after injecting a synthetic form of ACTH into the vein. If the level of ACTH does not increase after injection, it is likely that the person has Addison's disease. Analysis of sodium and potassium in the blood may also be measured.
Other tests such as insulin-induced hypoglycemia tests and imaging tests may also be ordered to rule out other causes of your symptoms.
Most people with Addison's disease can lead normal, healthy lives with proper treatment.
What Causes Addison's Disease?
The adrenal glands are responsible for producing various hormones, including cortisol and adrenaline. Cortisol helps to regulate metabolism, blood pressure, and the body's response to stress. Adrenaline is responsible for the "fight or flight" response, providing the body with a burst of energy in times of danger. When the adrenal glands fail to produce these hormones, it can lead to Addison's Disease. In severe cases, Addison's disease can be life-threatening.
The exact cause of Addison's disease is unknown. But it is believed to be caused by an autoimmune reaction or damage to the adrenal glands due to infection or trauma.
Treatment For Addison's Disease
Addison's disease treatment generally involves medication. One common form of Addison's disease treatment is hormone replacement therapy, in which patients are given synthetic versions of the hormones that their bodies are not producing. This can help to correct the imbalances that cause Addison's disease and alleviate its symptoms.
Some common types of hormone replacement therapy include oral corticosteroids such as hydrocortisone, prednisone, and methylprednisolone. These hormones are typically given on a schedule that mimics the natural fluctuations of cortisol levels throughout the day.
Another type of hormone replacement therapy is fludrocortisone acetate, which helps to replace the hormone aldosterone. Most people with Addison's disease can live normal, healthy lives with proper treatment.
Conclusion
Addison's disease is a rare but serious condition. Symptoms of Addison's disease can be subtle at first and may mimic other conditions such as stress or the flu.
Addison's disease treatment involves taking hormones to replace the missing ones that are supposed to be produced by the adrenal glands. In some cases, lifelong treatment with replacement hormones may be necessary.
You can now avail Addison's disease testing in the comfort of your home. Book Addison's disease Tests today with Metropolis India and keep your health in check.
Frequently Asked Question
How is Addison's Disease diagnosed?
You may need to undergo some tests, including a blood test, an ACTH stimulation test, and an insulin-induced hypoglycemia test to diagnose Addison’s disease. Imaging tests may also be ordered to rule out other causes of your symptoms.
P.S: Have Addison’s disease diagnosis done at home with the expert team of Metropolis India.
Can Addison's Disease be prevented?
Yes, with proper medication and treatment, you can prevent Addison’s disease and keep your health in check.
What Are The Major Symptoms of Addison's Disease?
Major symptoms of Addison’s disease include:
- Weight Loss
- Fatigue
- Low blood pressure
- Darkening skin
- Muscle weakness
- Loss of appetite
- Lightheadedness or fainting upon standing (orthostatic hypotension)
- Salt cravings
- Abdominal pain
- Diarrhoea or constipation





















 WhatsApp
WhatsApp